The 1940s was a decade of change and growth for Toronto. The city faced many challenges and opportunities during this time. From the impact of World War II to post-war recovery, Toronto experienced significant transformations that shaped its future.
World War II and Its Impact
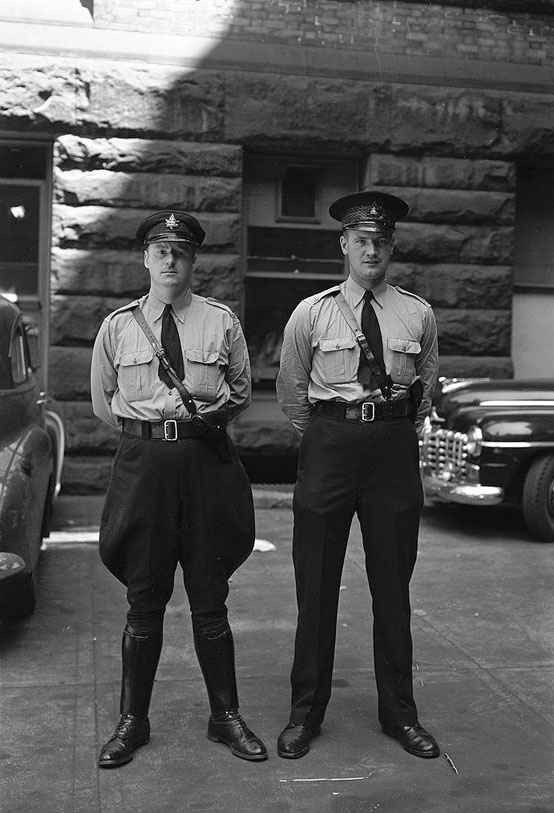
World War II had a profound impact on Toronto. The city played a crucial role in supporting the war effort. Many men and women from Toronto joined the military, leaving their families and jobs behind. The local economy shifted to support the production of war materials. Factories that once made consumer goods were now producing weapons, uniforms, and other military supplies.
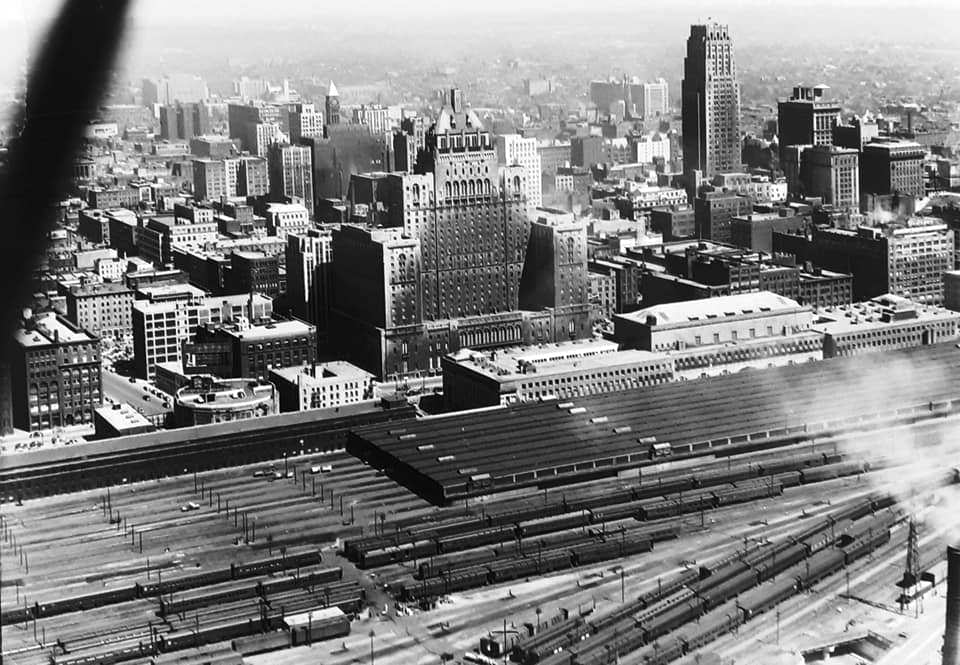
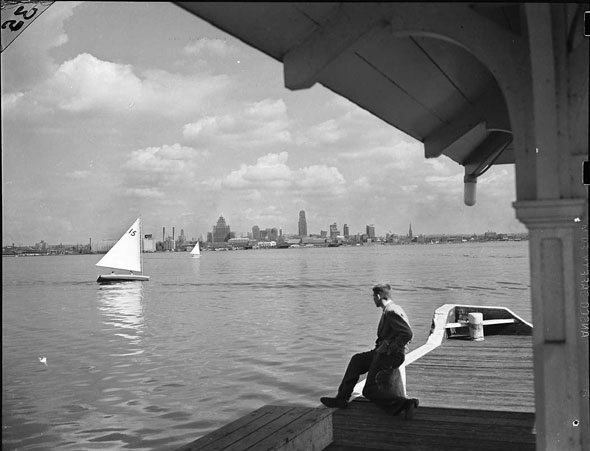
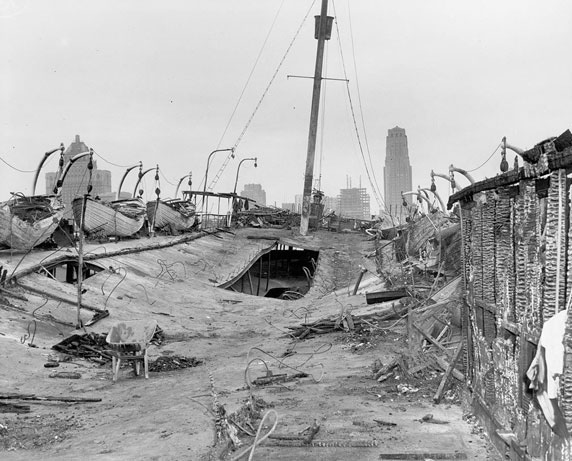
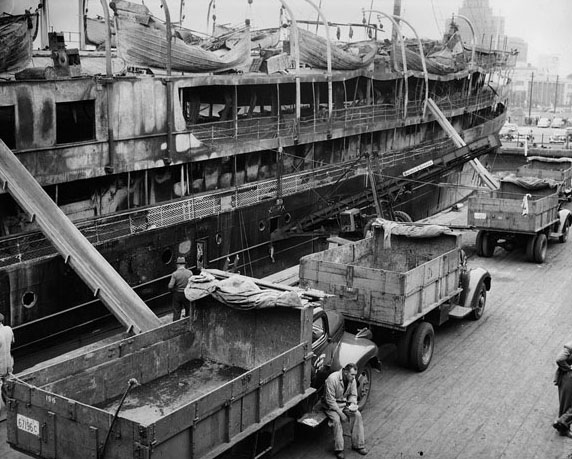
Toronto’s waterfront was bustling with activity during the war. The Royal Canadian Navy used the city’s port to build and repair ships. The Toronto Harbour Commission worked hard to ensure that the port could handle the increased traffic. This effort was vital for the transportation of troops and supplies.
Read more
Rationing was a significant part of life in Toronto during the war. Residents had to use ration cards to buy essential items like food, clothing, and fuel. This system was put in place to ensure that everyone had access to limited resources. People were encouraged to grow their own vegetables in “Victory Gardens” to supplement their food supply.
Women’s Roles and Contributions
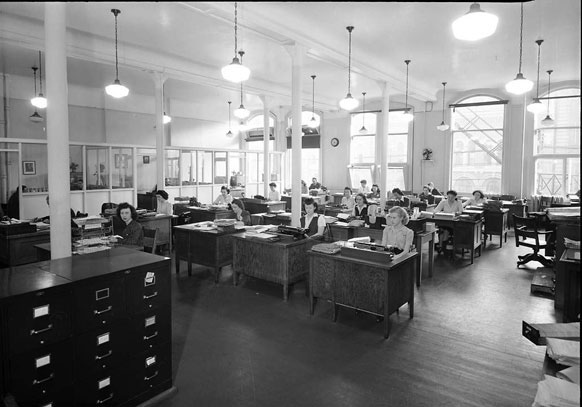
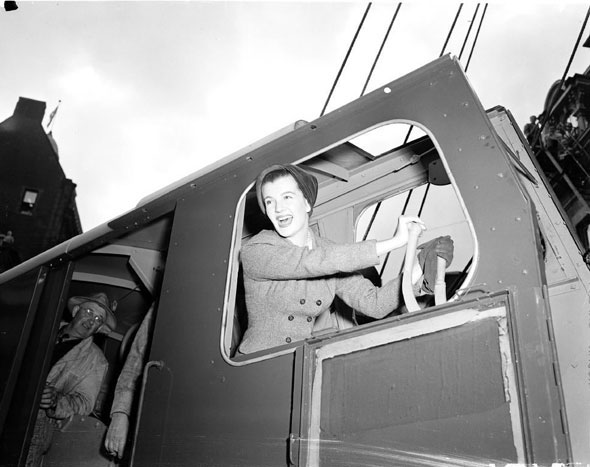
The war also changed the roles of women in Toronto. With many men serving overseas, women took on jobs that were traditionally held by men. They worked in factories, offices, and shops, contributing to the war effort and keeping the local economy running. This shift challenged traditional gender roles and laid the groundwork for future changes in women’s rights.
Women’s organizations in Toronto were very active during the war. Groups like the Canadian Women’s Army Corps and the Women’s Royal Canadian Naval Service provided support and training for women who wanted to serve in the military. Other organizations focused on volunteer work, such as knitting socks and scarves for soldiers or organizing fundraising events for war charities.
Immigration and Population Growth
Toronto’s population grew significantly during the 1940s. The city became a destination for immigrants seeking a better life. Many people came from Europe, fleeing the devastation of the war. These new residents brought their cultures, traditions, and skills, contributing to Toronto’s diversity.
The city worked hard to accommodate the growing population. New housing developments were built to provide homes for the influx of people. Neighborhoods like Don Mills and Regent Park were developed to offer affordable housing options. These areas quickly became vibrant communities, adding to the city’s dynamic character.
Post-War Economic Boom
After World War II ended in 1945, Toronto experienced an economic boom. The city’s industries shifted from war production to consumer goods. Factories that had made military supplies now produced household items, cars, and electronics. This shift created many jobs and helped boost the local economy.
Toronto’s financial sector also grew during this time. Banks and insurance companies expanded their operations, and the Toronto Stock Exchange became one of the most important financial centers in North America. The construction industry thrived, with new office buildings, homes, and infrastructure projects springing up across the city.
Transportation and Infrastructure
The 1940s saw significant improvements in Toronto’s transportation and infrastructure. The city invested in expanding its road network to accommodate the increasing number of cars. Major roads and highways were built or improved, making it easier for people to travel around the city and beyond.
Public transportation also received attention. The Toronto Transit Commission (TTC) expanded its services, adding new streetcar lines and bus routes. This made it more convenient for residents to commute to work, school, and other activities. The TTC’s improvements were crucial for supporting the city’s growing population and economy.
Toronto’s airport, known as Malton Airport (later Pearson International Airport), expanded during the 1940s. This growth helped establish Toronto as an important hub for air travel. The airport’s development was essential for connecting the city to other parts of Canada and the world.
Cultural Developments
The cultural scene in Toronto flourished during the 1940s. The city’s theaters, museums, and galleries offered a wide range of entertainment and educational opportunities. The Royal Ontario Museum and the Art Gallery of Ontario attracted many visitors with their diverse collections and exhibits.
Toronto’s music scene was vibrant in the 1940s. Jazz, big band, and classical music were popular among residents. The city’s concert halls and clubs hosted performances by local and international artists. Radio also played a significant role in bringing music and news to the people of Toronto.
Sports were an important part of life in Toronto during the 1940s. The Toronto Maple Leafs, the city’s NHL team, enjoyed great success, winning the Stanley Cup several times during the decade. Baseball, football, and other sports also had enthusiastic followings. Local sports events brought the community together and provided a sense of pride and excitement.
Education and Innovation
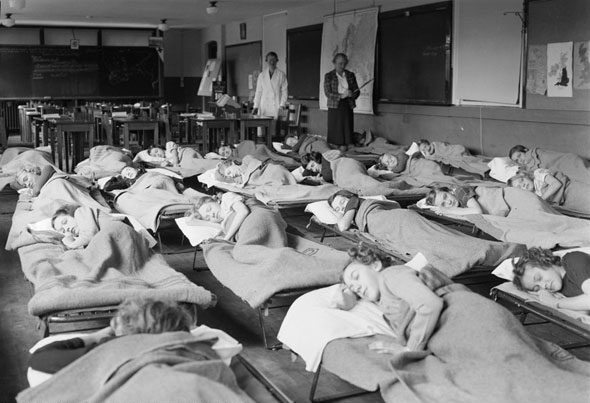
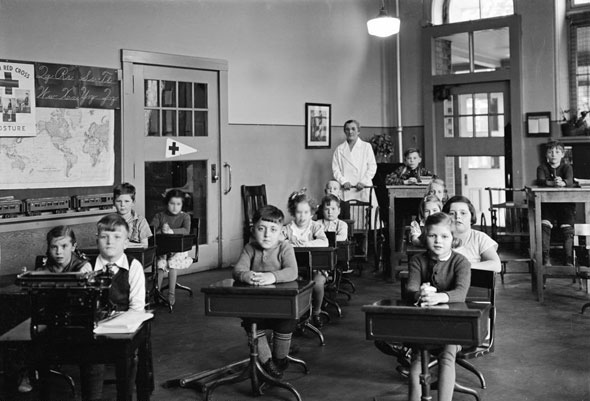
Education was a priority for Toronto in the 1940s. The city invested in its schools and universities to ensure that residents had access to quality education. The University of Toronto and Ryerson Institute of Technology (now Ryerson University) expanded their programs and facilities, attracting students from across Canada and beyond.
Innovation was a key focus for Toronto during this decade. Research institutions and universities worked on various projects, contributing to advancements in science, technology, and medicine. These efforts helped position Toronto as a leader in innovation and research.
Social Changes
The 1940s brought significant social changes to Toronto. The experiences of World War II and the post-war period influenced the city’s social fabric. People from different backgrounds and cultures lived and worked together, fostering a sense of community and understanding.
The war also highlighted the importance of social services. Toronto’s government and various organizations worked to improve healthcare, housing, and other services for residents. These efforts aimed to ensure that everyone had access to the support they needed.
Entertainment and Leisure
Entertainment and leisure activities were an important part of life in Toronto during the 1940s. The city’s movie theaters were popular destinations, showing the latest films from Hollywood and other parts of the world. Radio programs, including dramas, comedies, and news broadcasts, provided entertainment and information for residents.
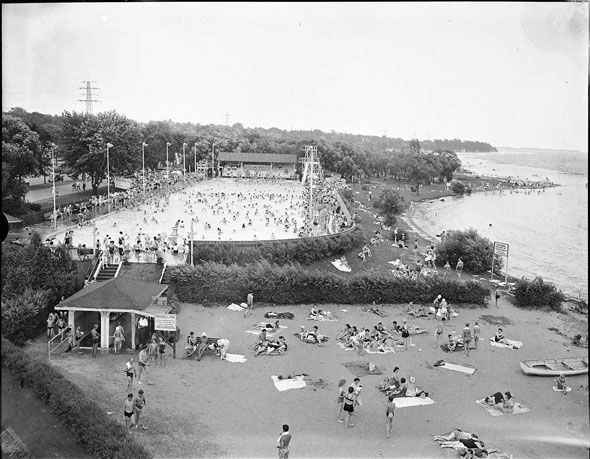
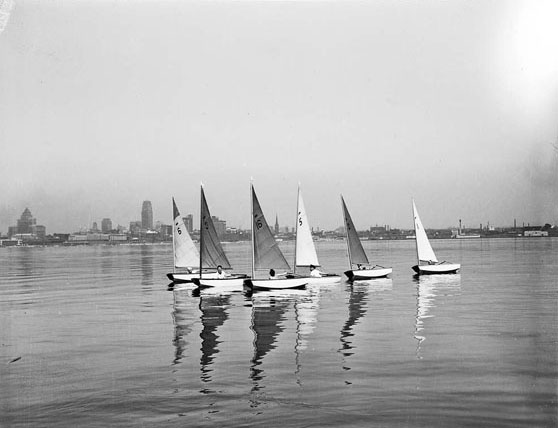
Outdoor activities were also popular in Toronto. Parks, beaches, and other recreational areas offered residents places to relax and enjoy nature. Sports like ice skating, hockey, and baseball were favorite pastimes, bringing people together and promoting a healthy lifestyle.
Shopping was another key aspect of leisure in Toronto. The city’s department stores and shops offered a wide range of goods, from clothing to household items. Shopping districts like Yonge Street and Queen Street became bustling centers of activity, attracting both locals and visitors.
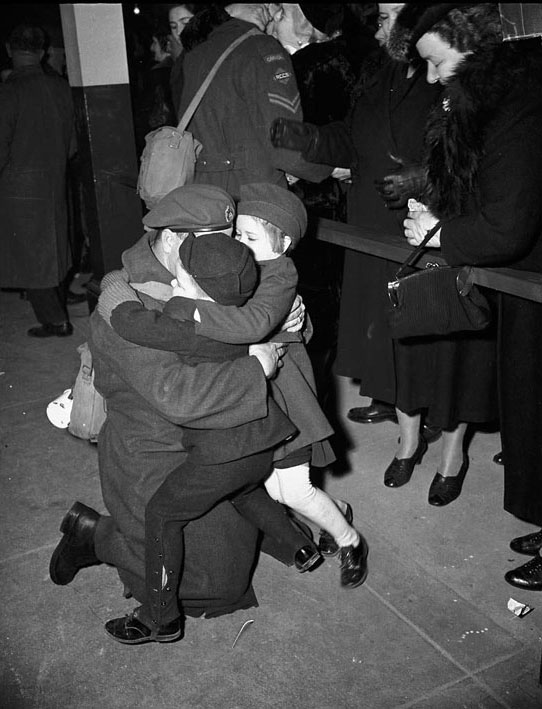
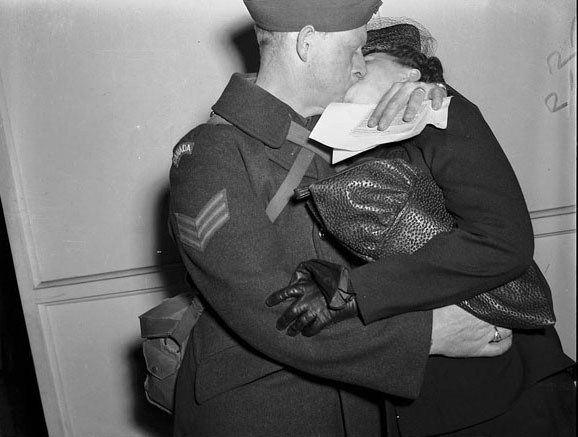
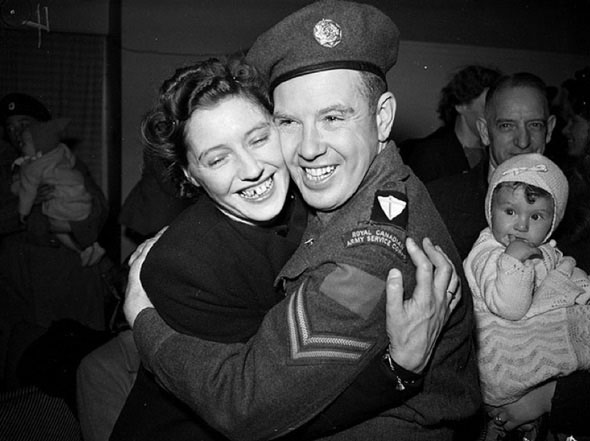
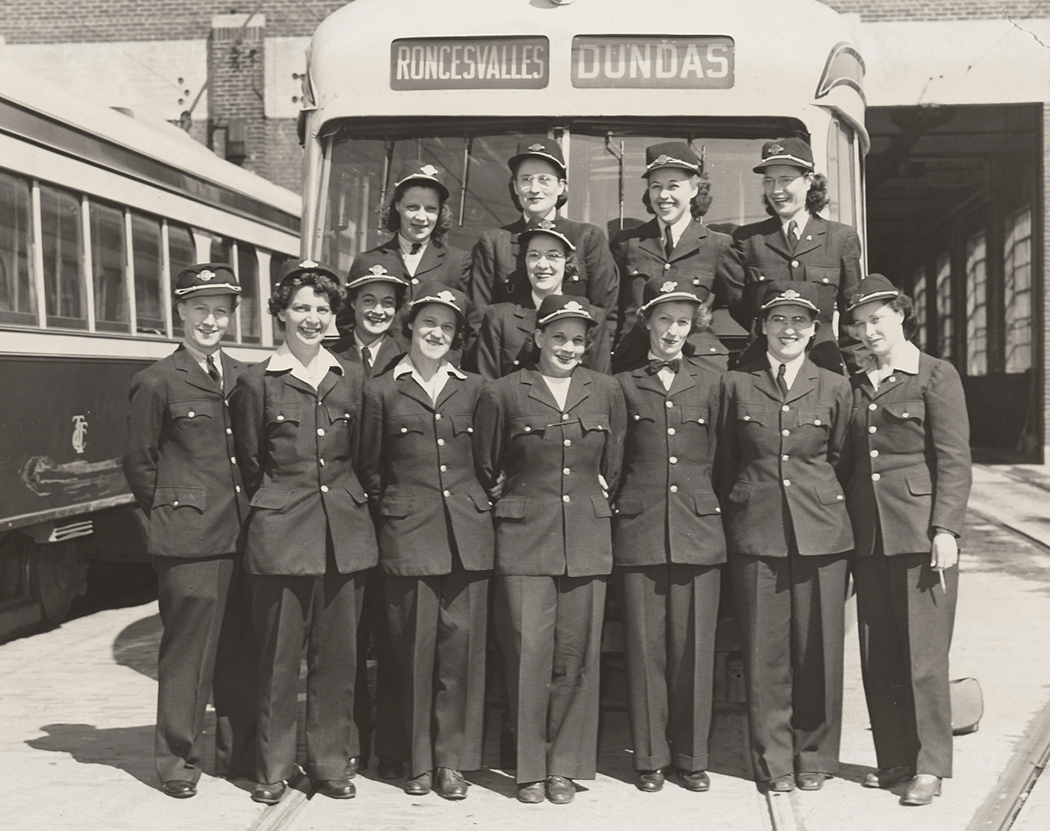
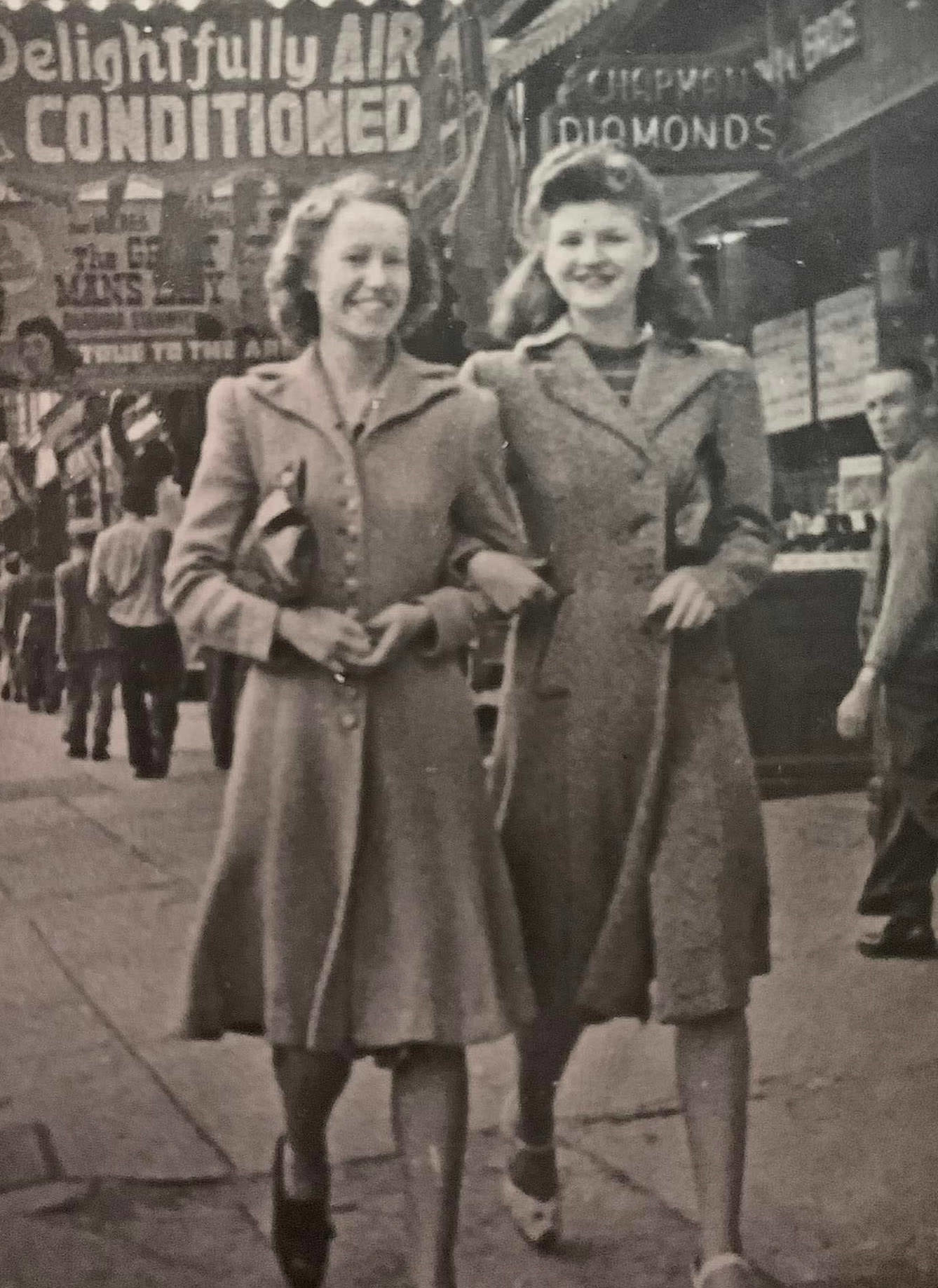
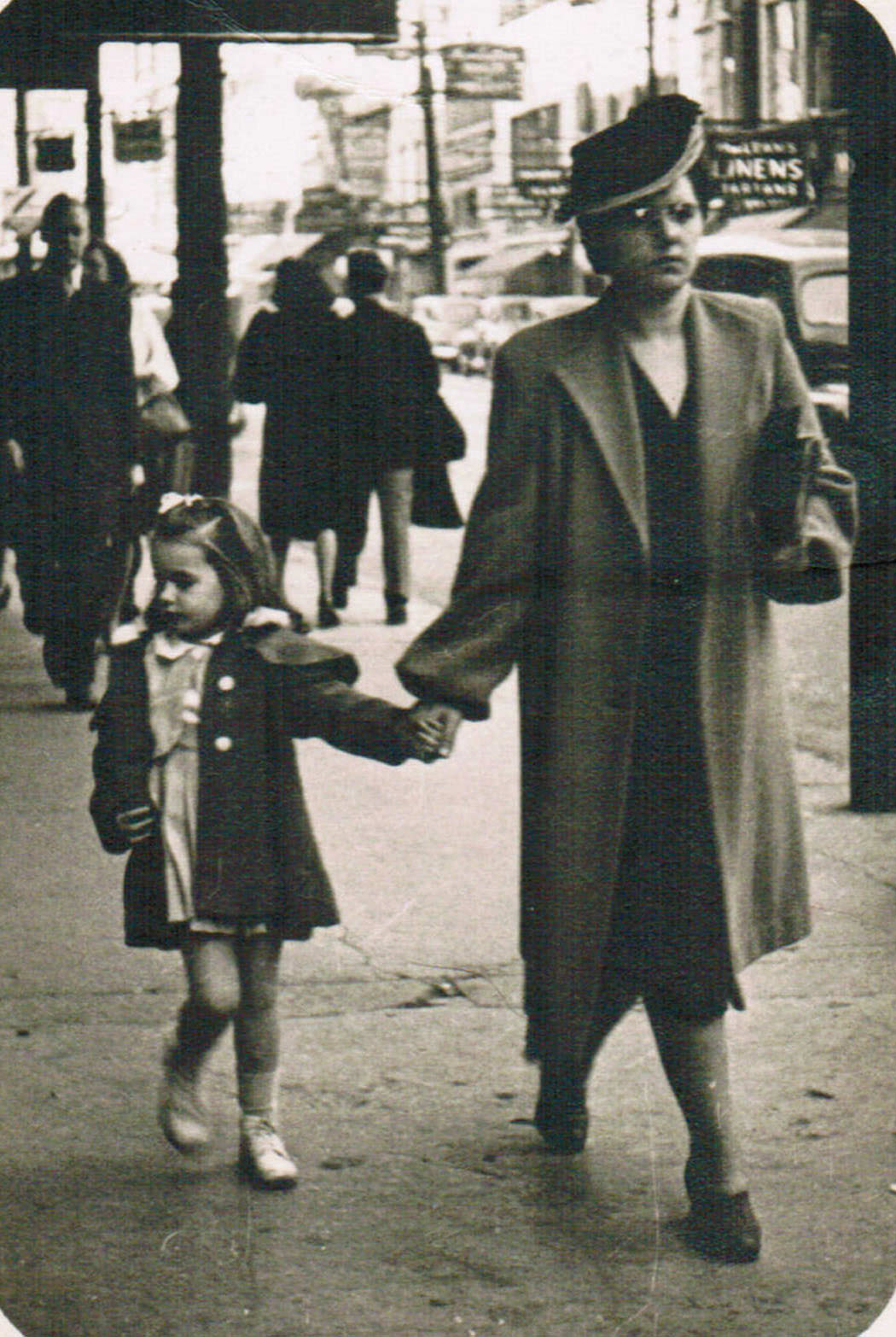
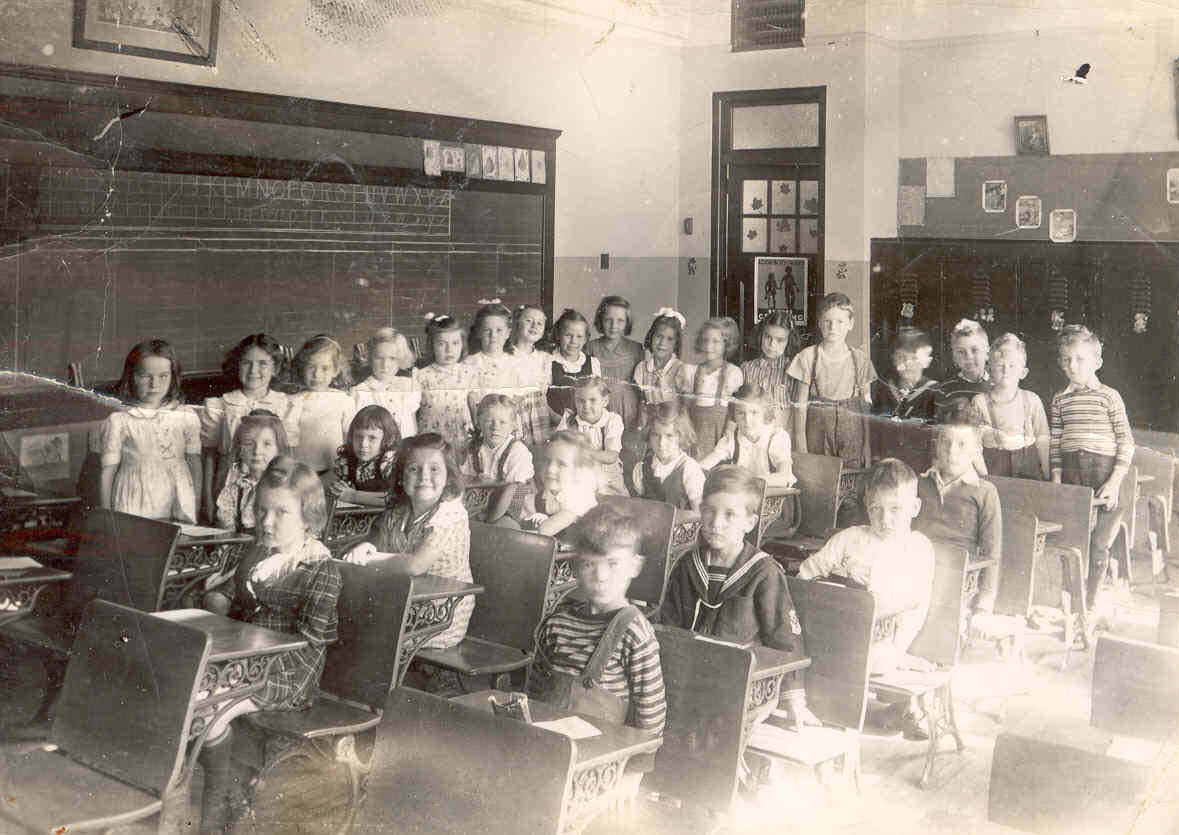
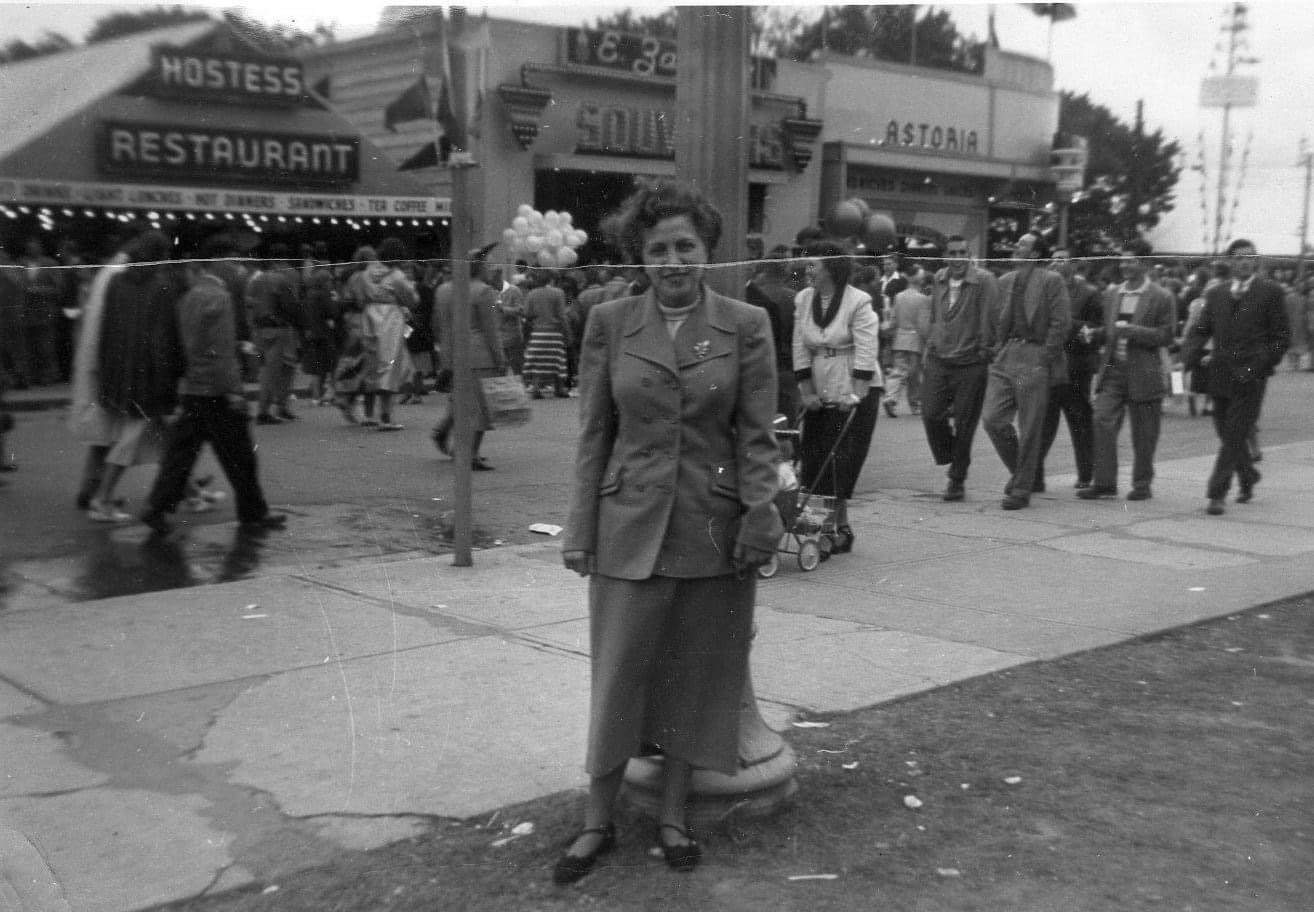
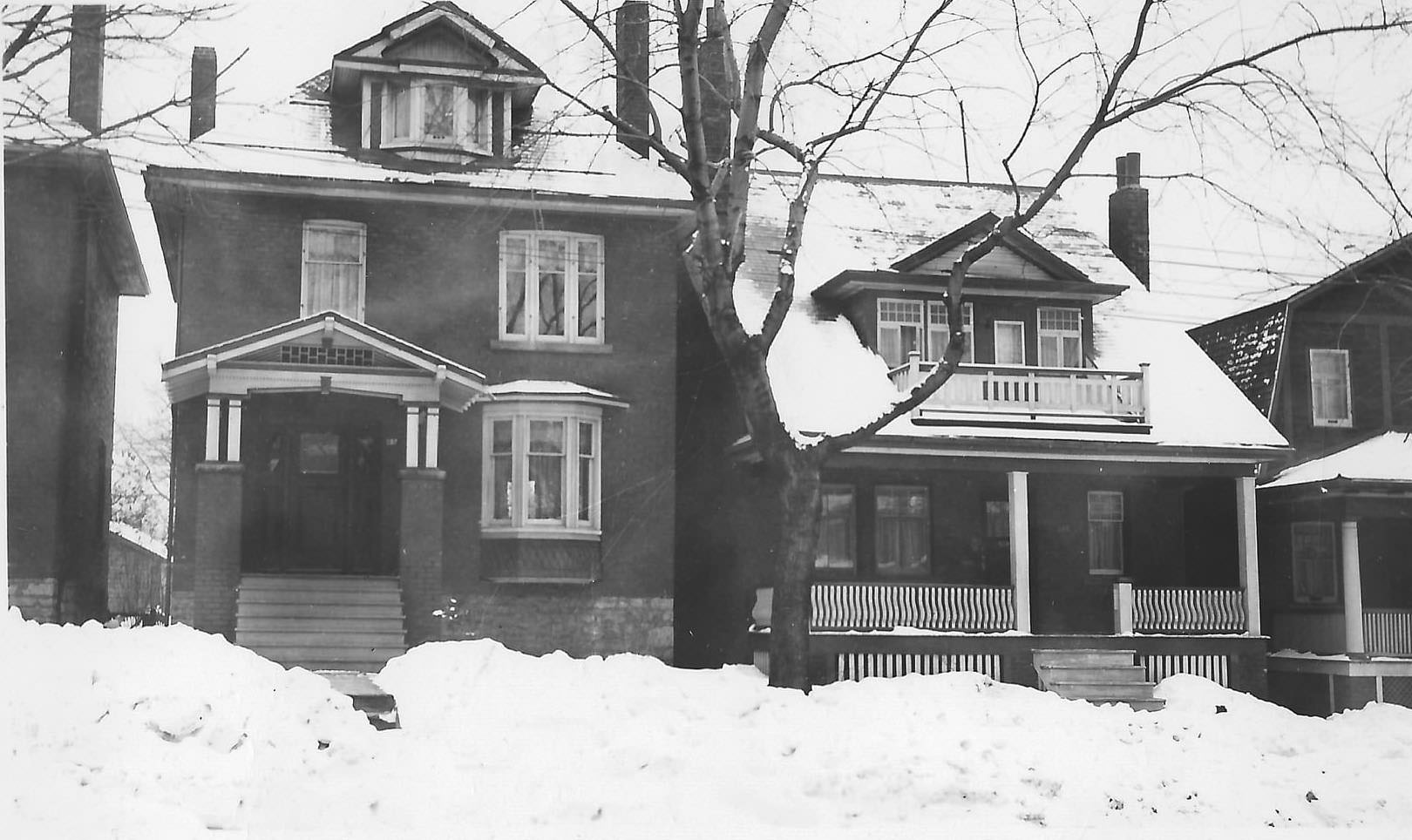
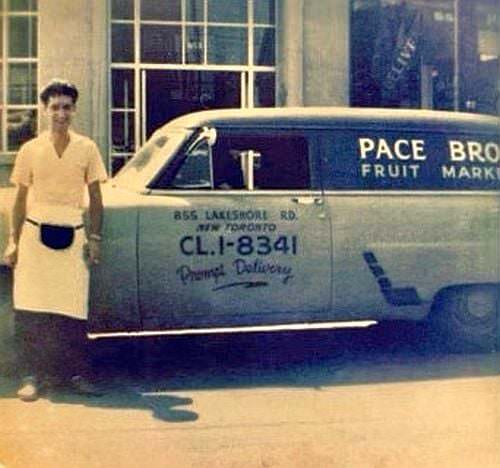
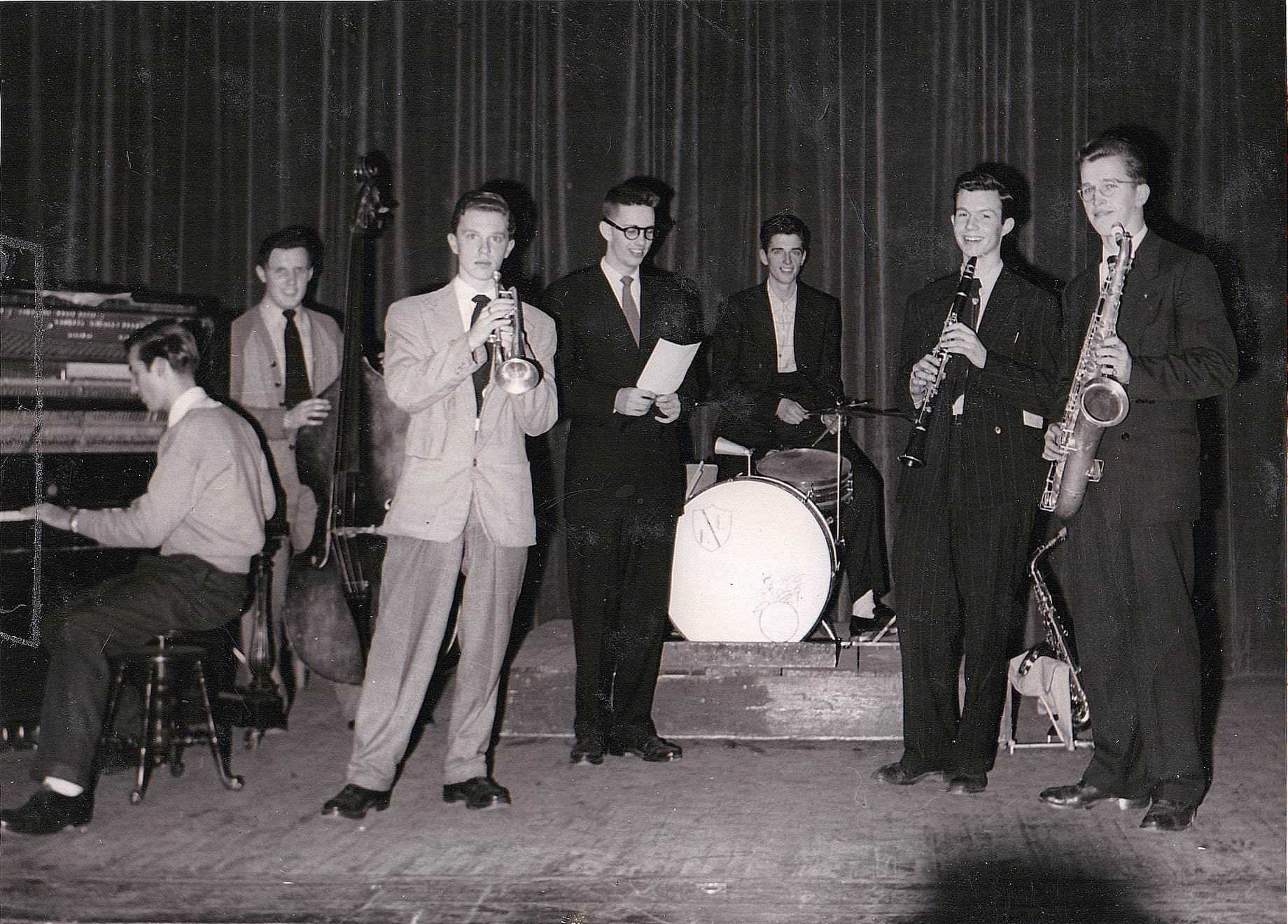
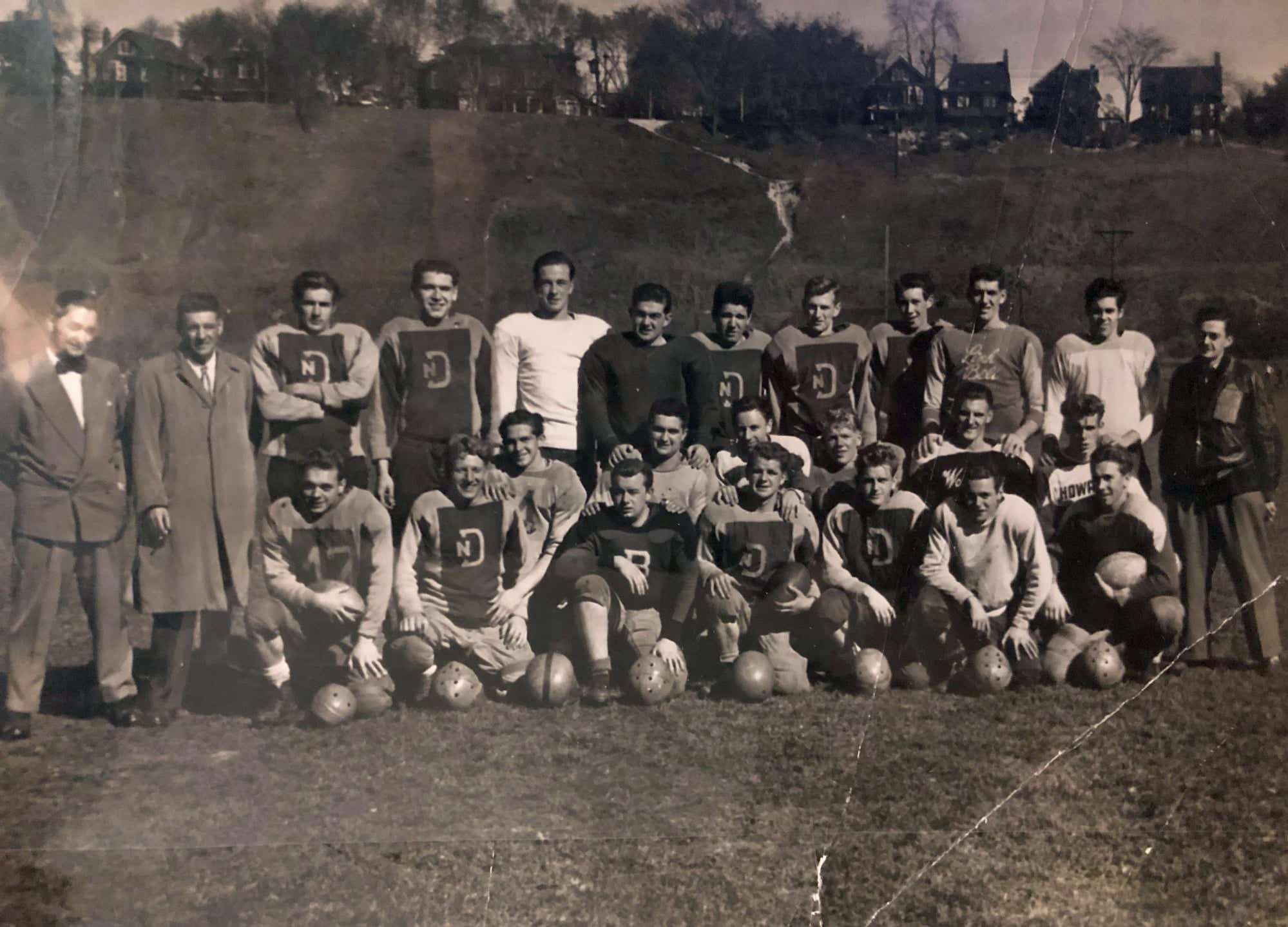
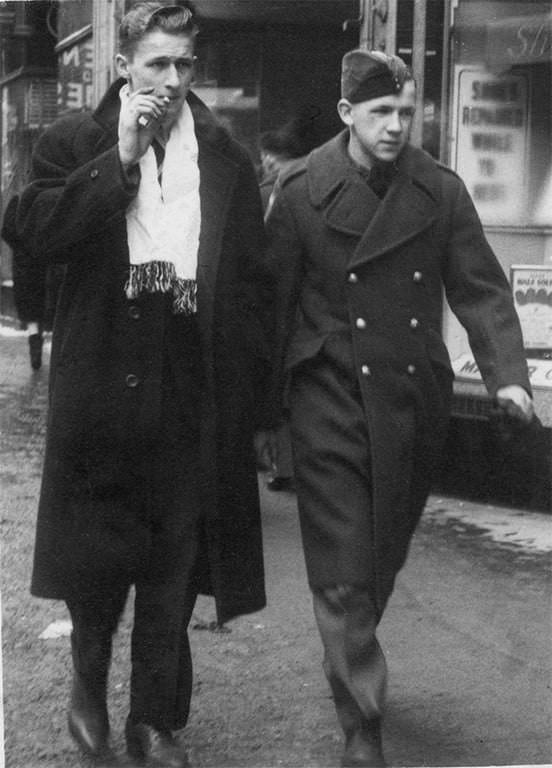
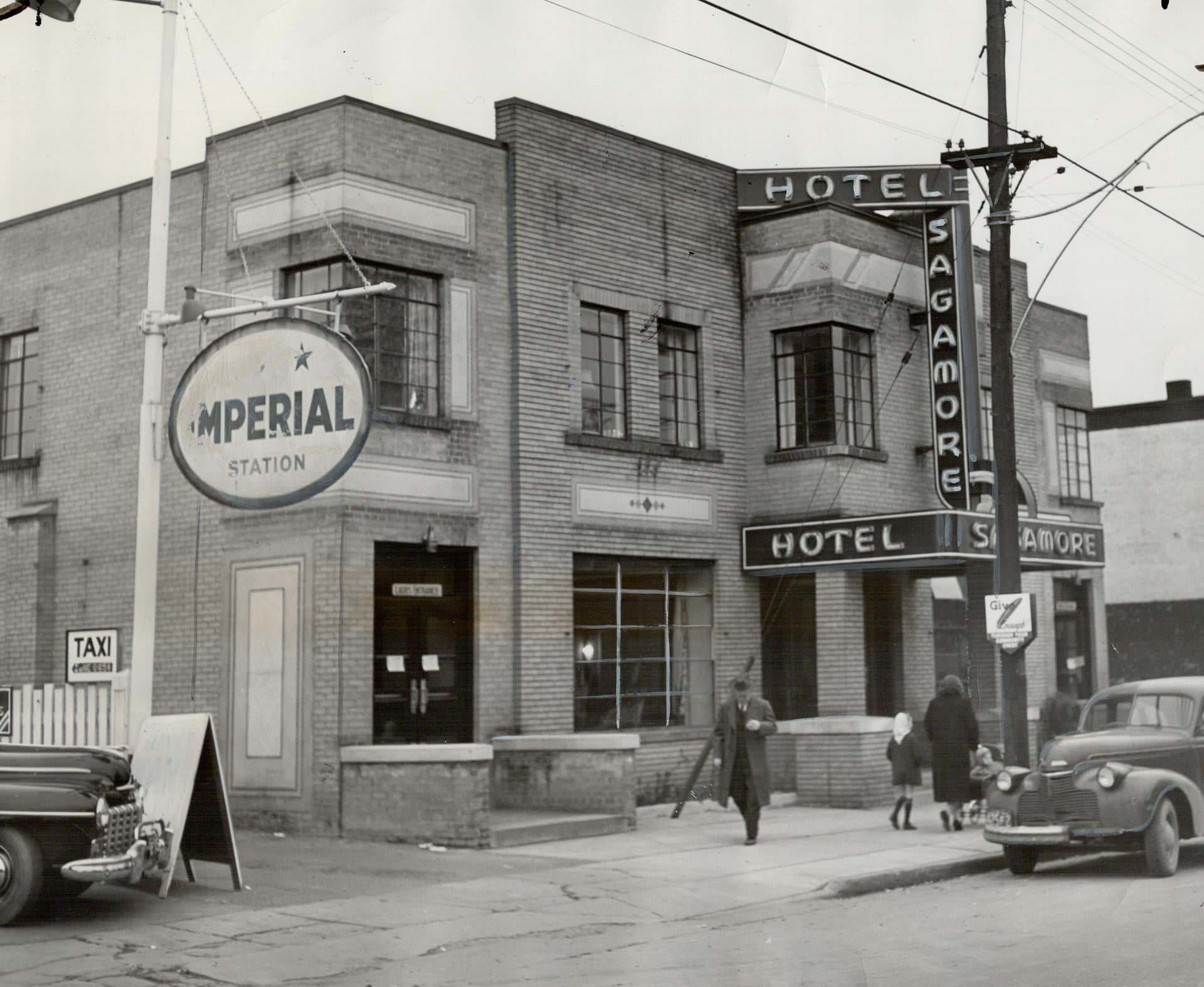
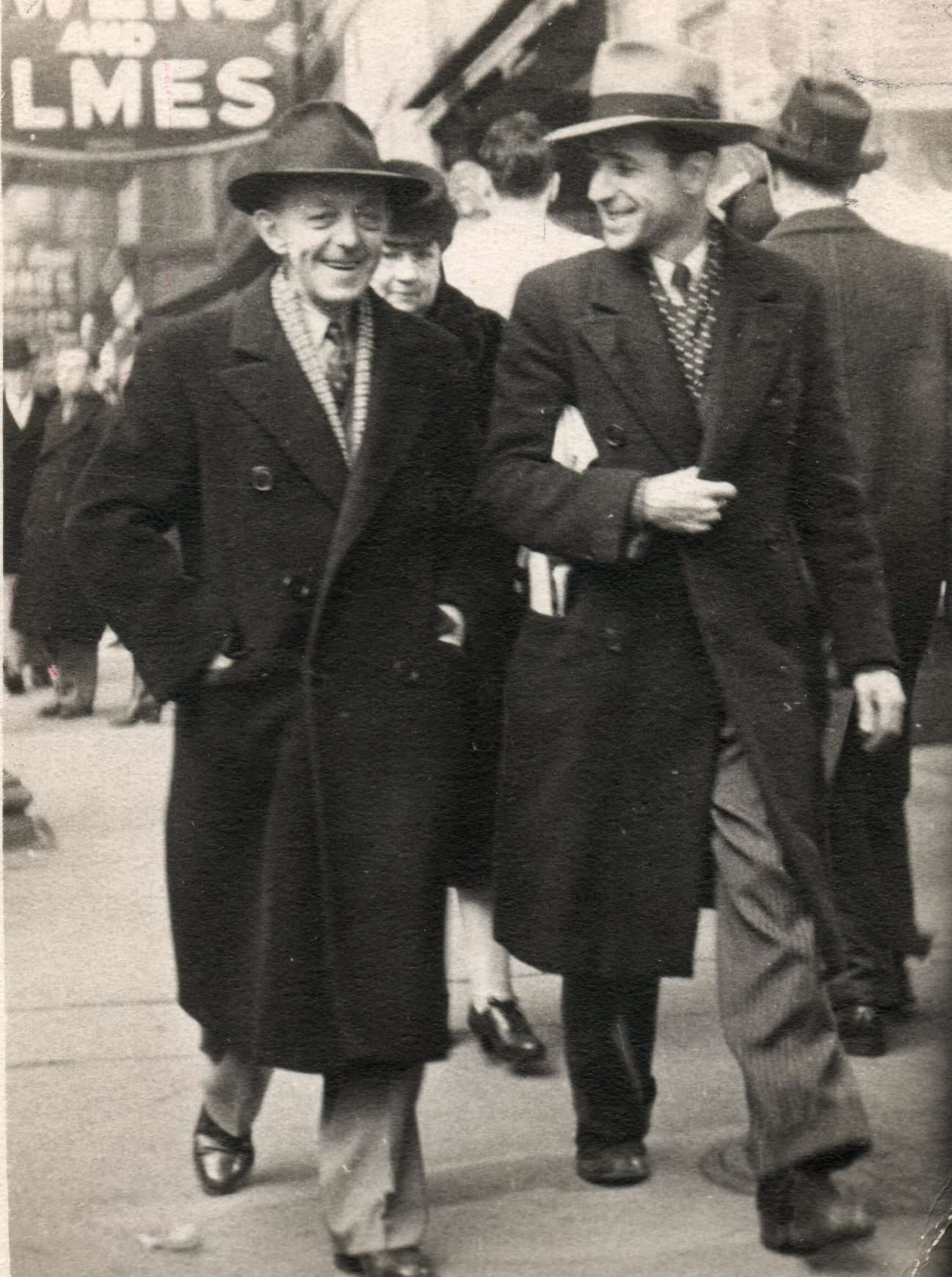
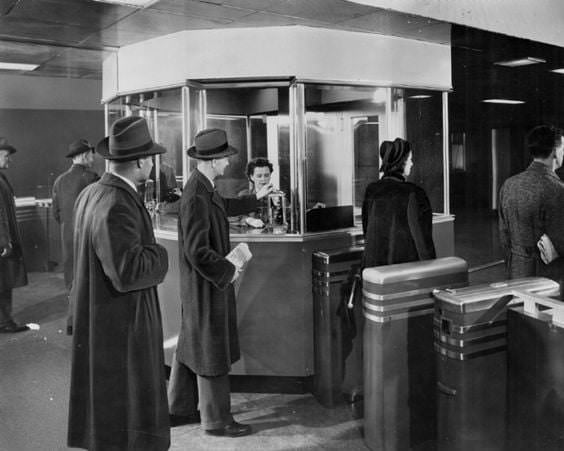
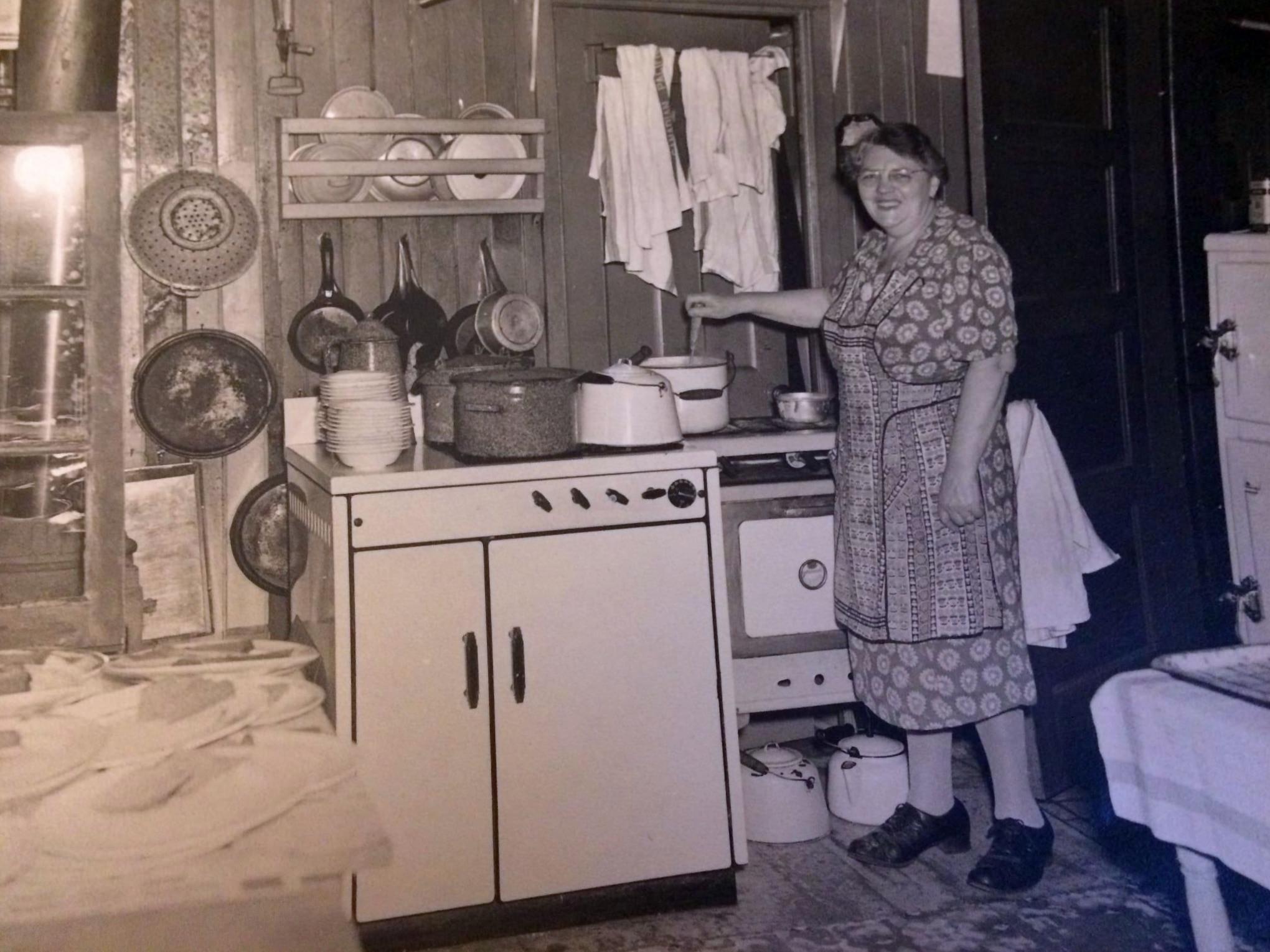
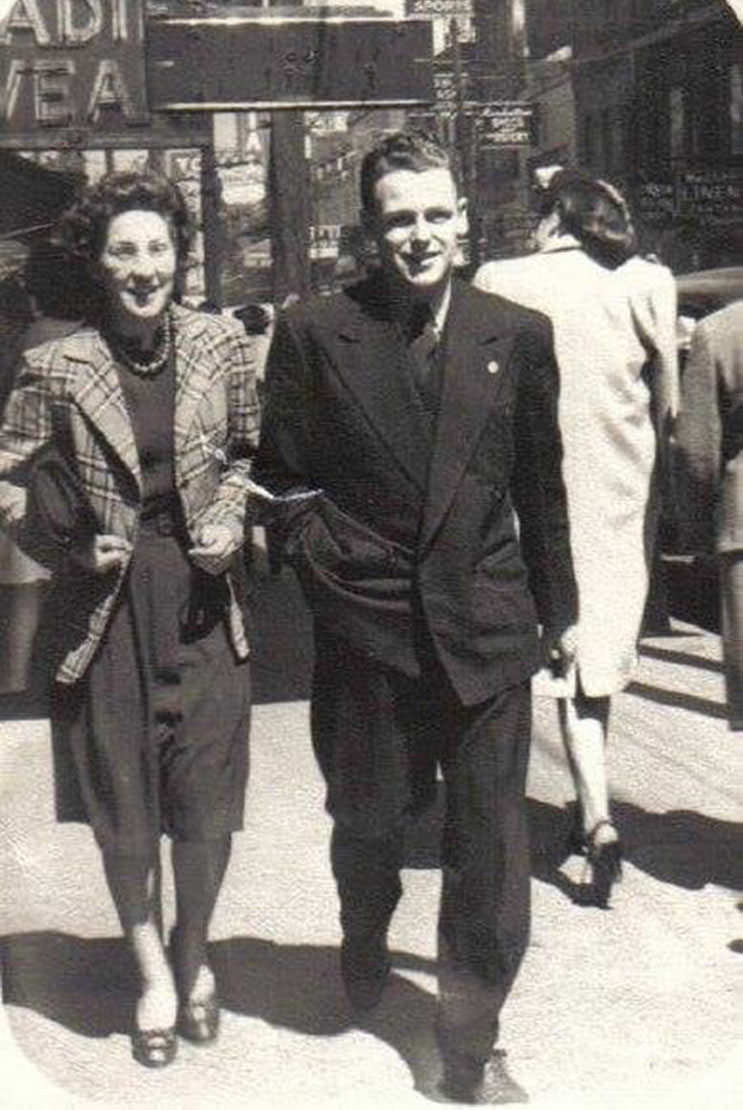
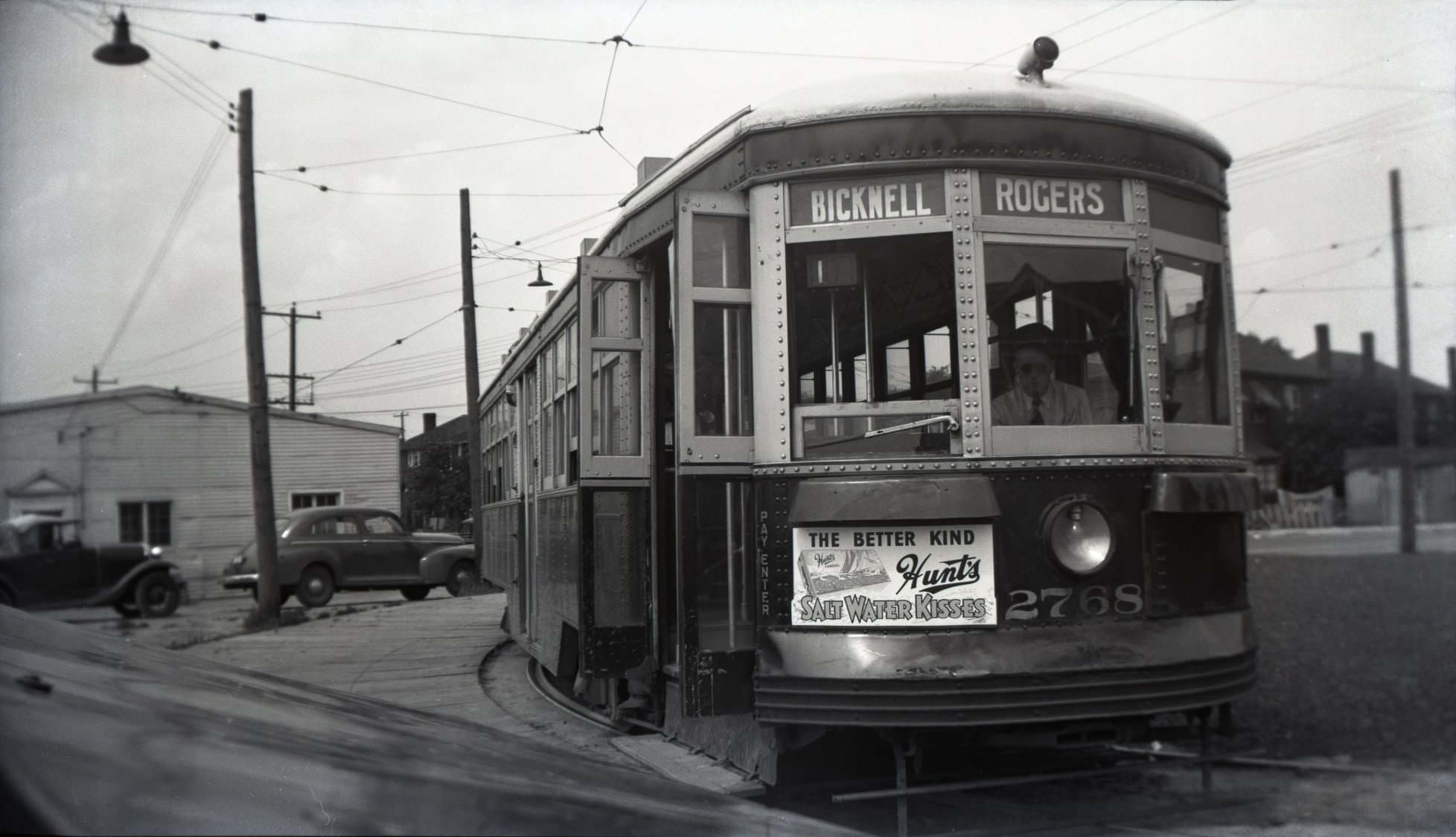
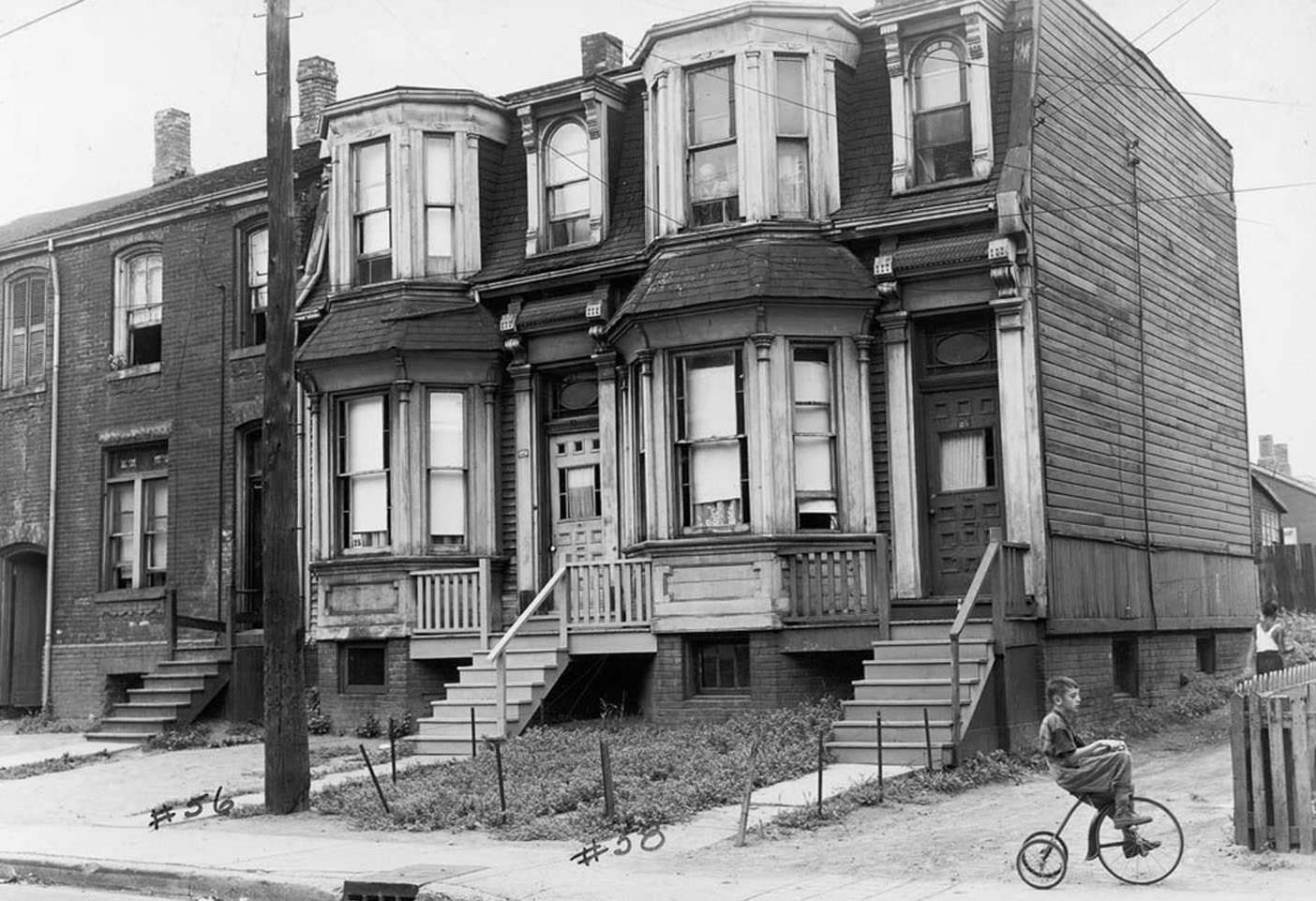
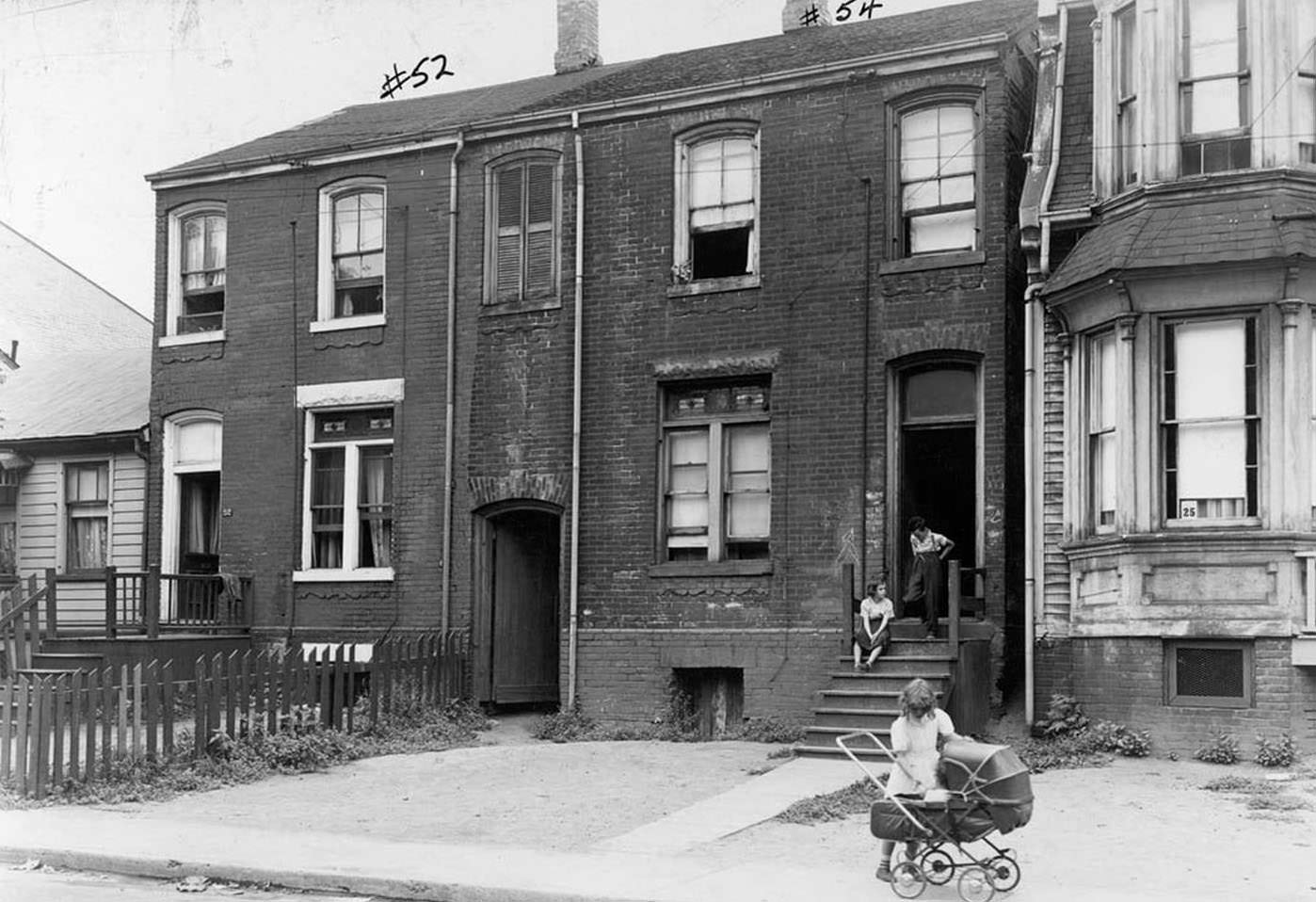
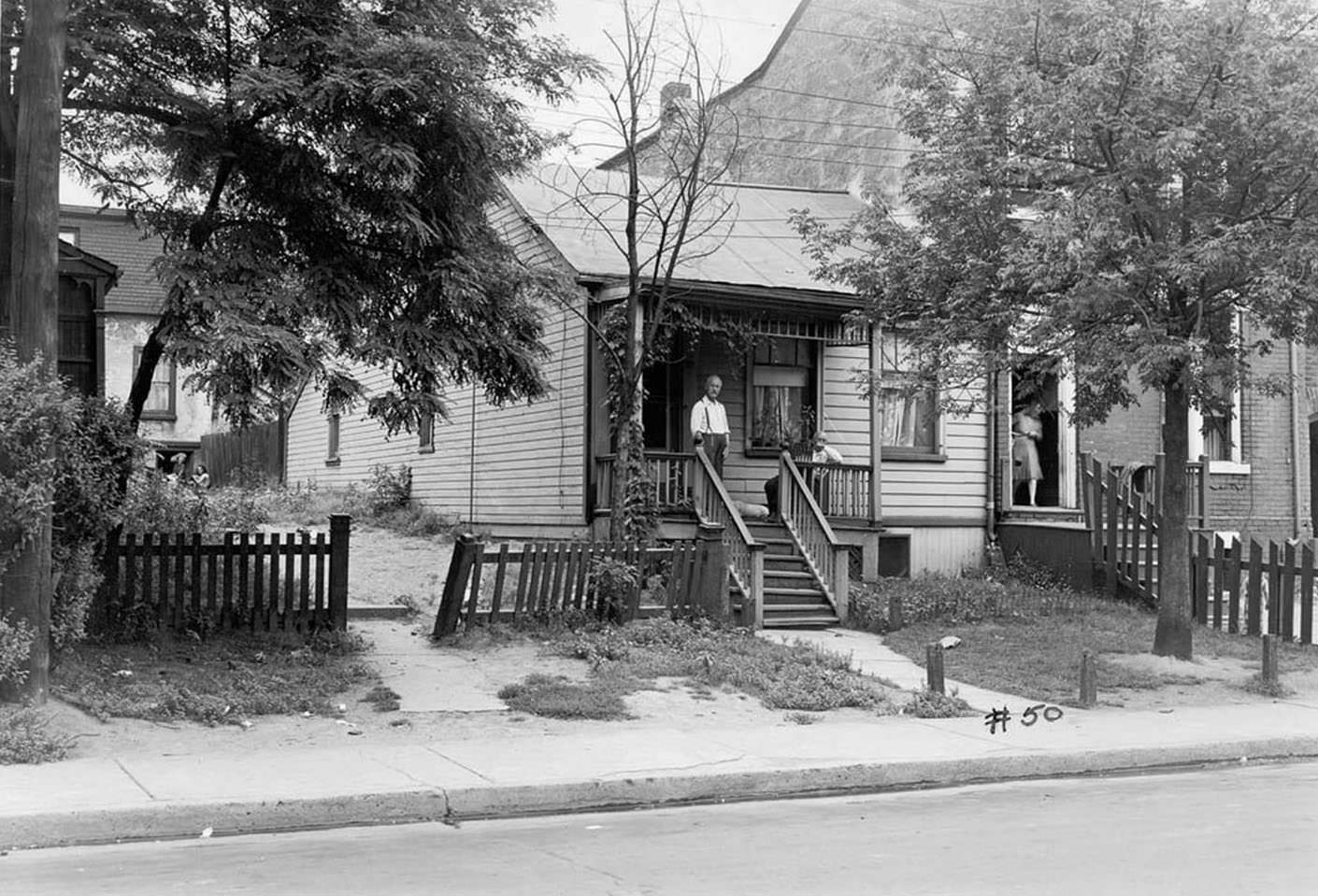
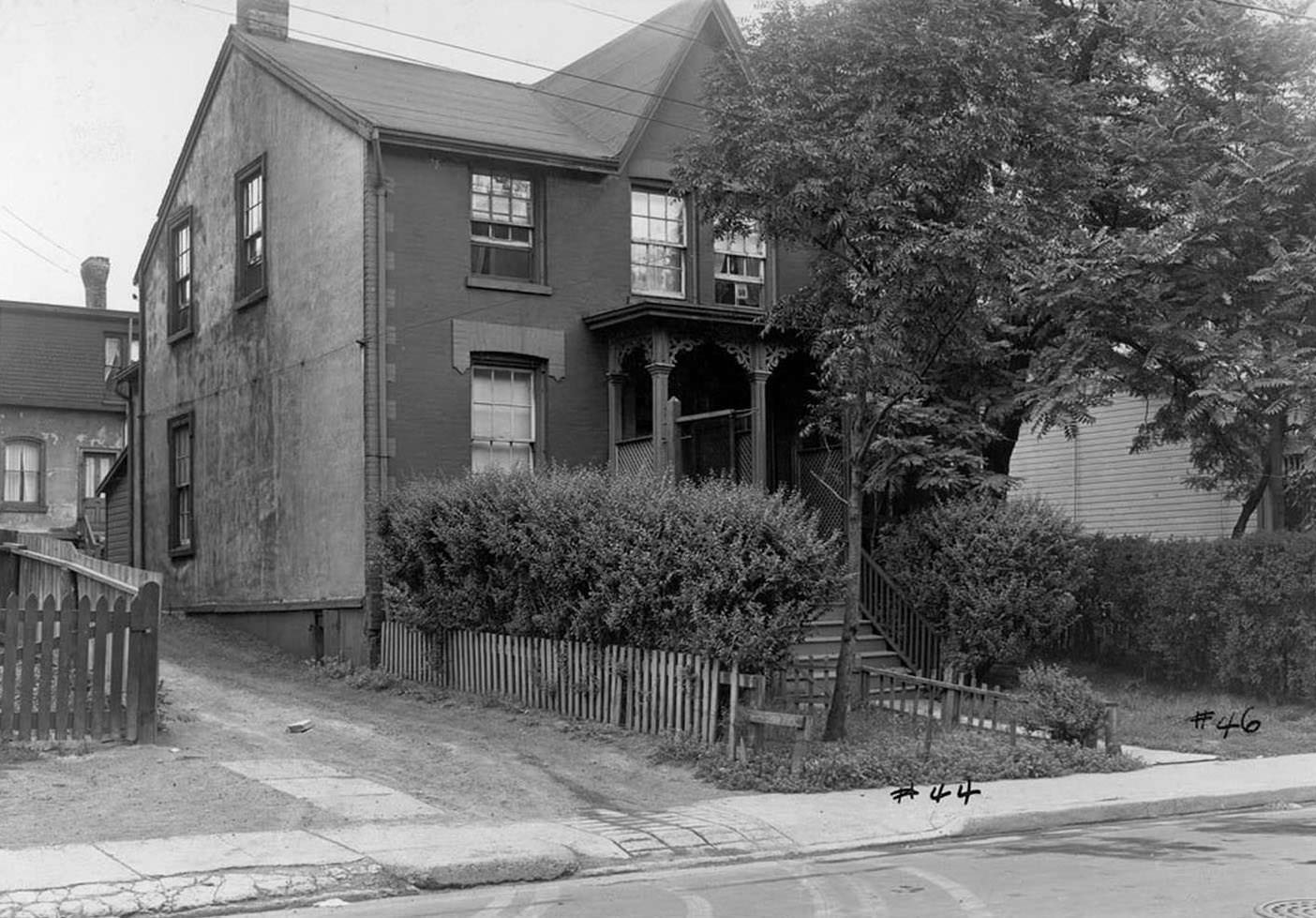
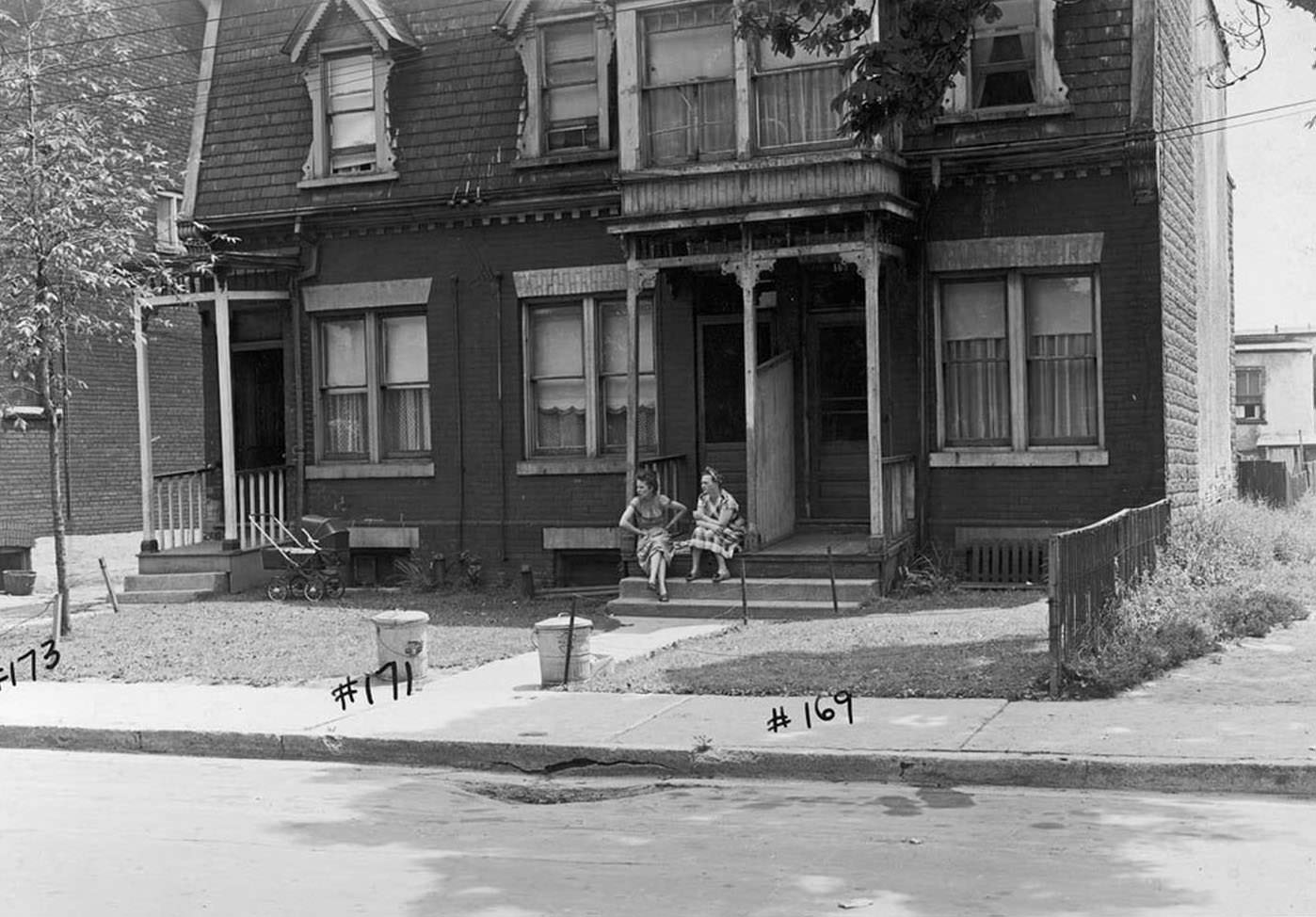
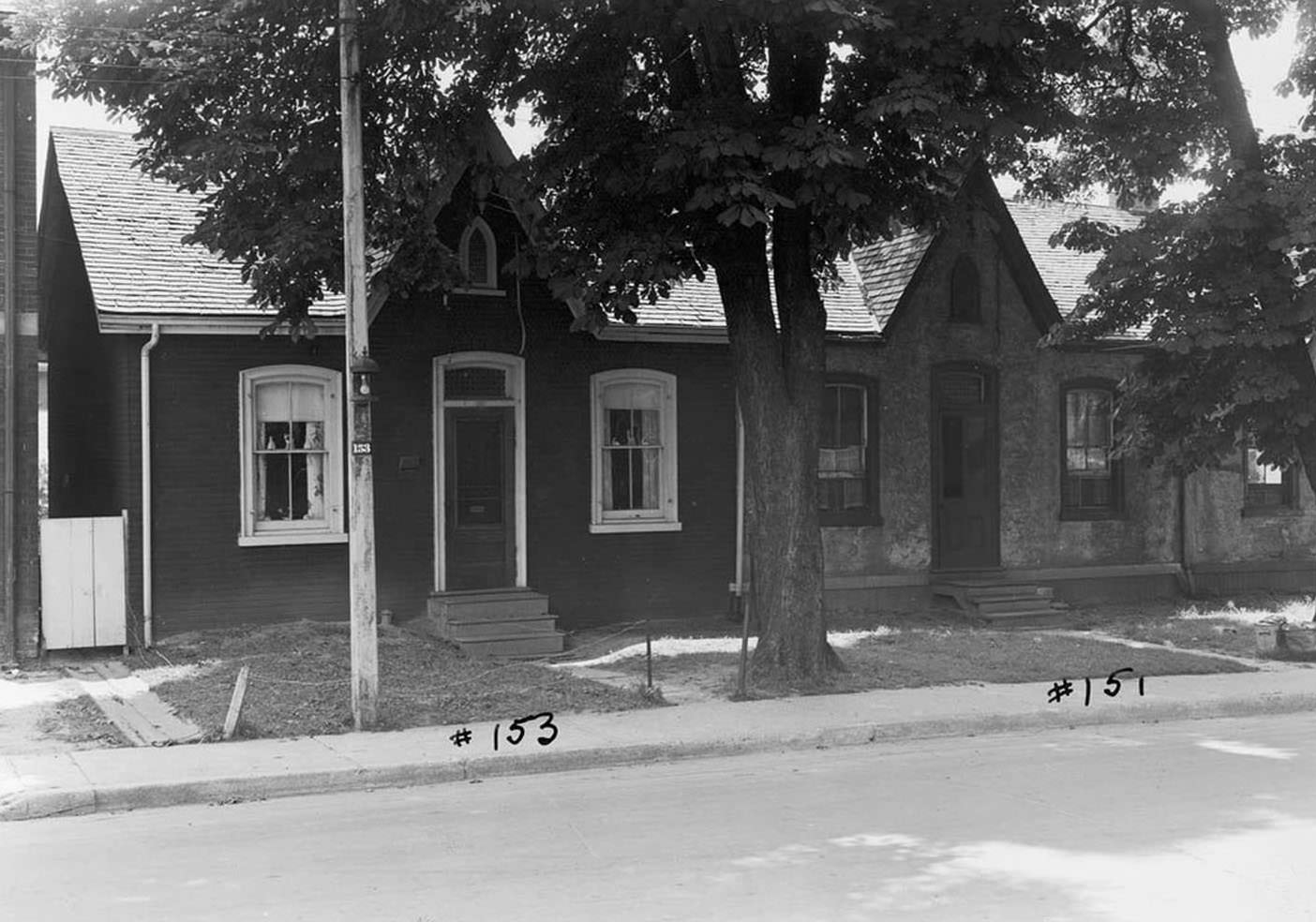
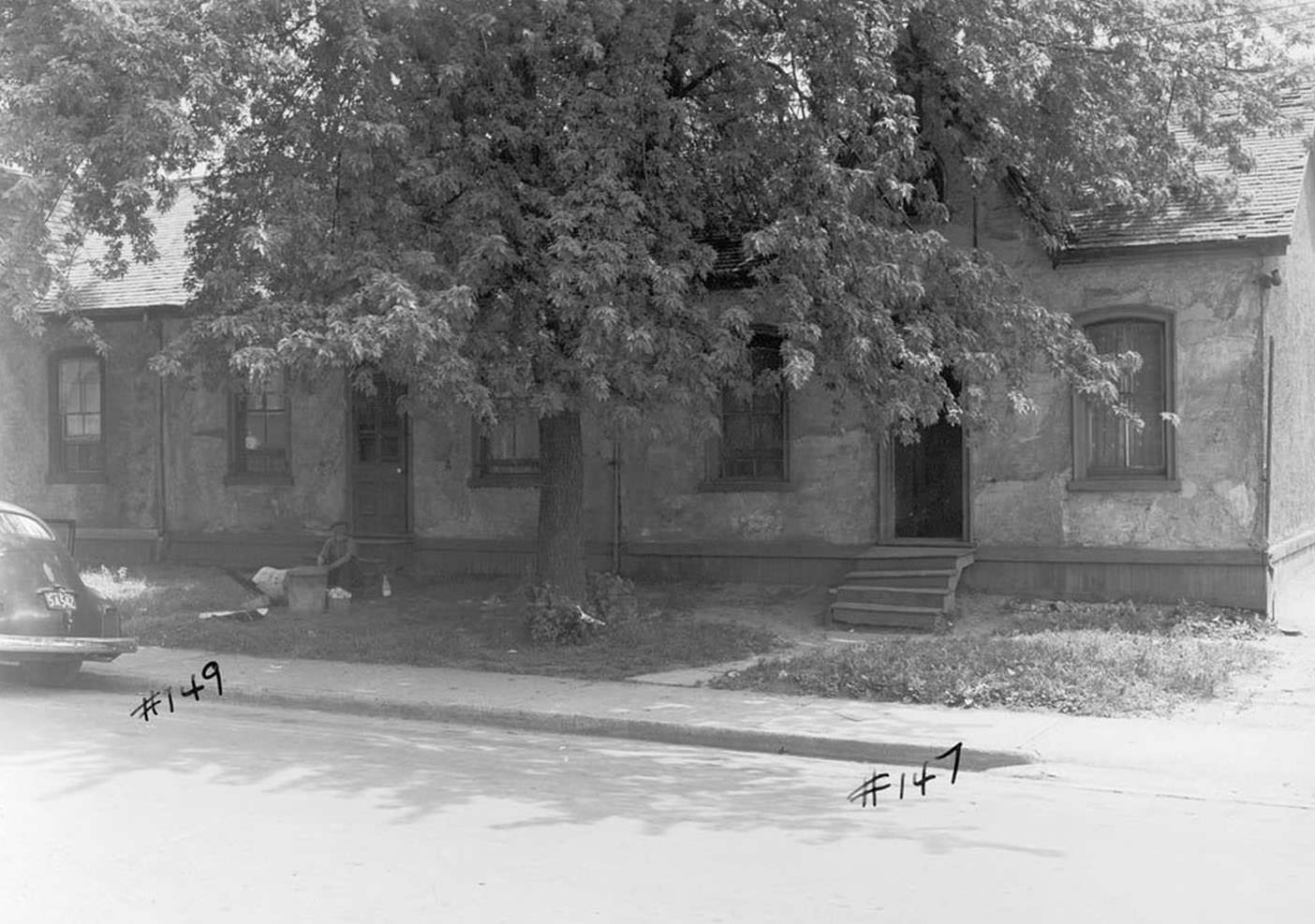
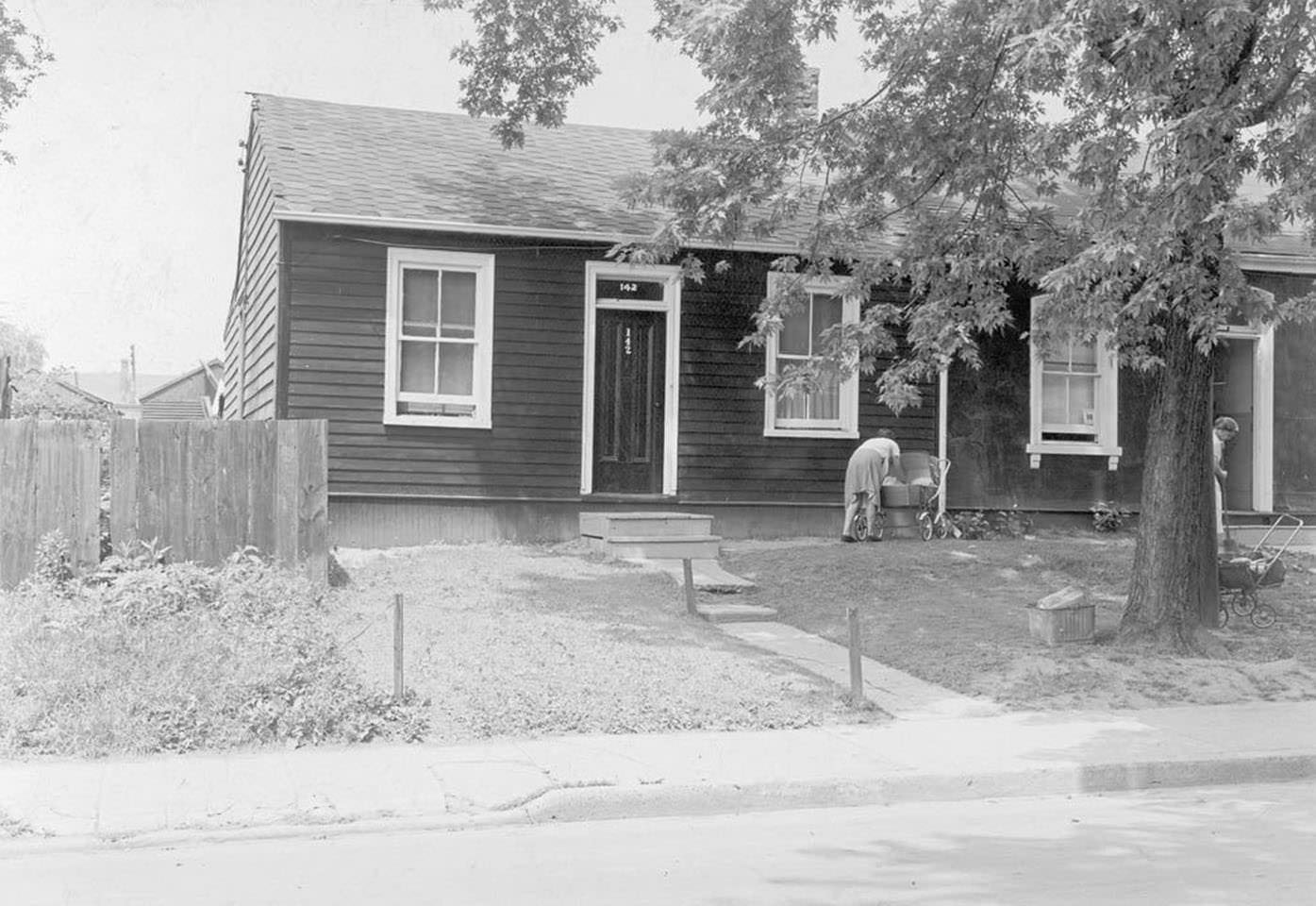
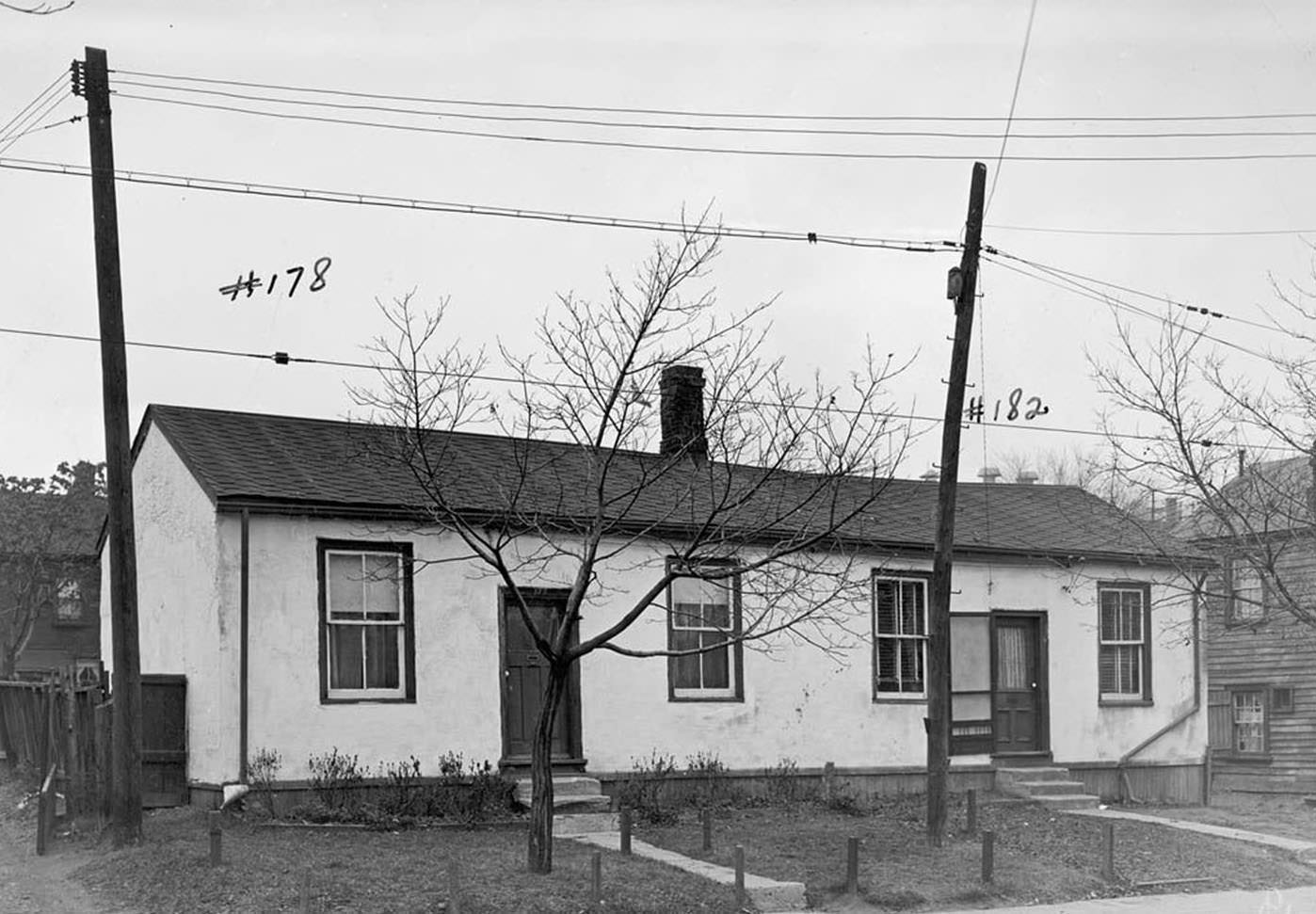
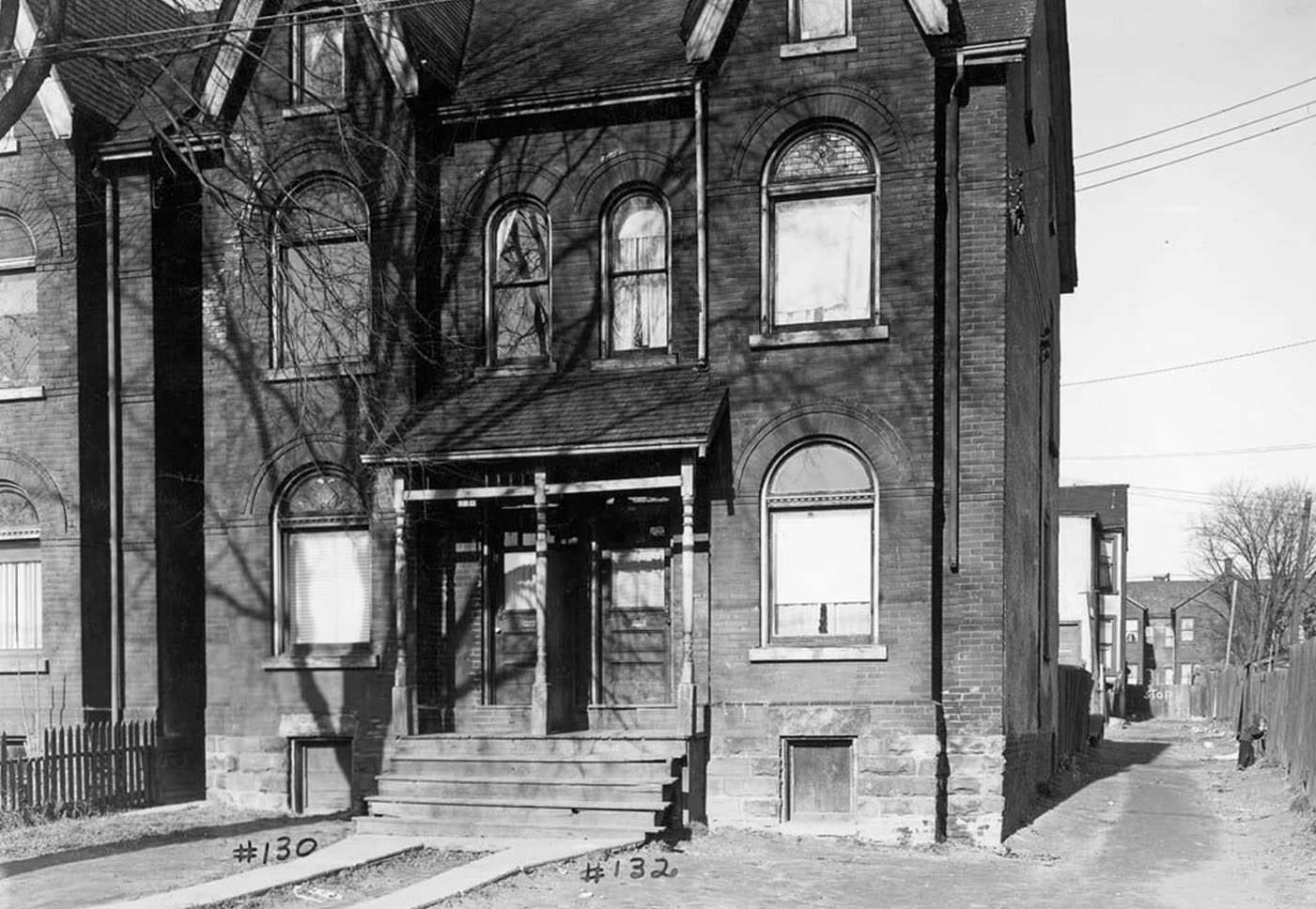
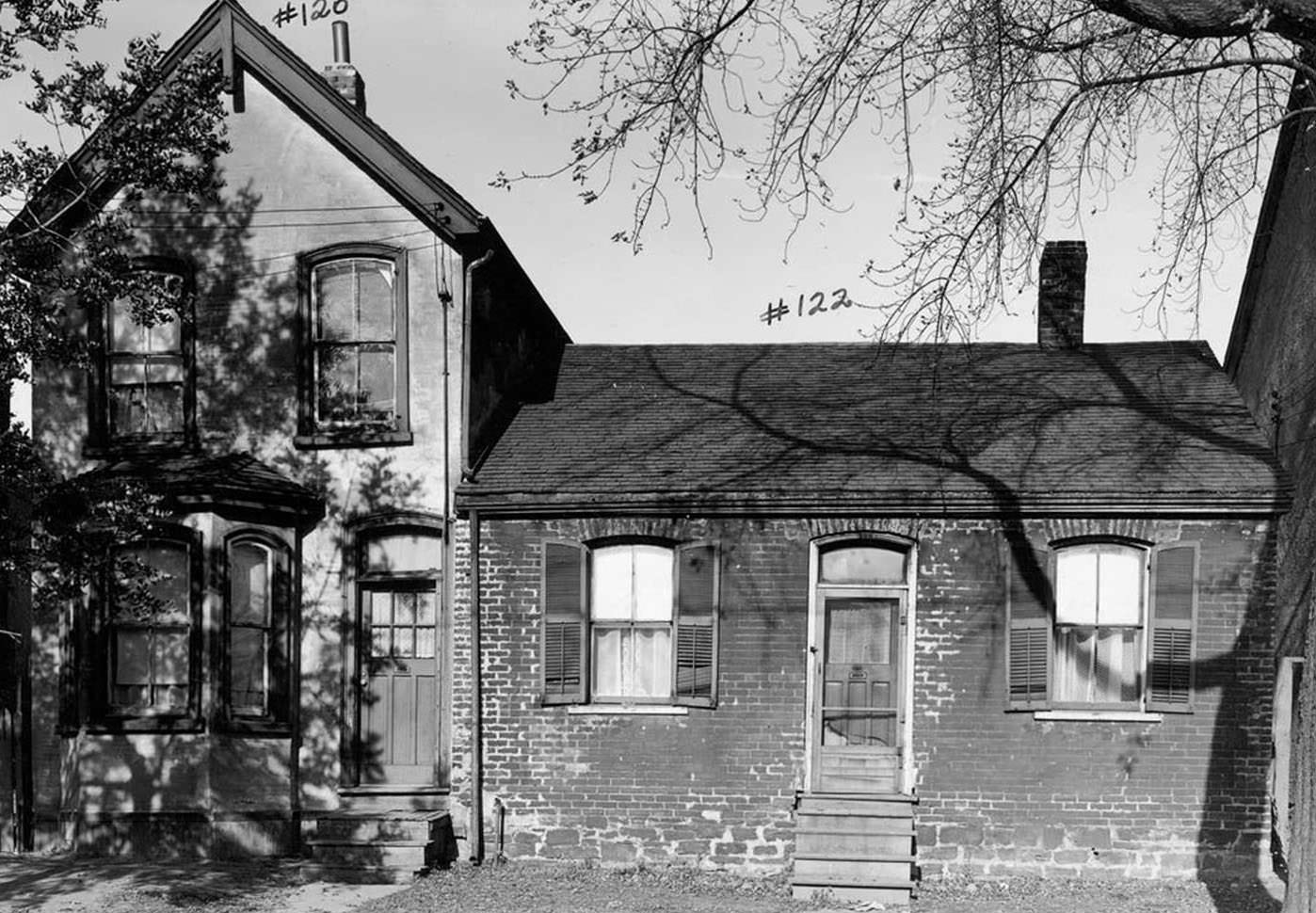
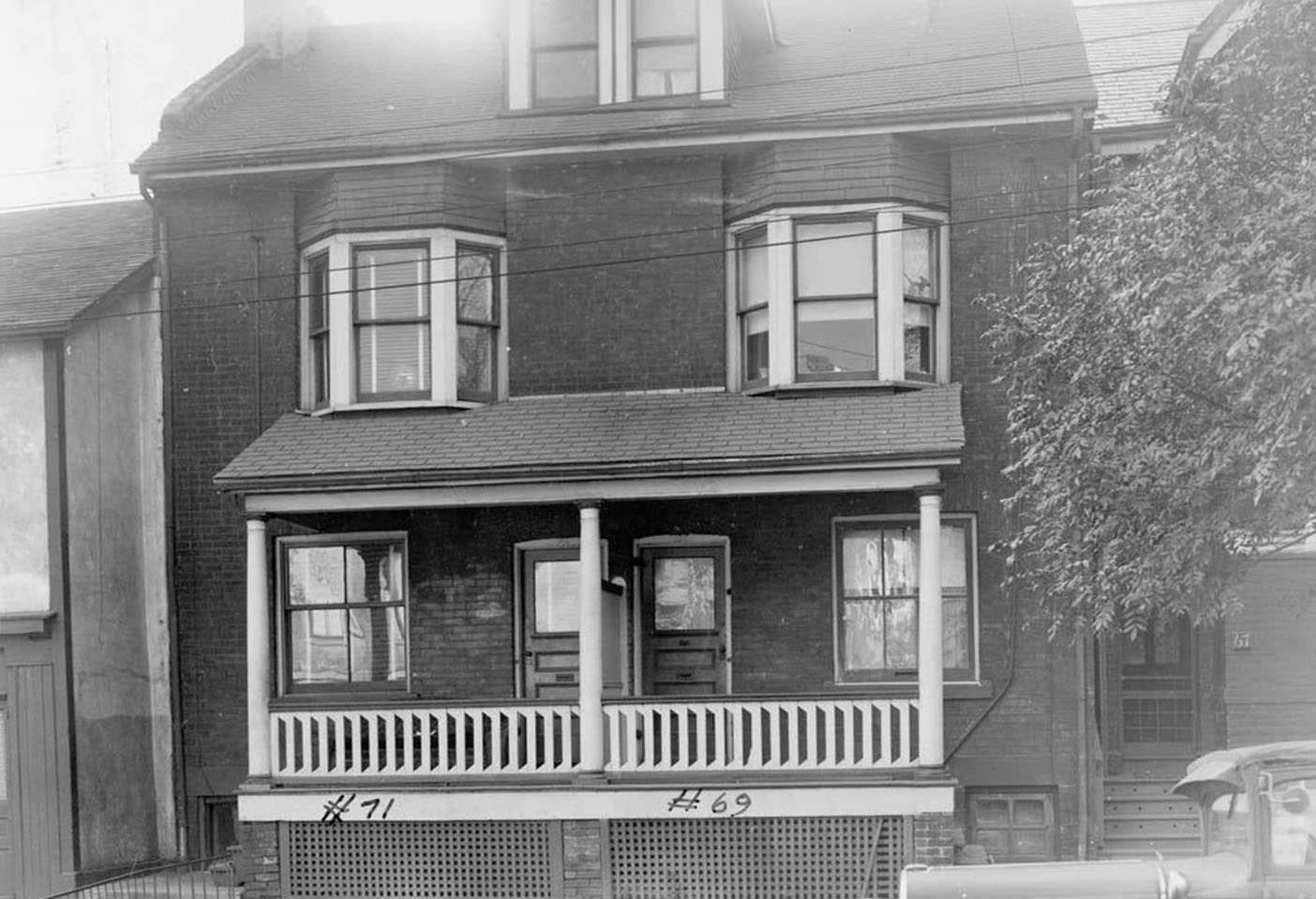
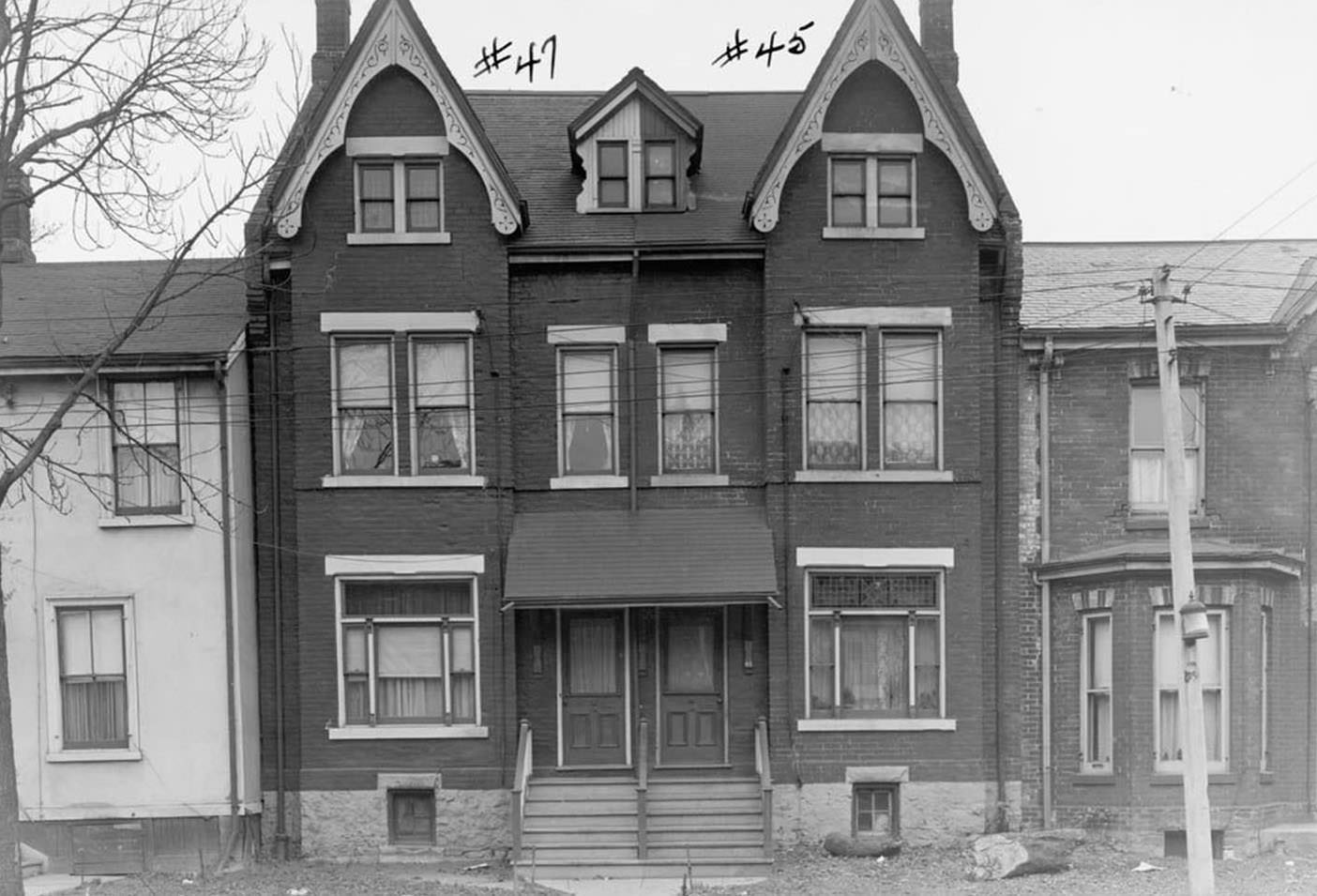
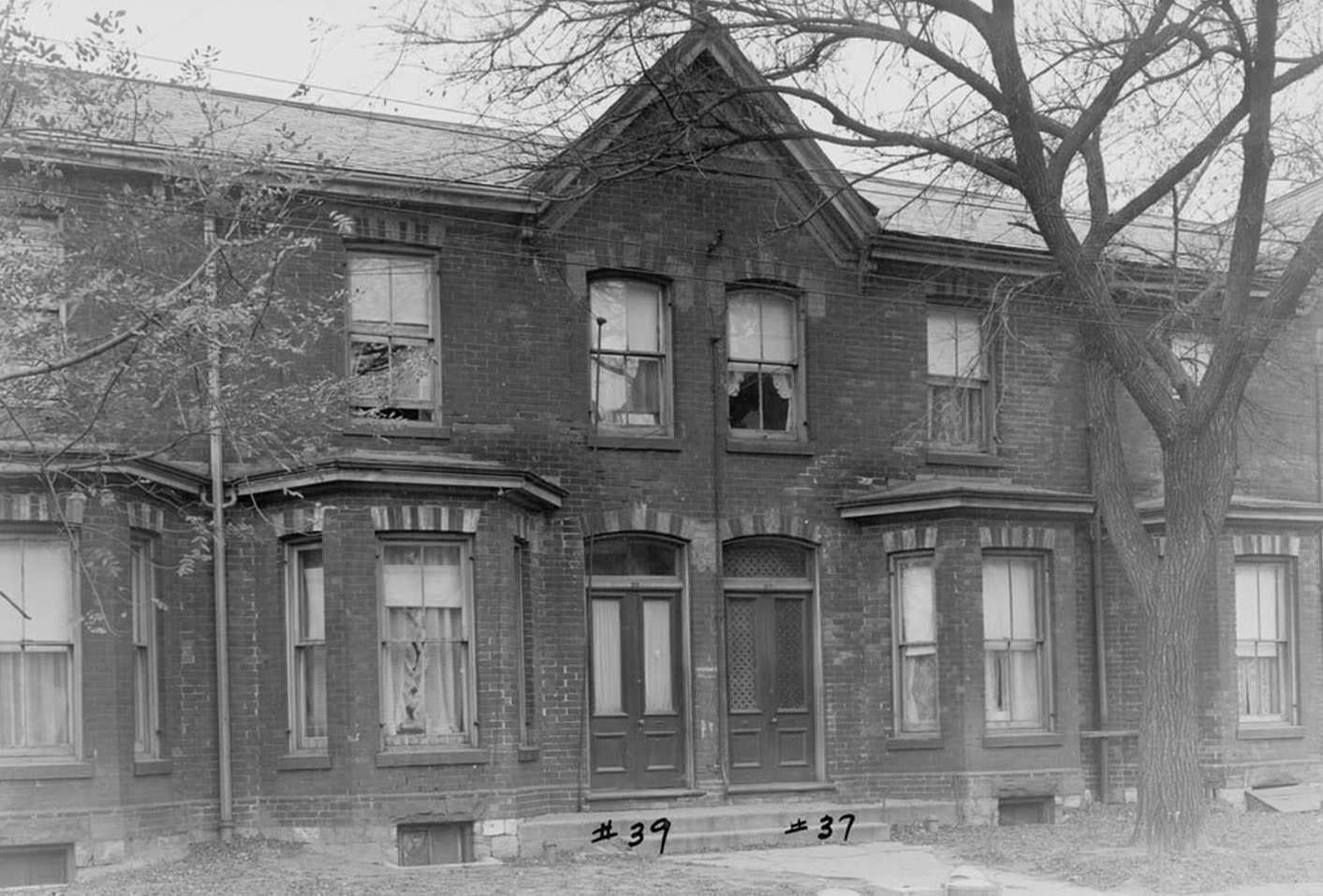
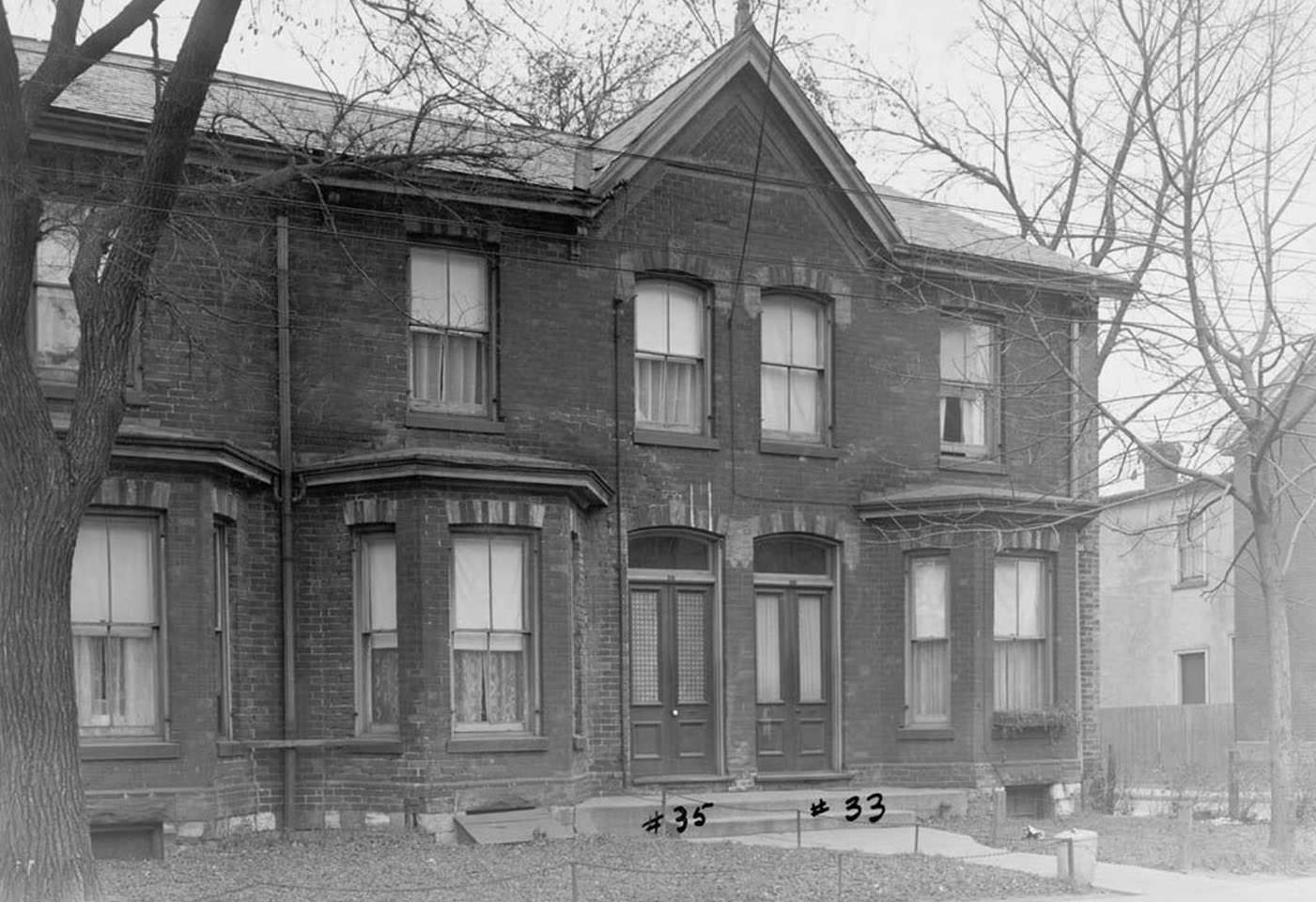
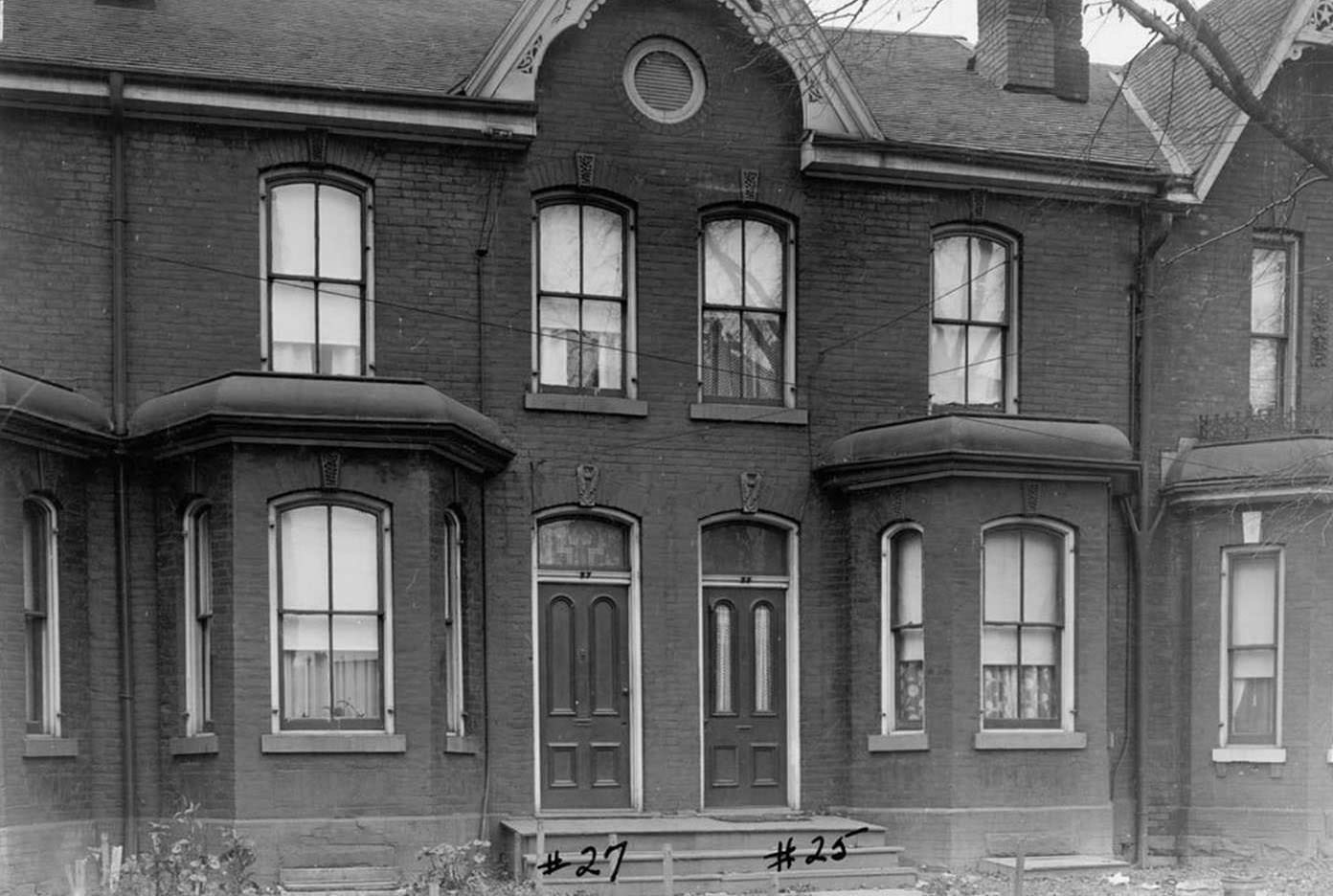
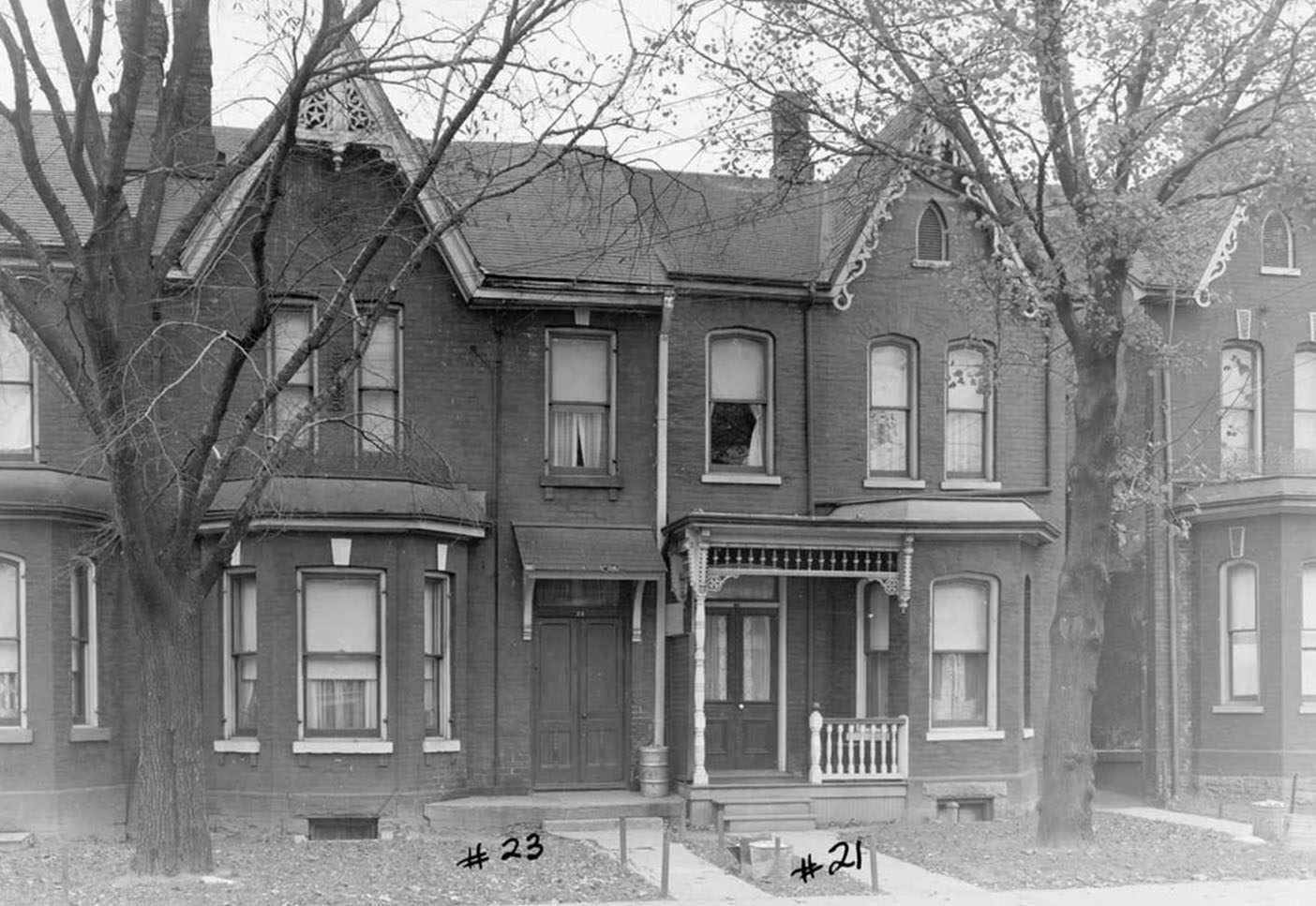
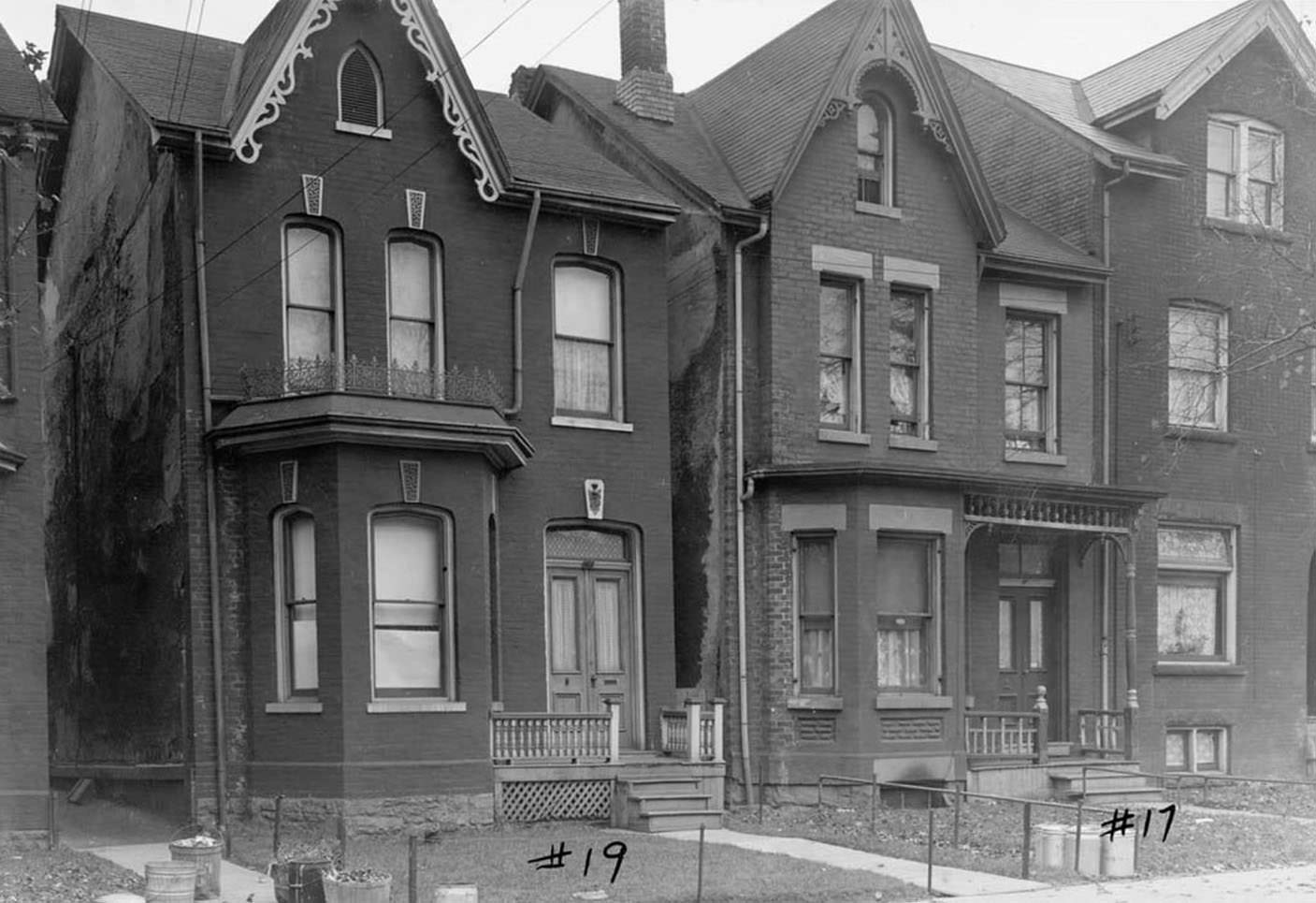
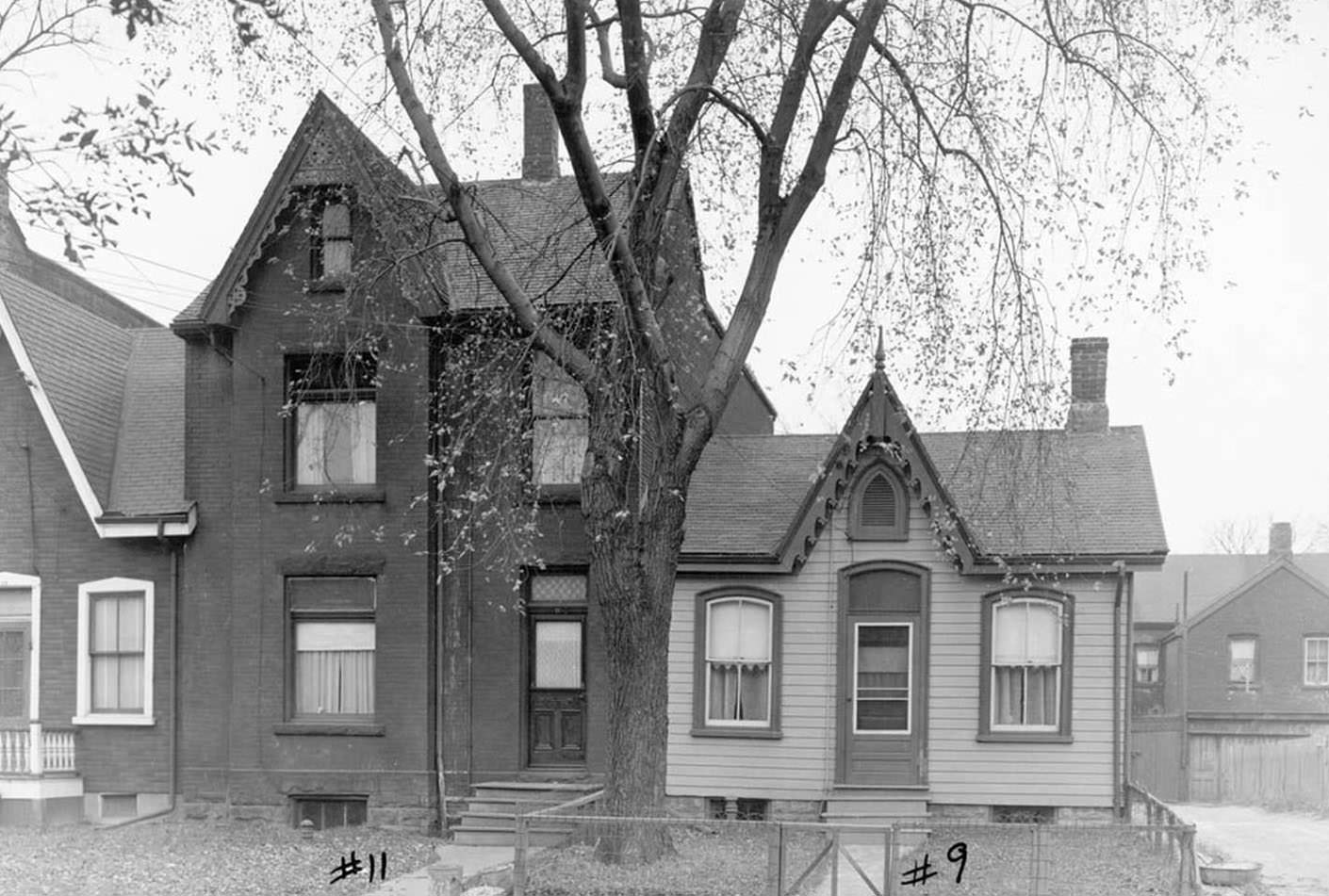
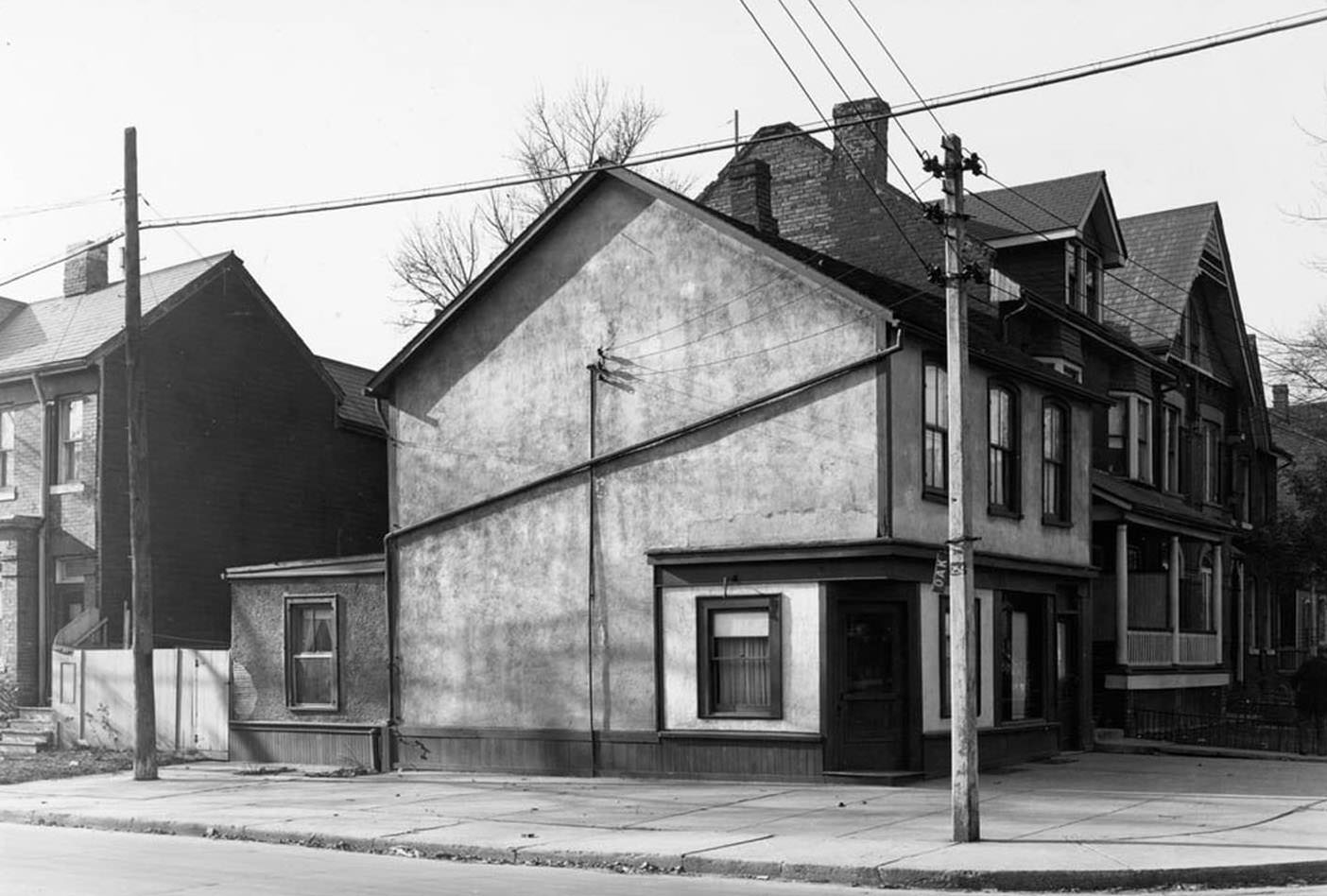
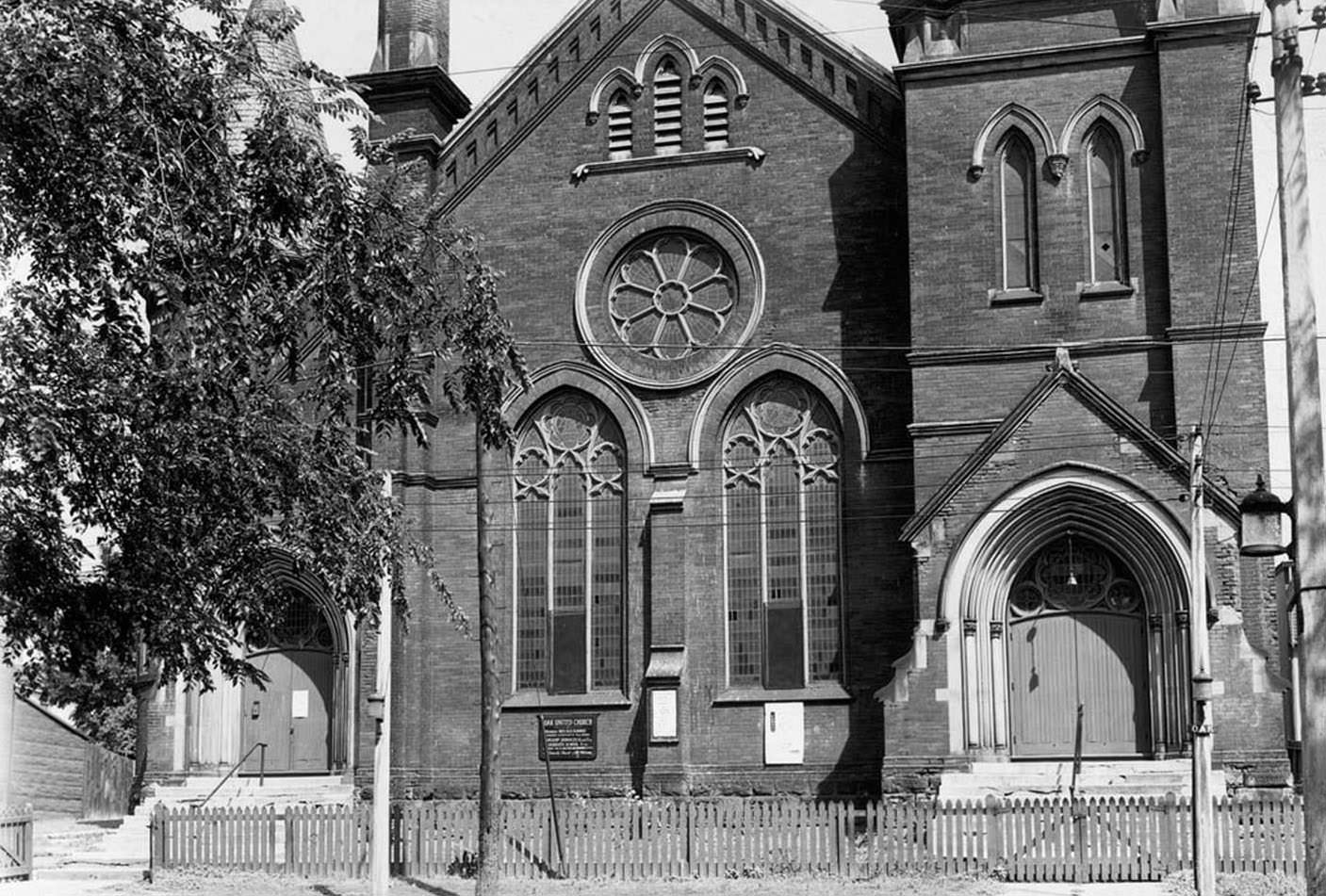
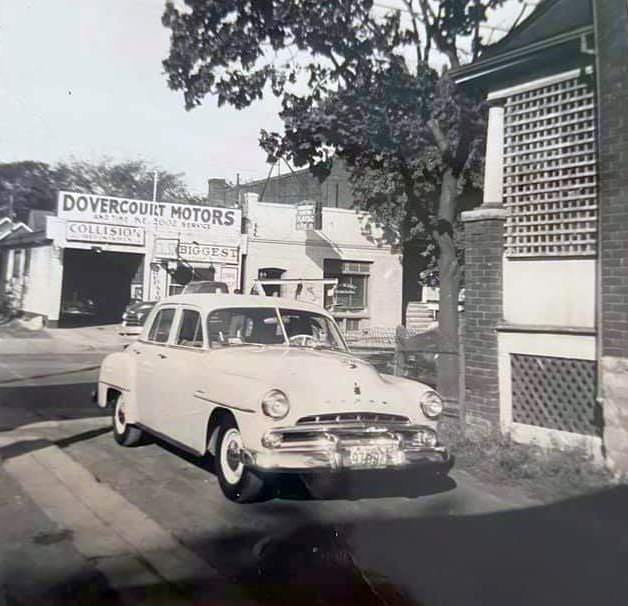
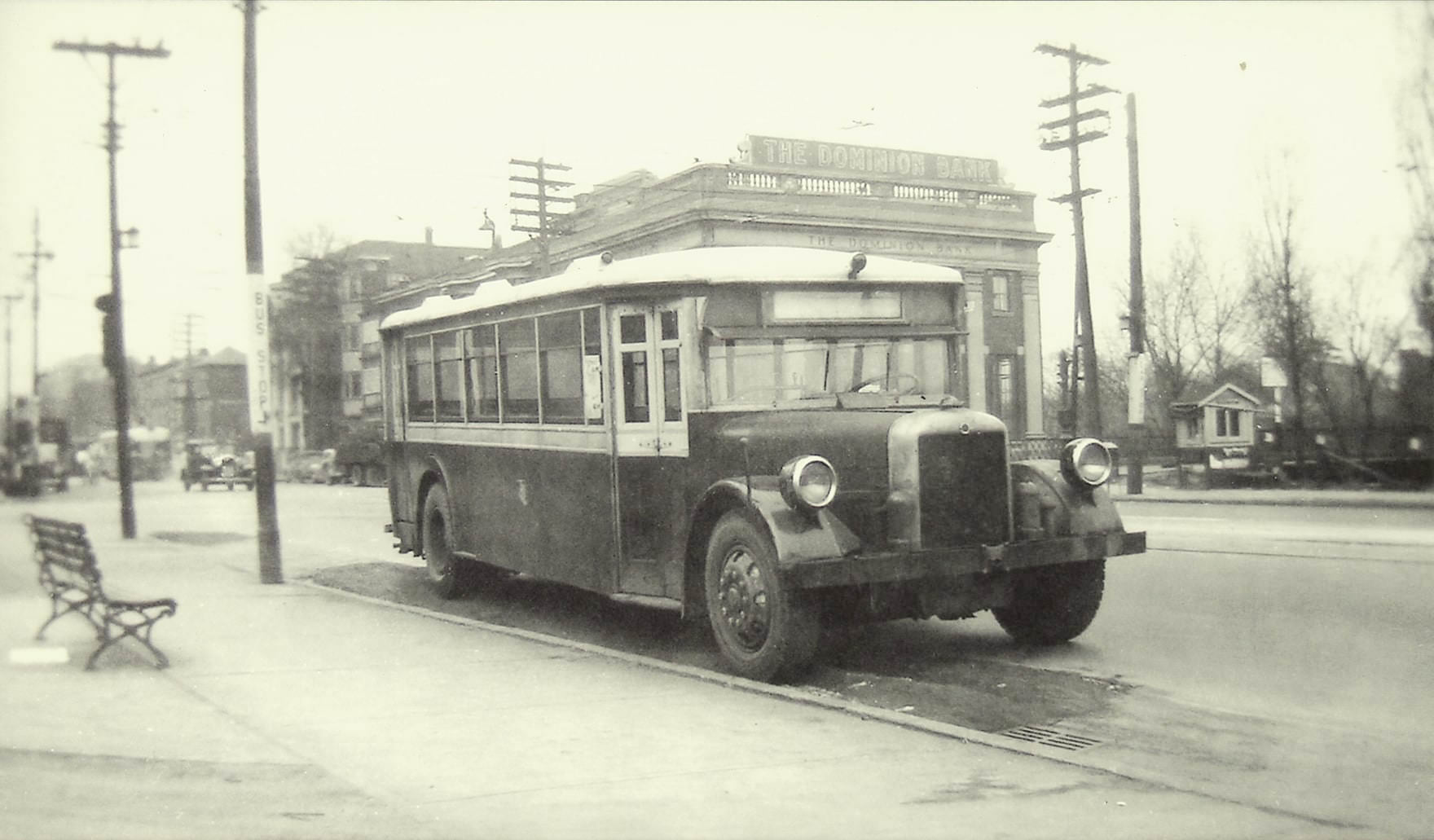
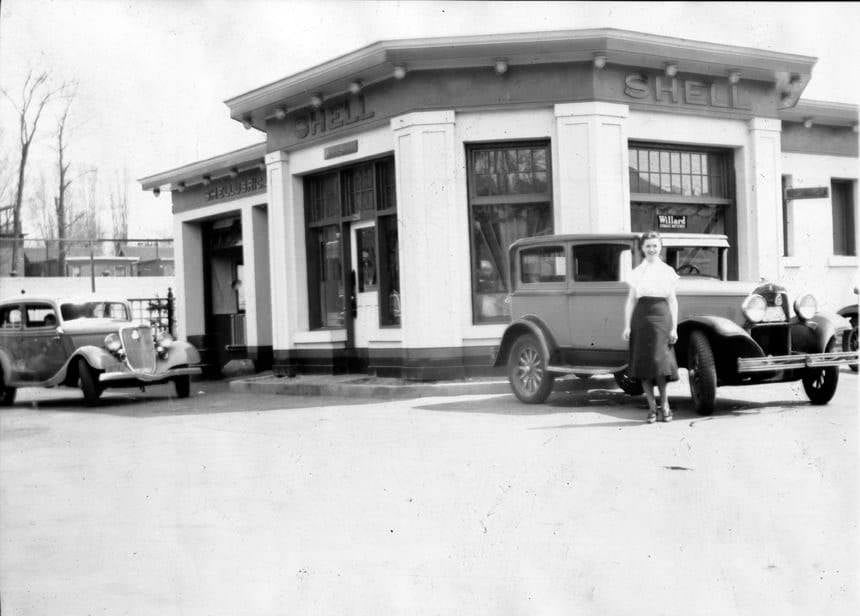
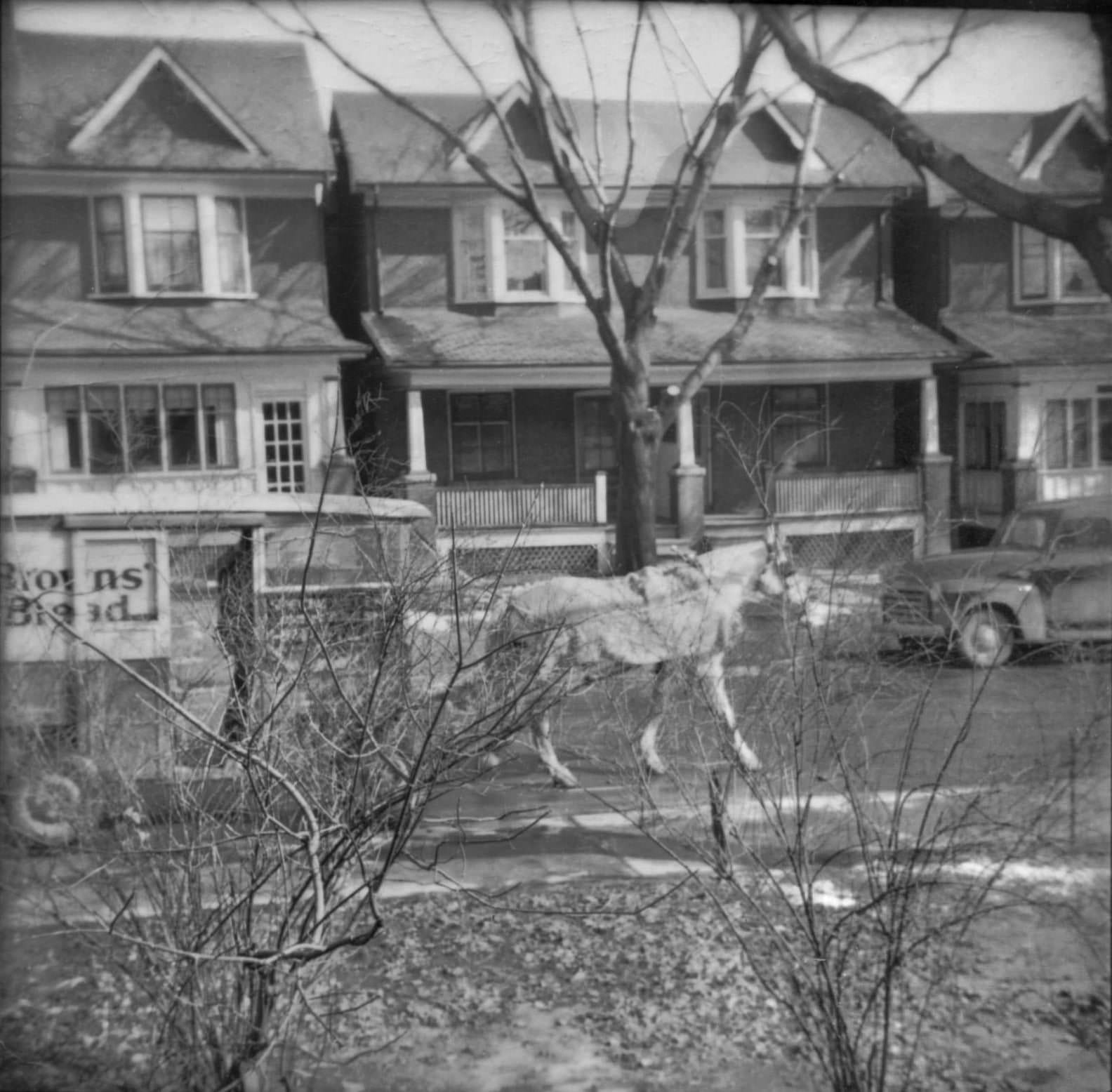
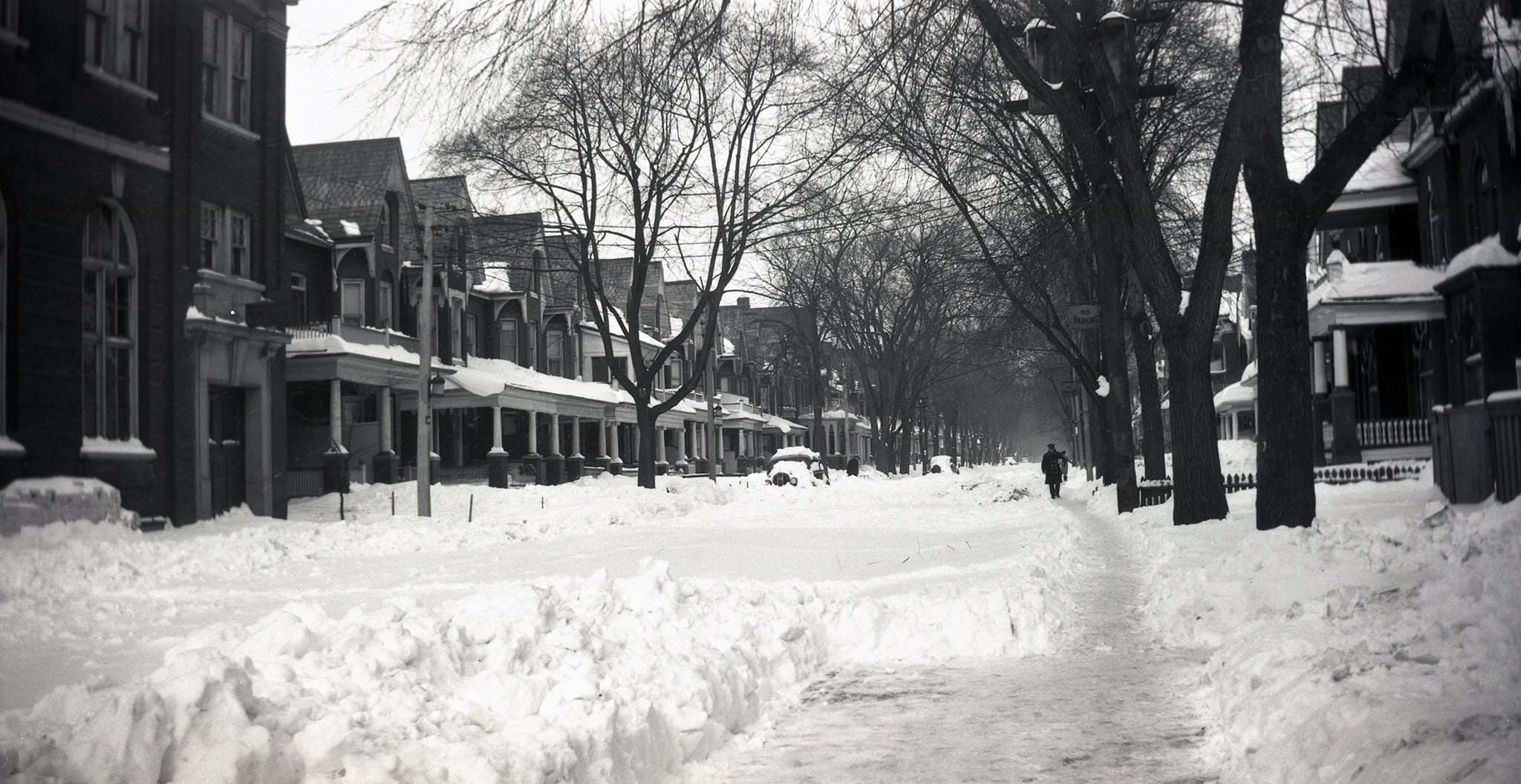
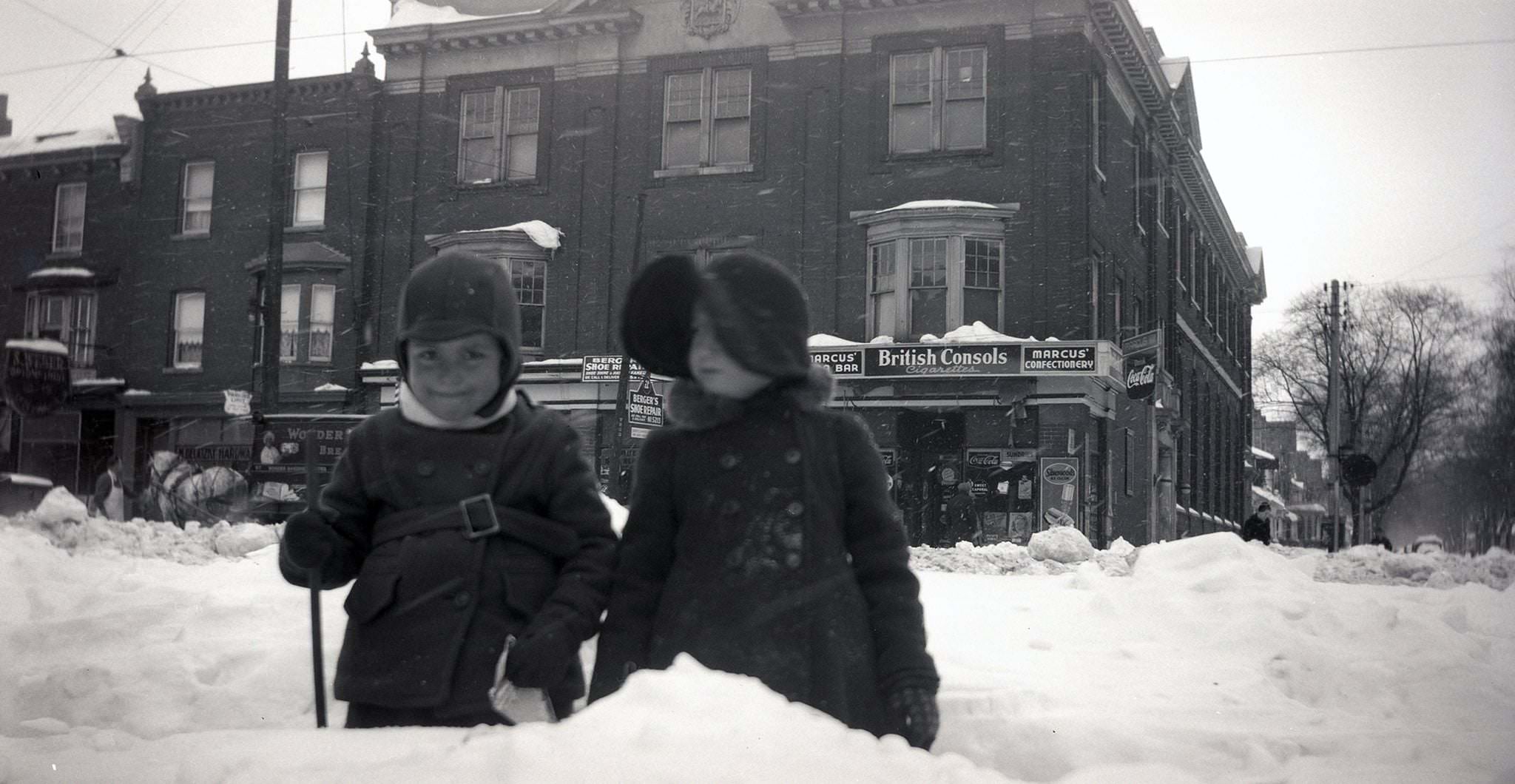
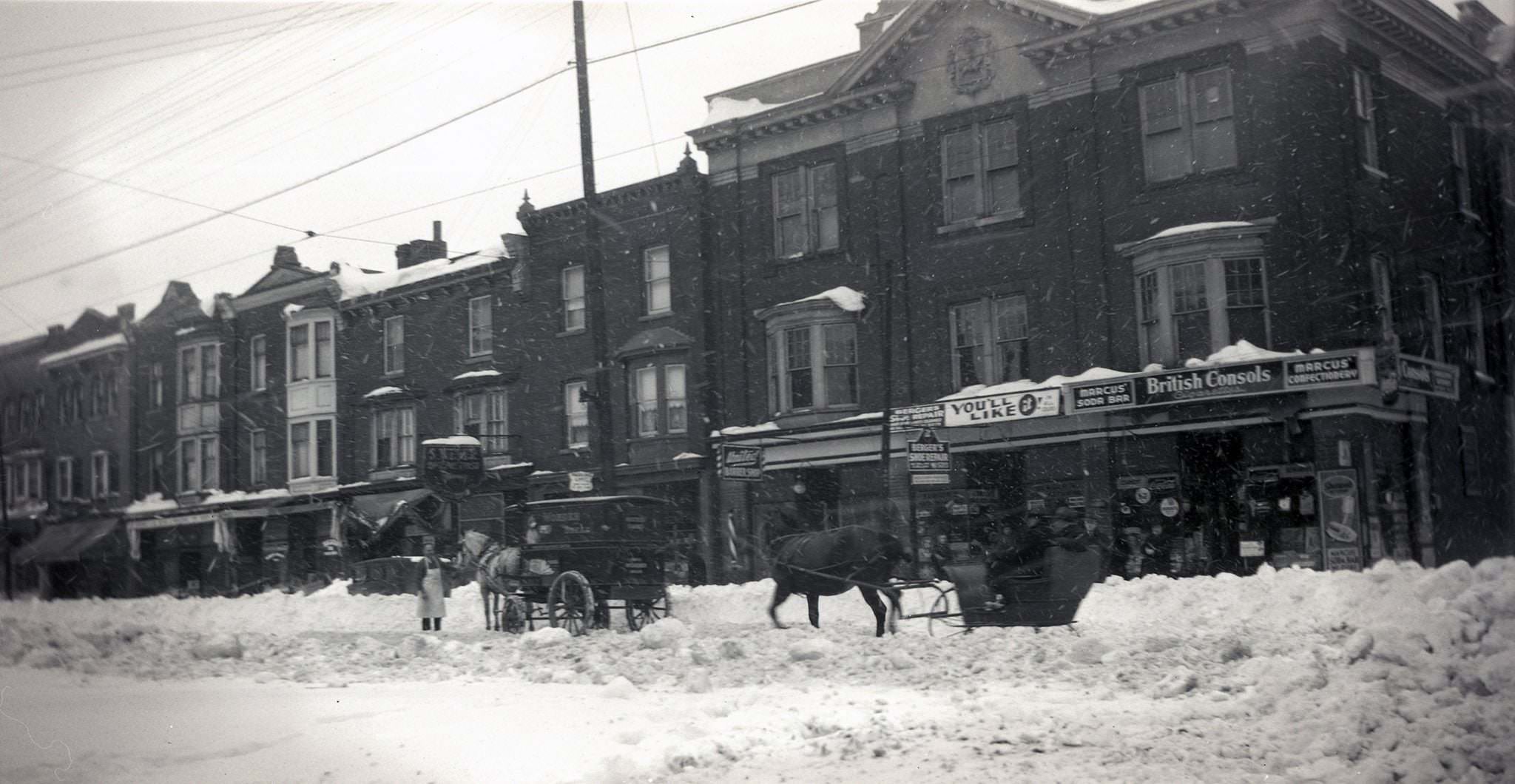
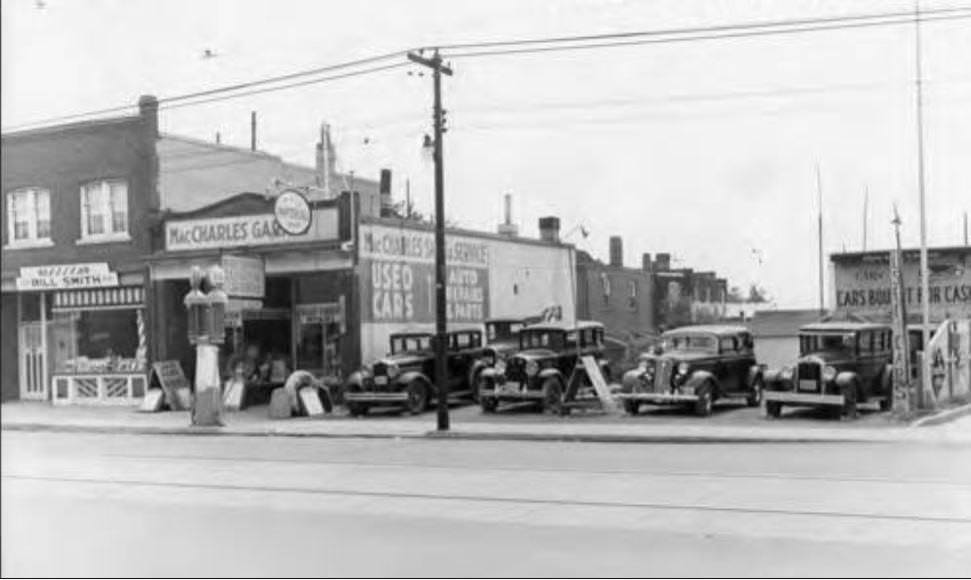
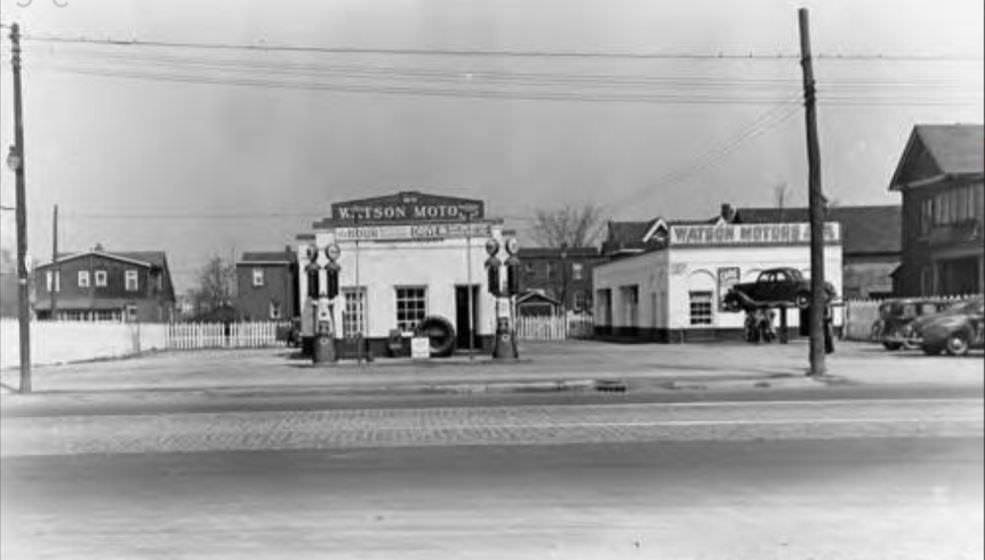
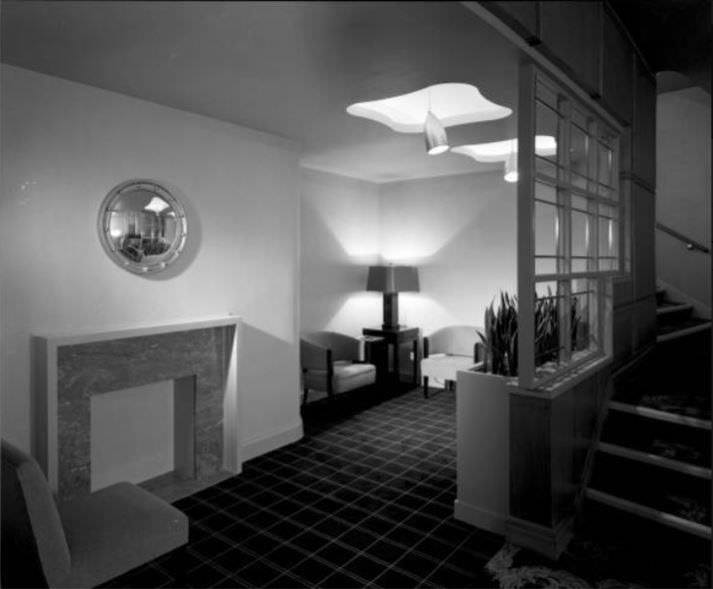
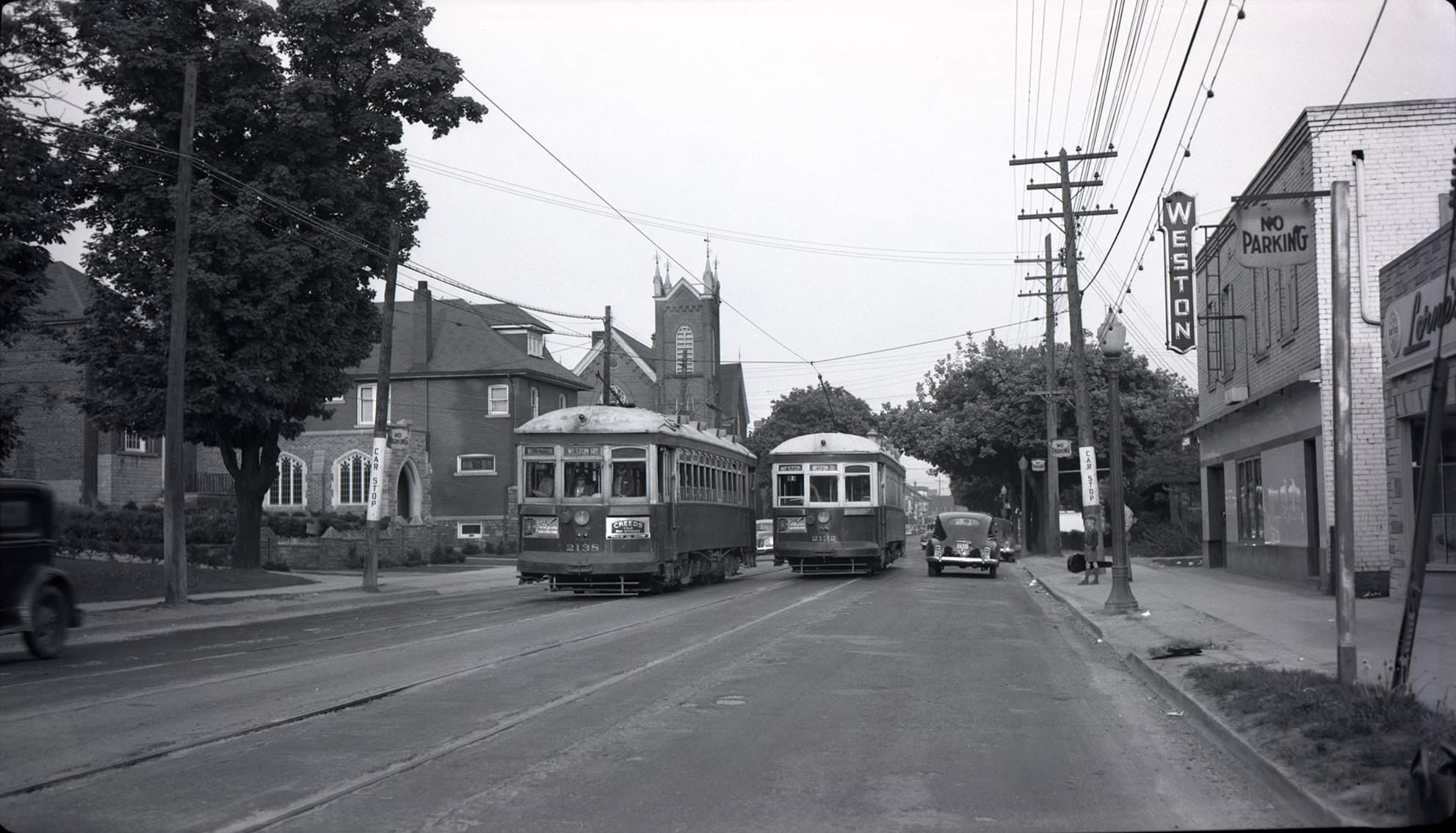
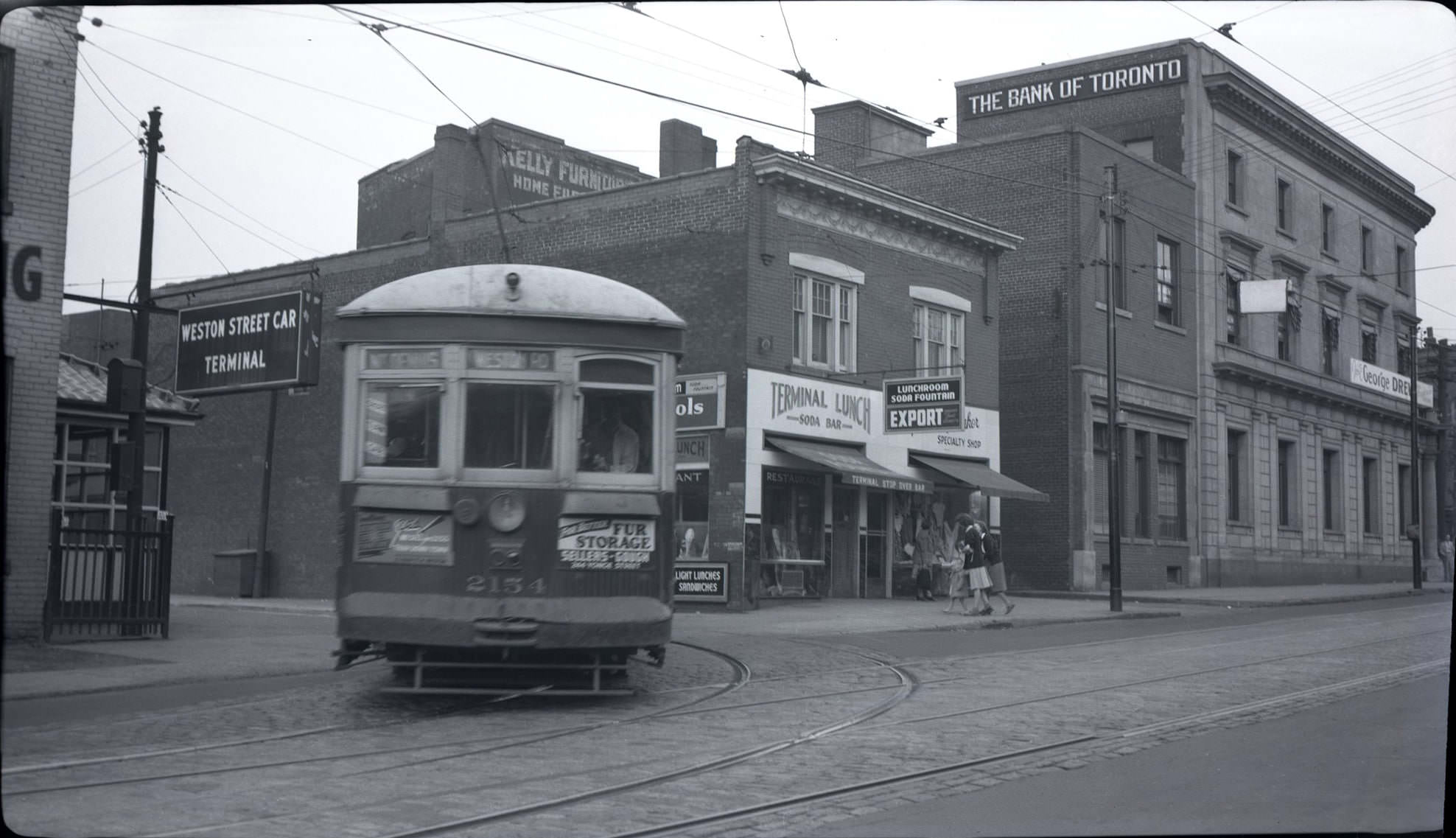
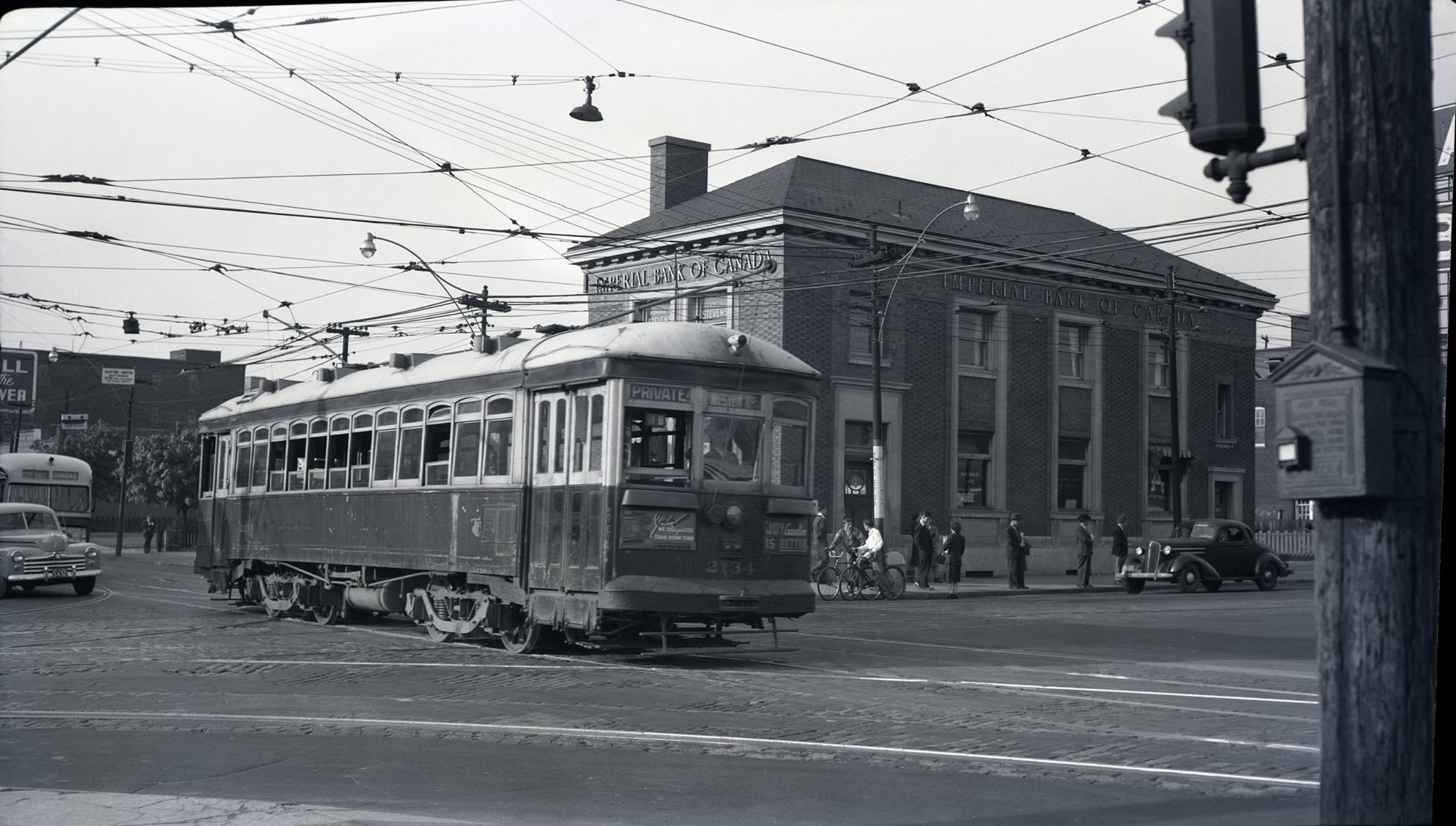
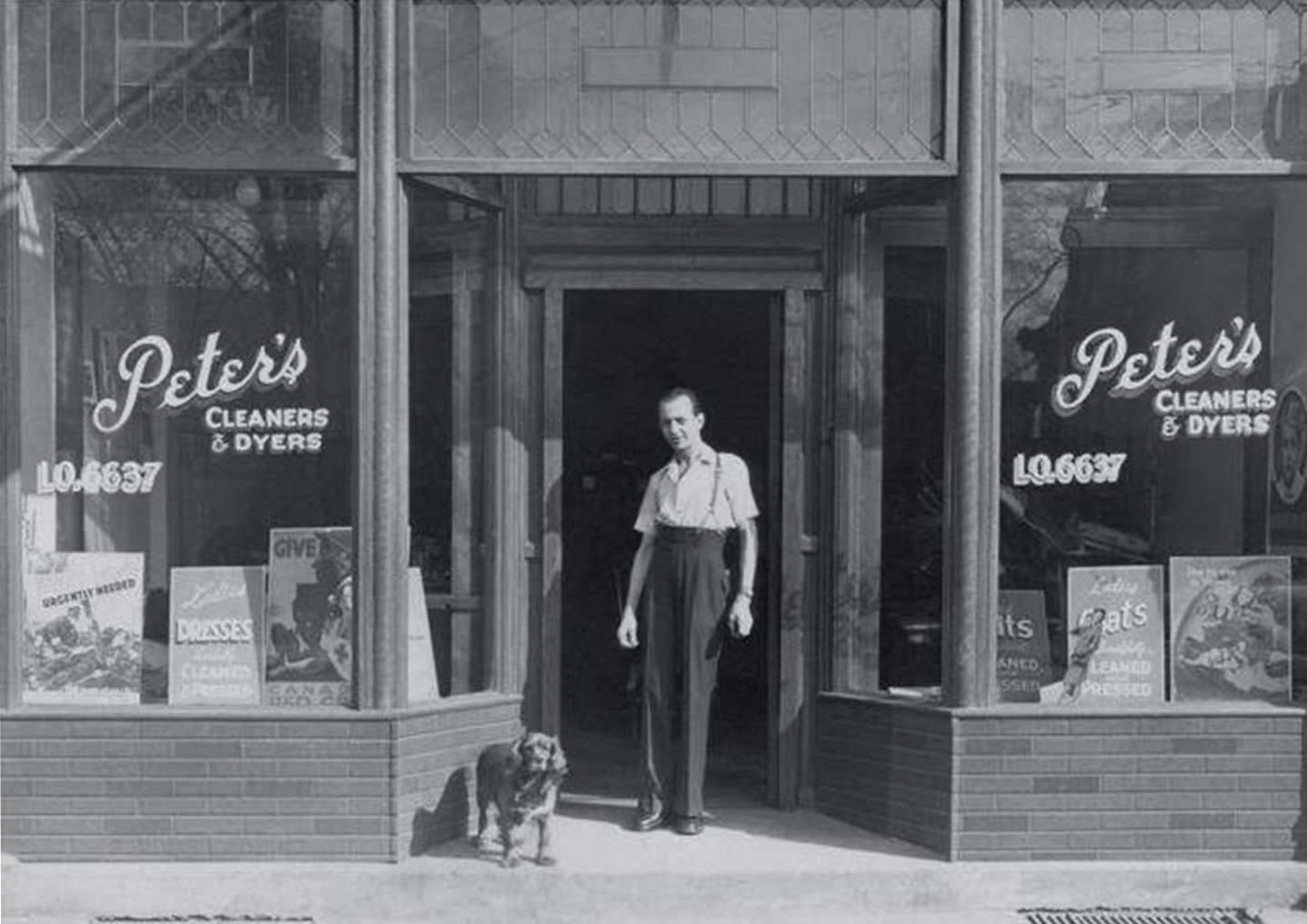
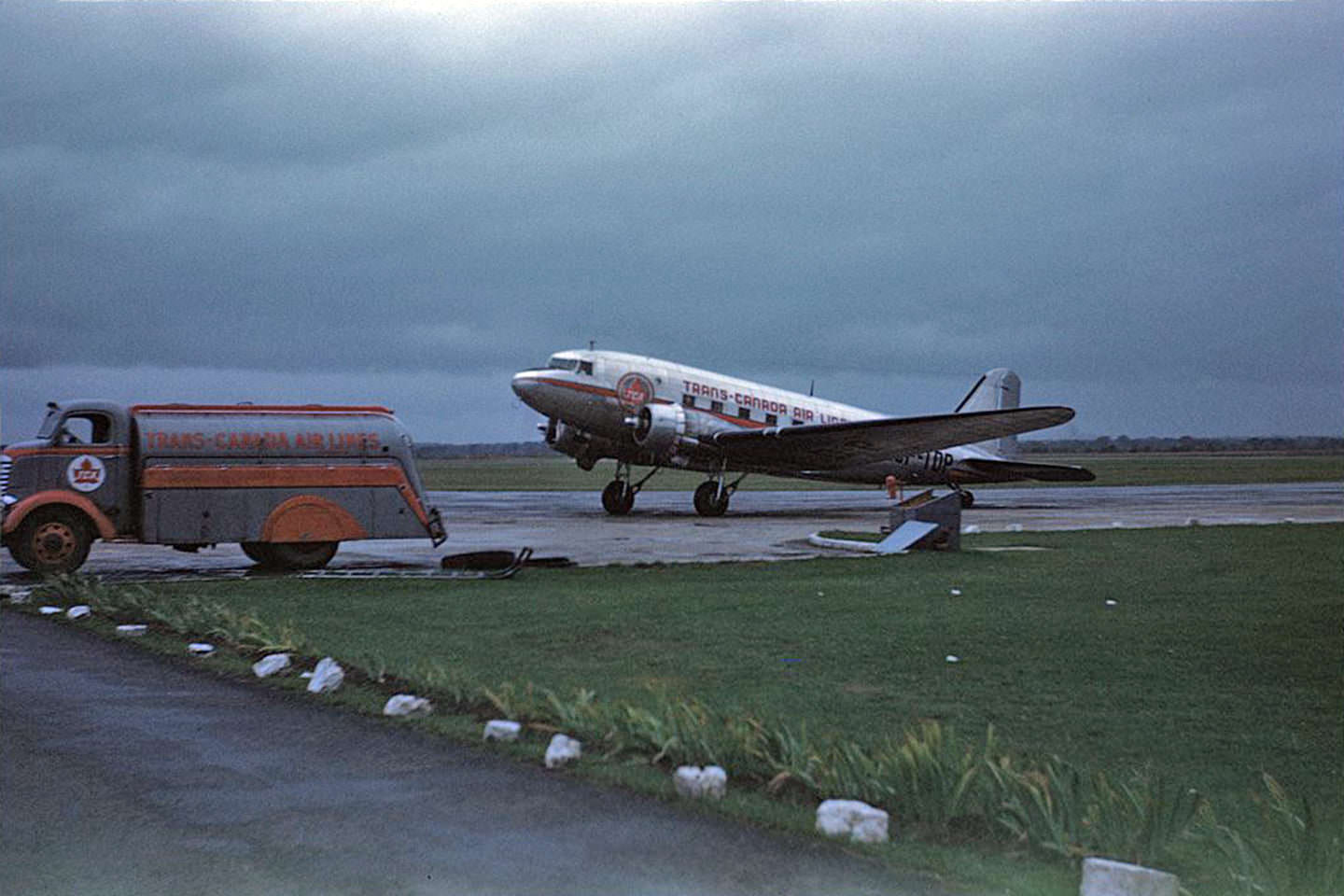
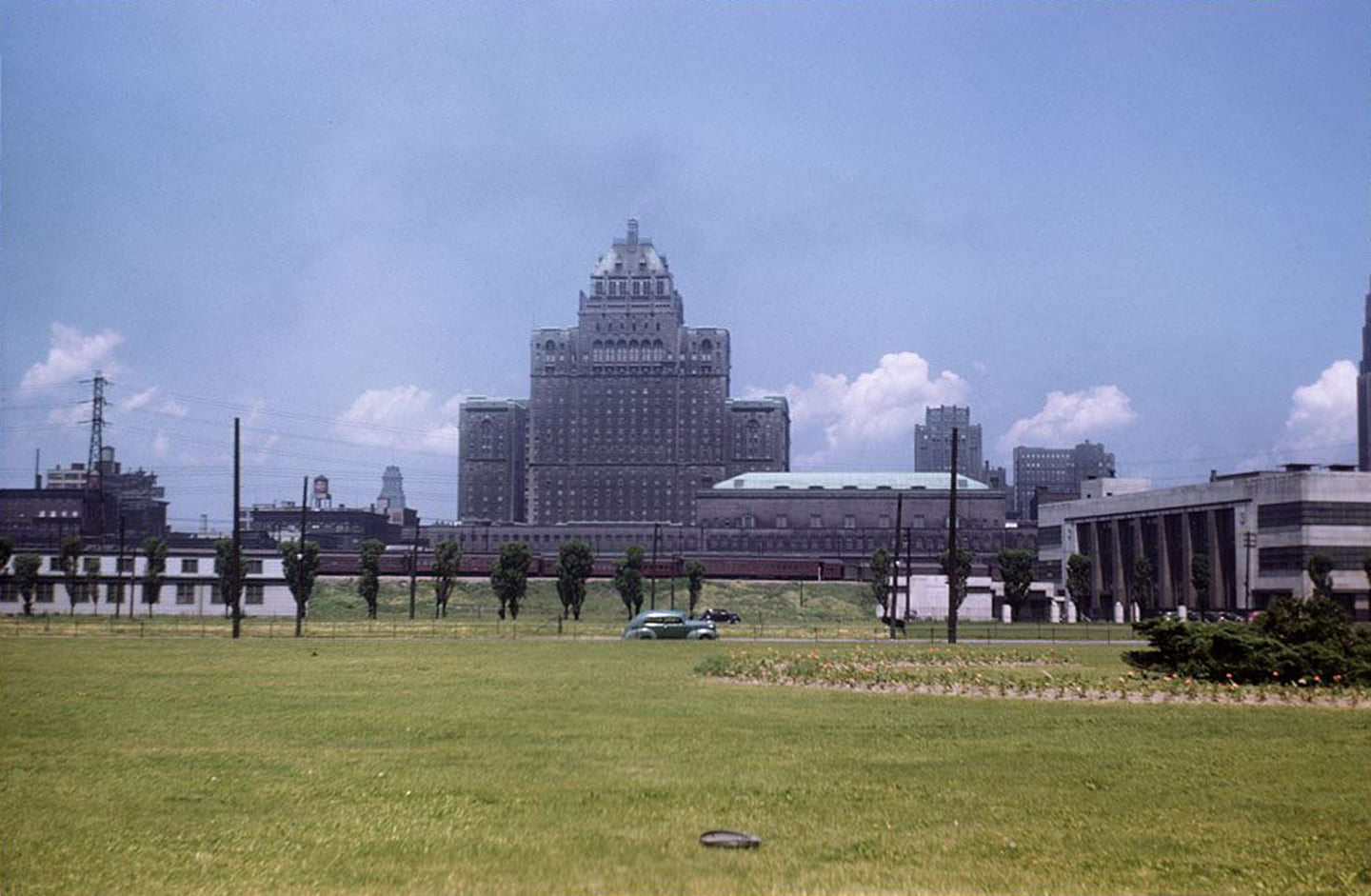
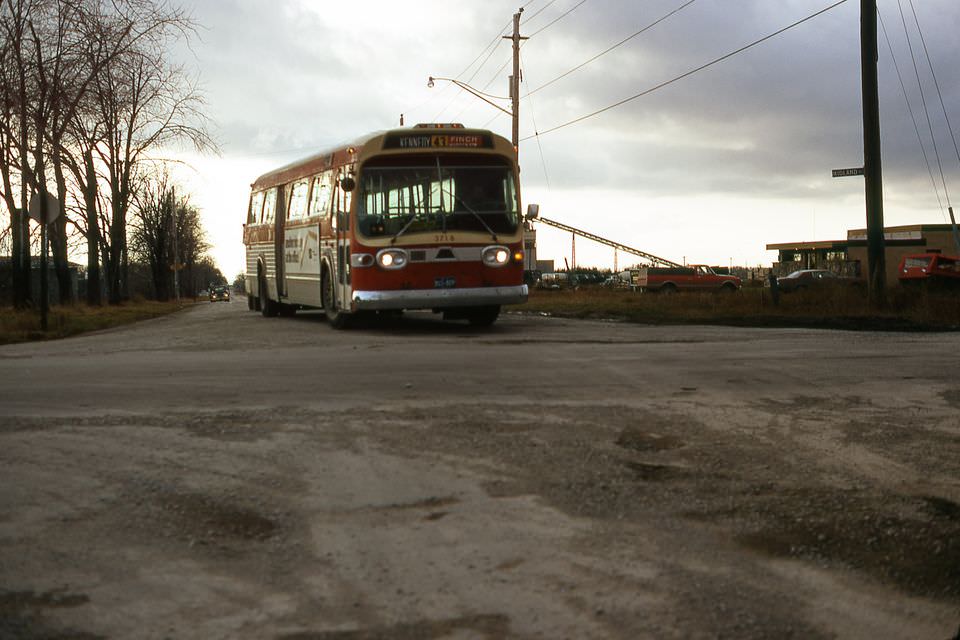
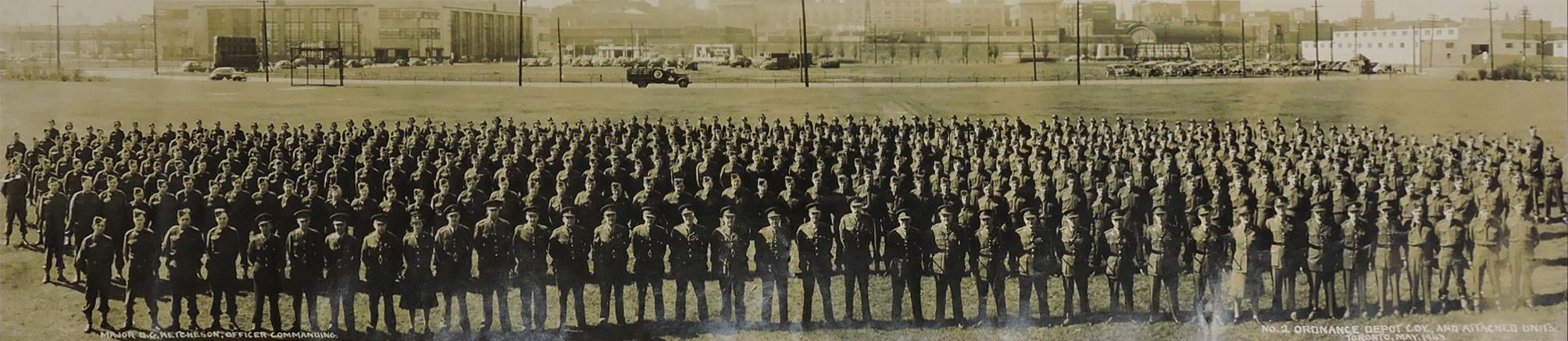
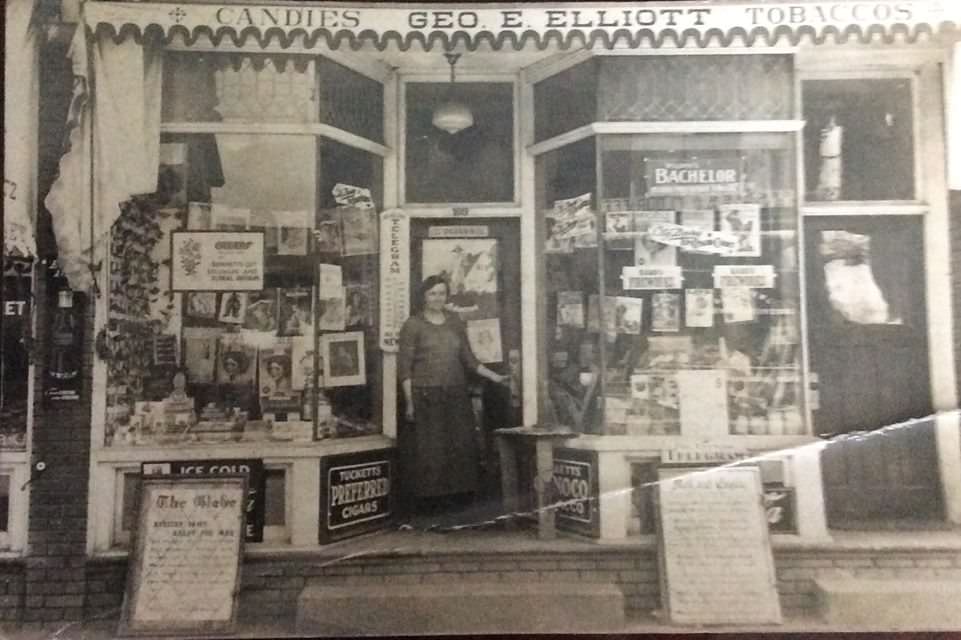
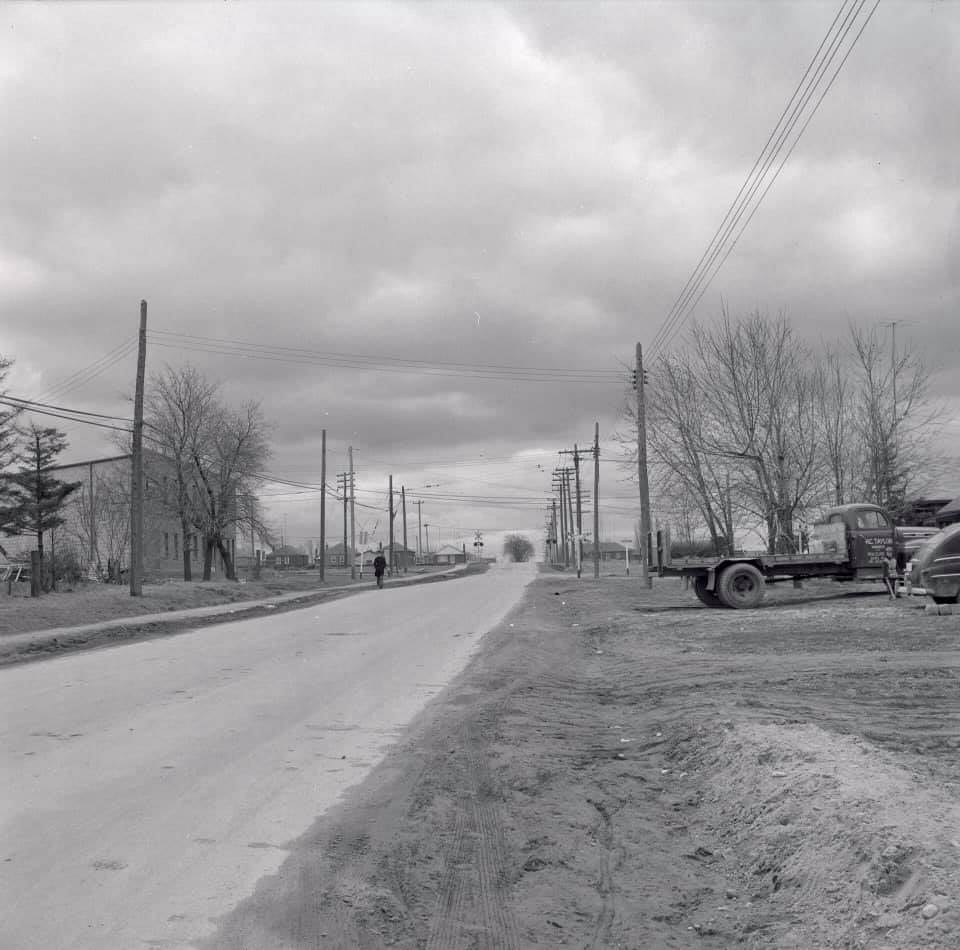
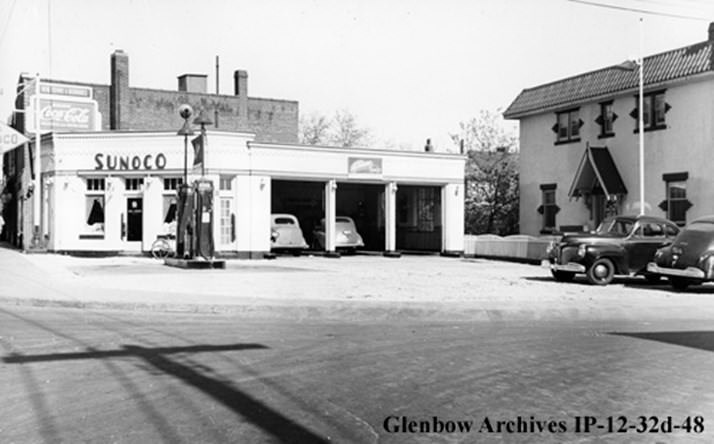
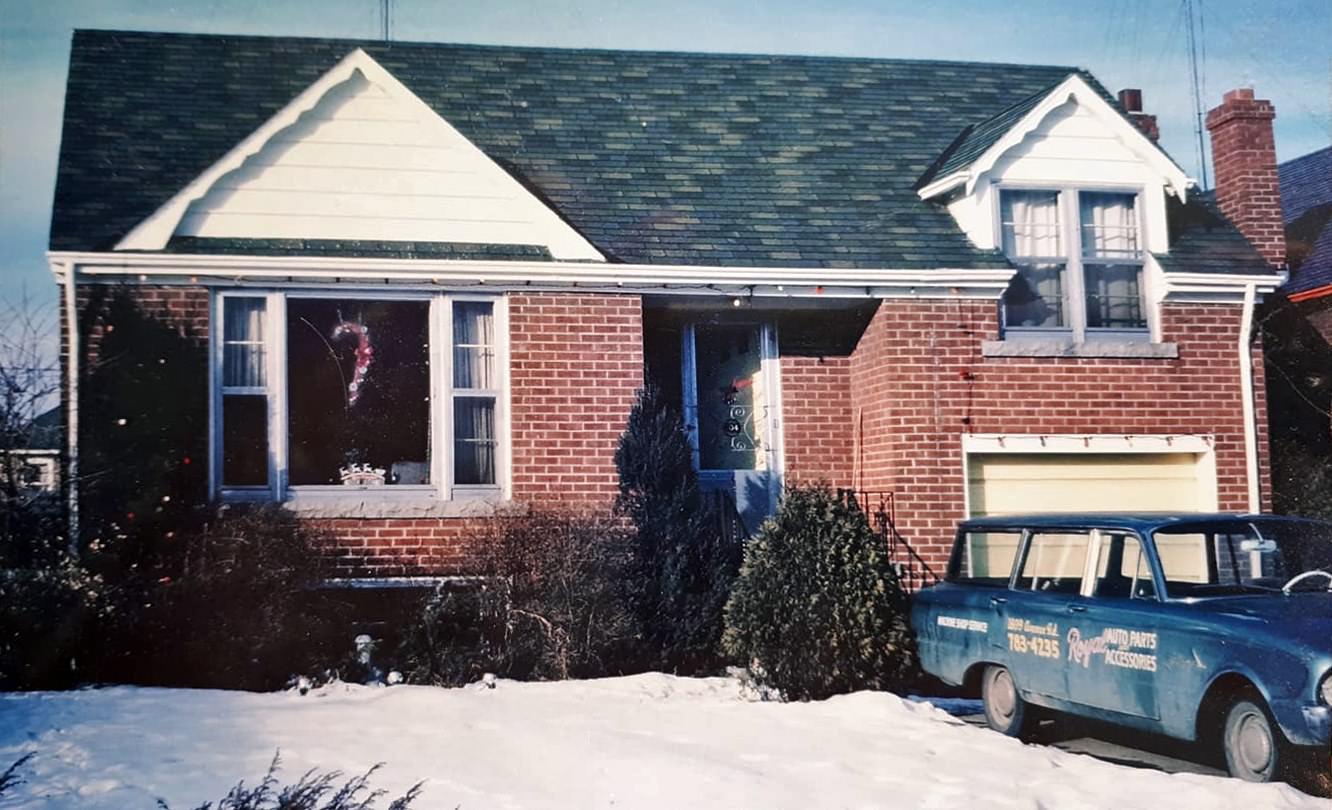
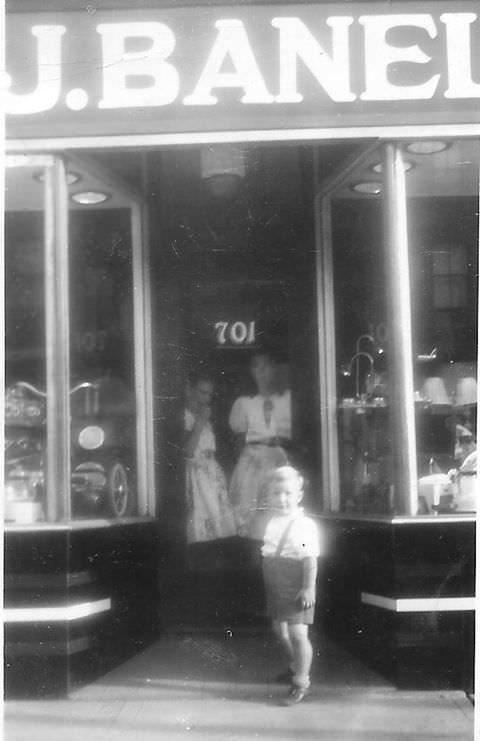
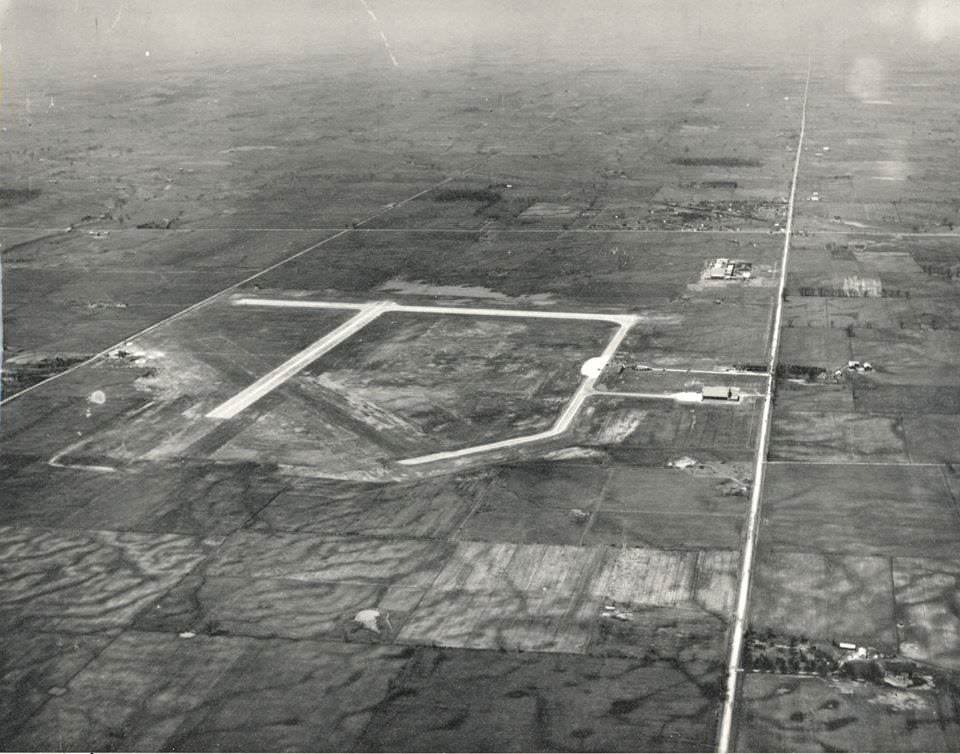
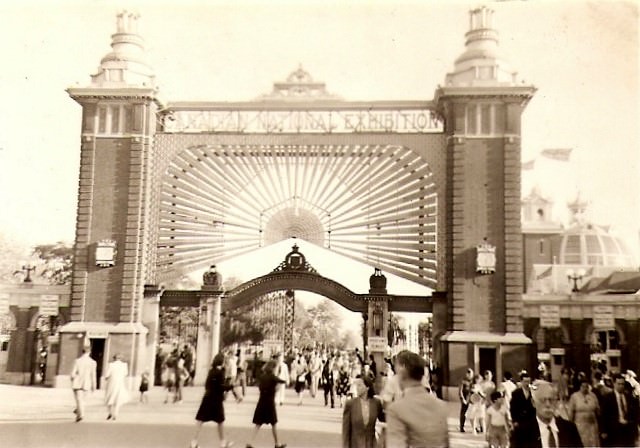
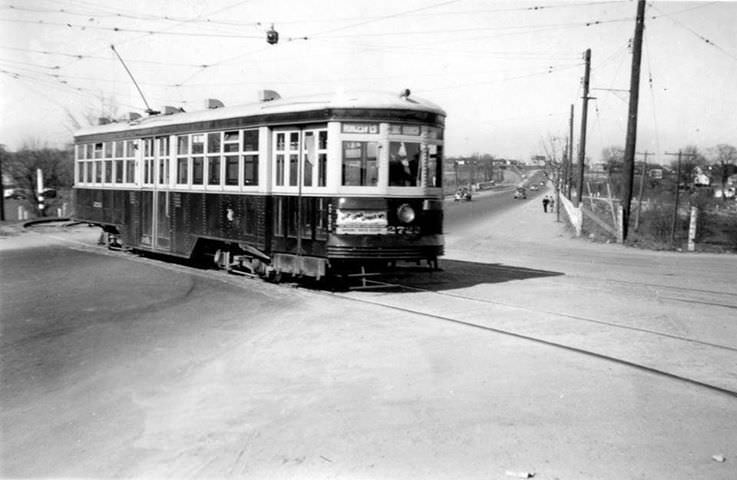
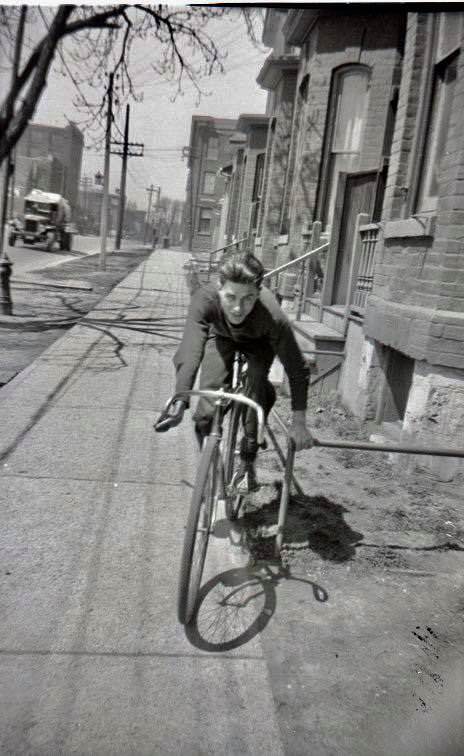
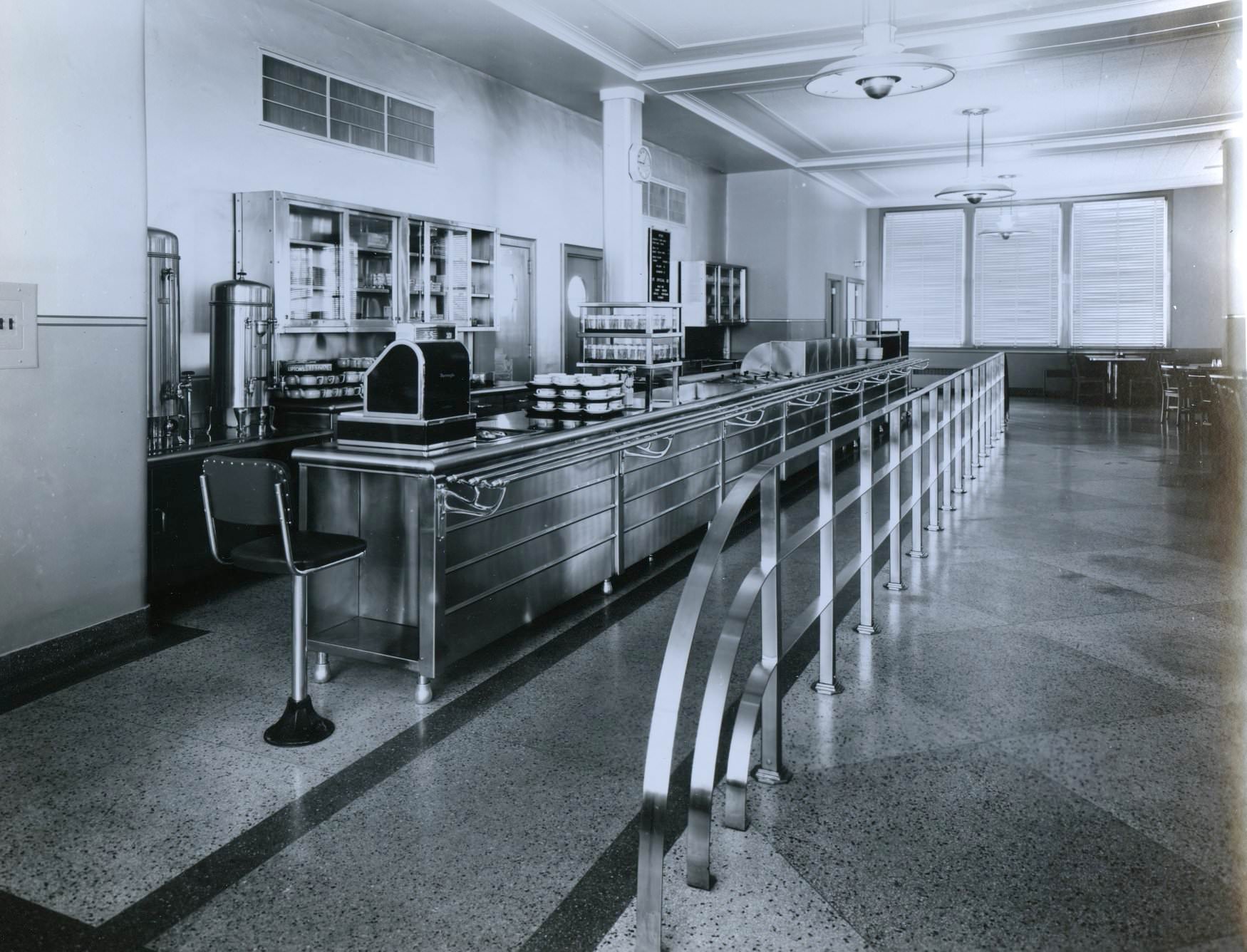
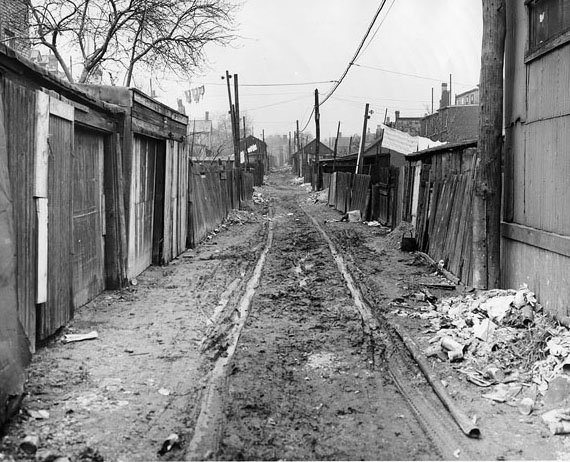
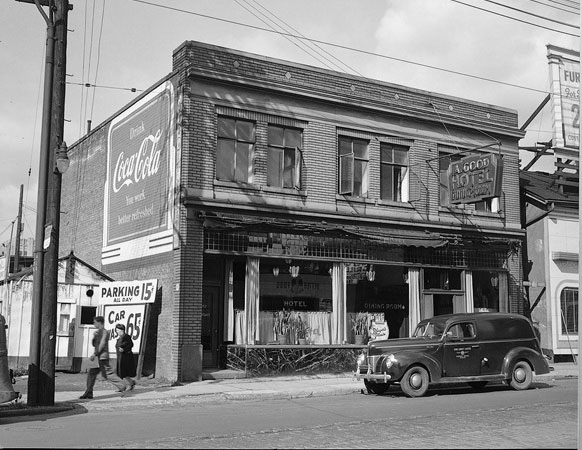
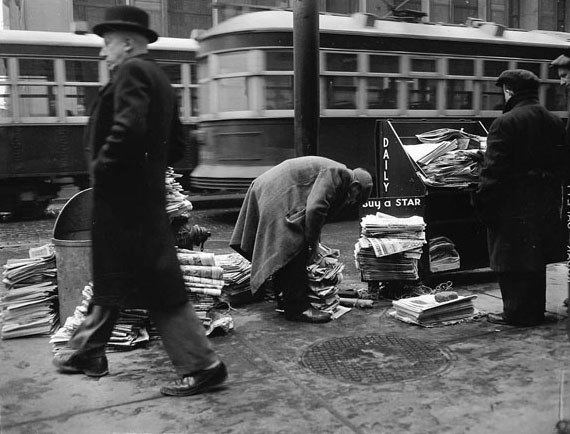
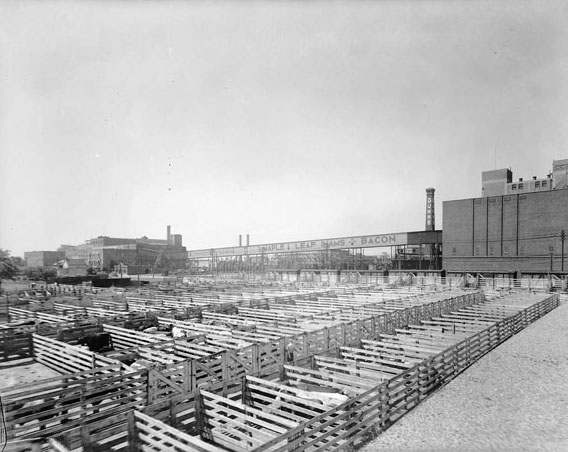
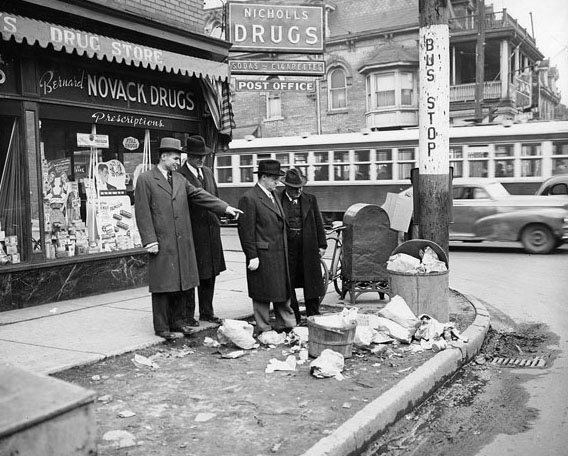
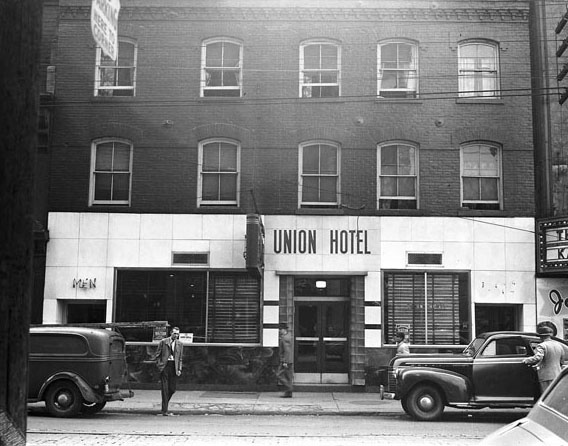
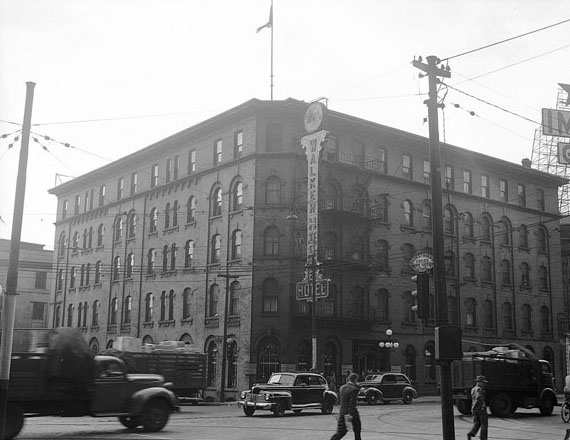
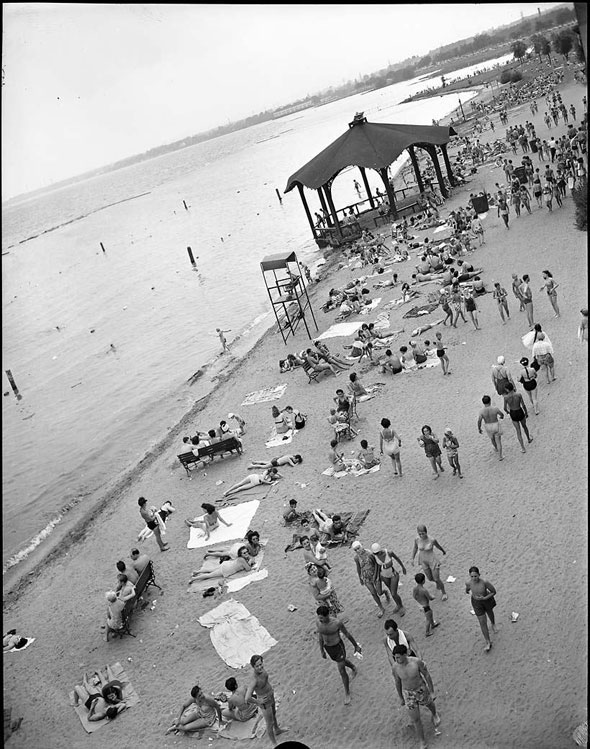
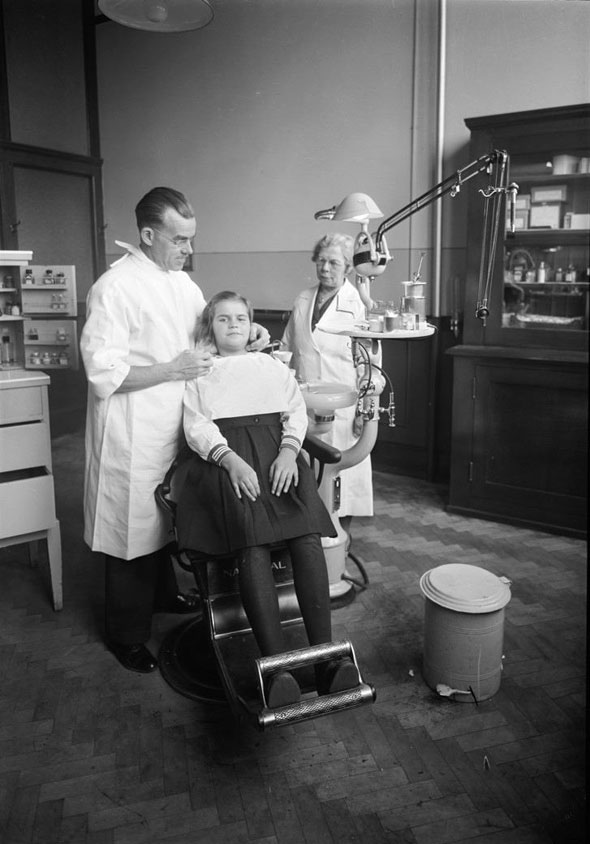
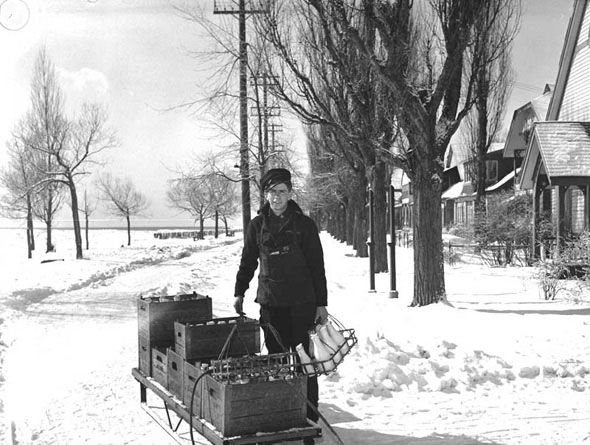
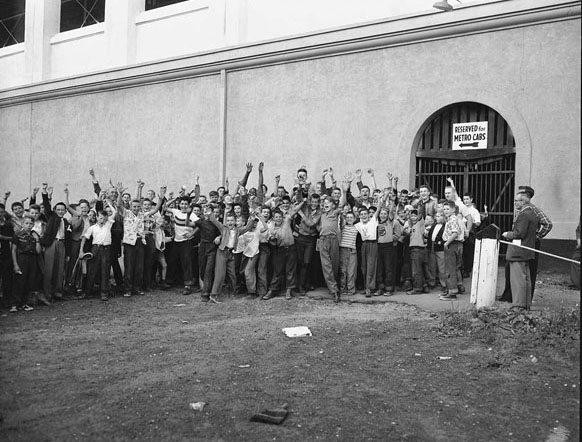
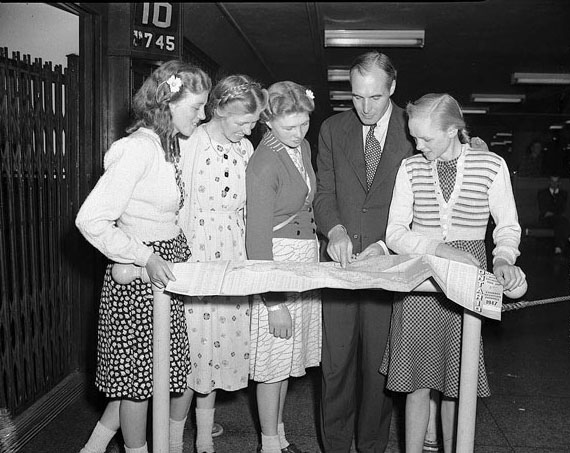




























































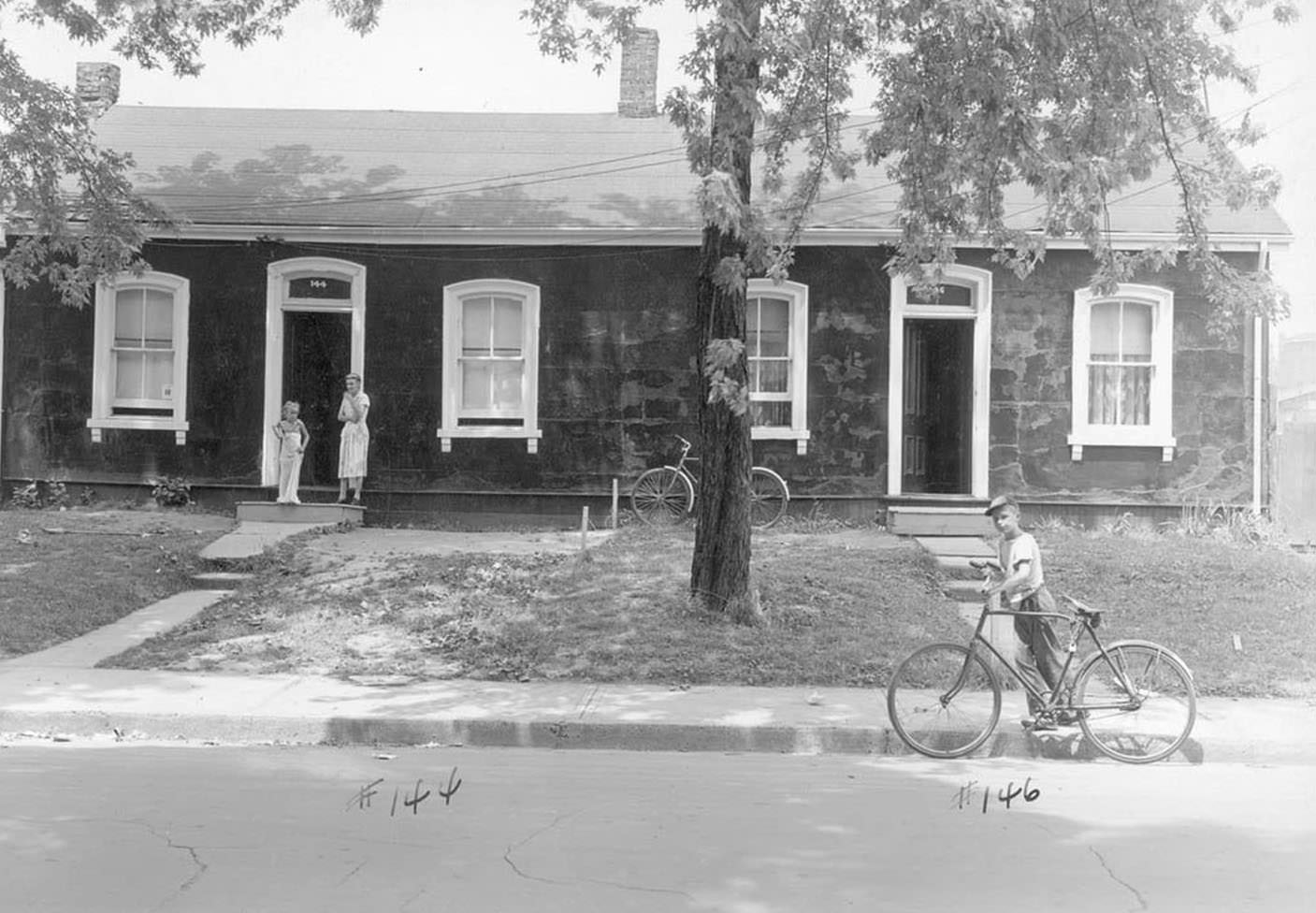












































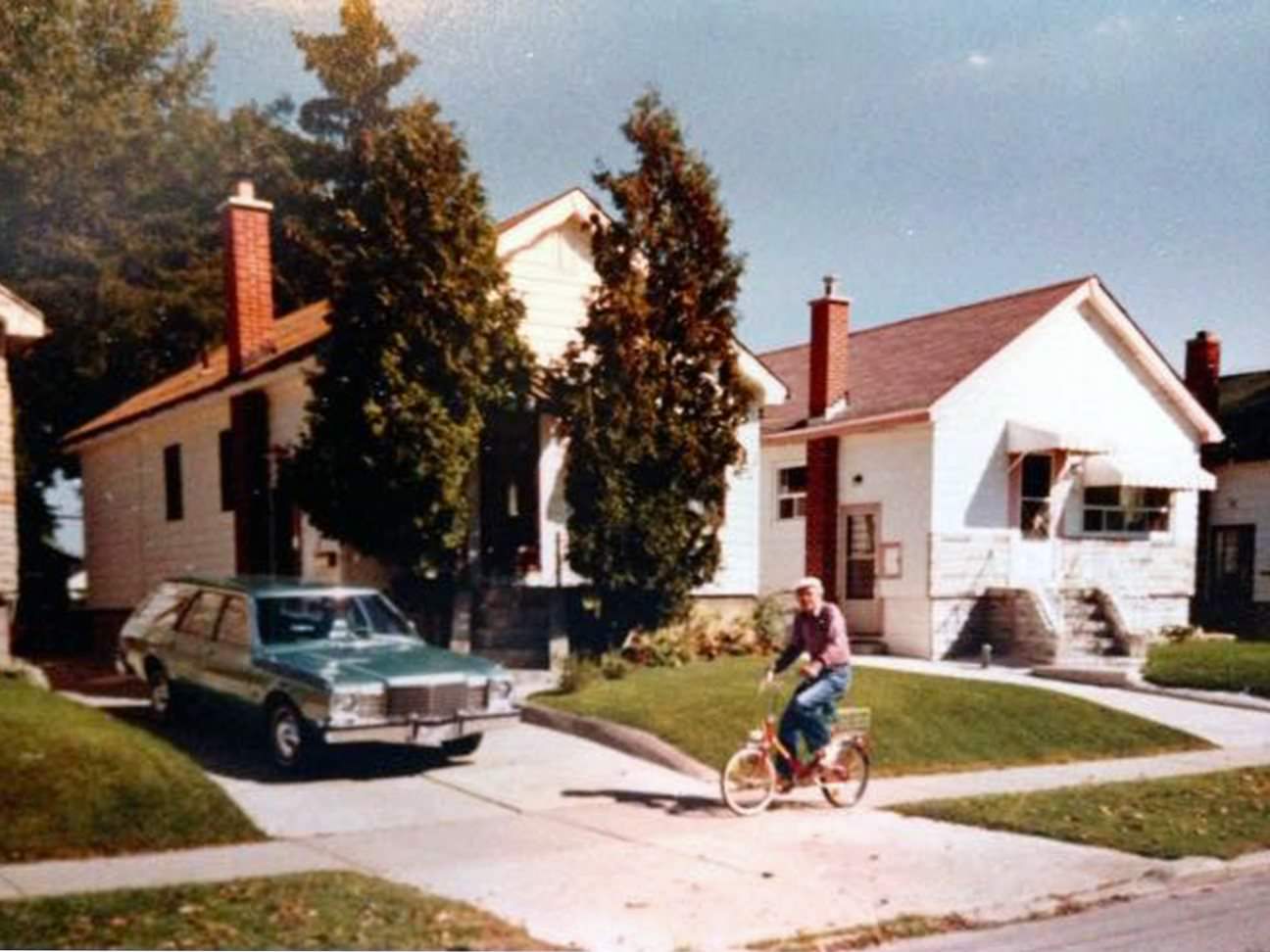


















































I can’t help but chuckle at the use of “the” in “the World War II,” although I admit I didn’t read the article and only glanced at the headline. It gives off a “Diabeetus” kind of vibe to me.
Very interesting. Thank you very much.
These are really great shots of normal life in that decade. Interesting. Thank you for posting.
Boomer here, I see my parents style in many of the photos, thank you.