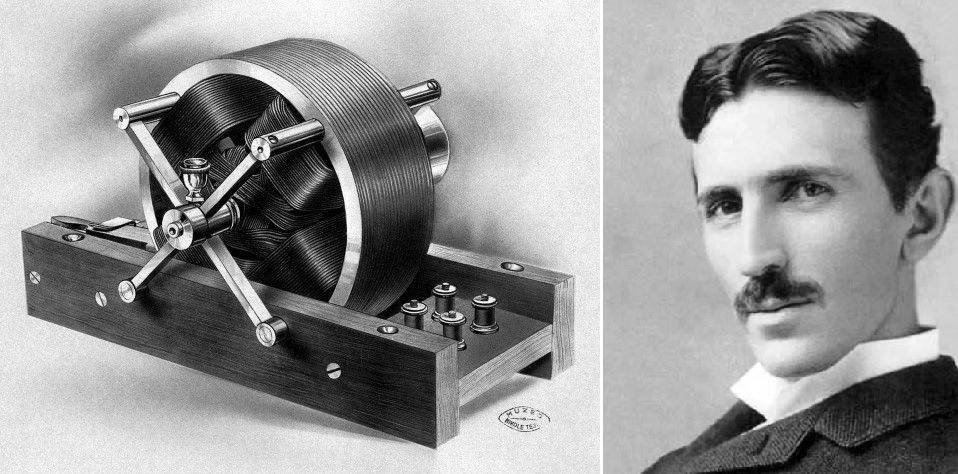
In 1882, Nikola Tesla had a flash of inspiration that resulted in one of his most important inventions: the AC (alternating current) motor. AC is electric current that repeatedly changes the direction it flows along a wire, unlike DC (direct current) which flows in one direction only. Inside Tesla’s motor, AC passes through a clever arrangement of current that repeatedly changes the direction it flows along a wire, unlike DC (direct current) which flows in one direction only. Inside Tesla’s motor, AC passes through a clever arrangement of spins the rotor (the rotating part).


