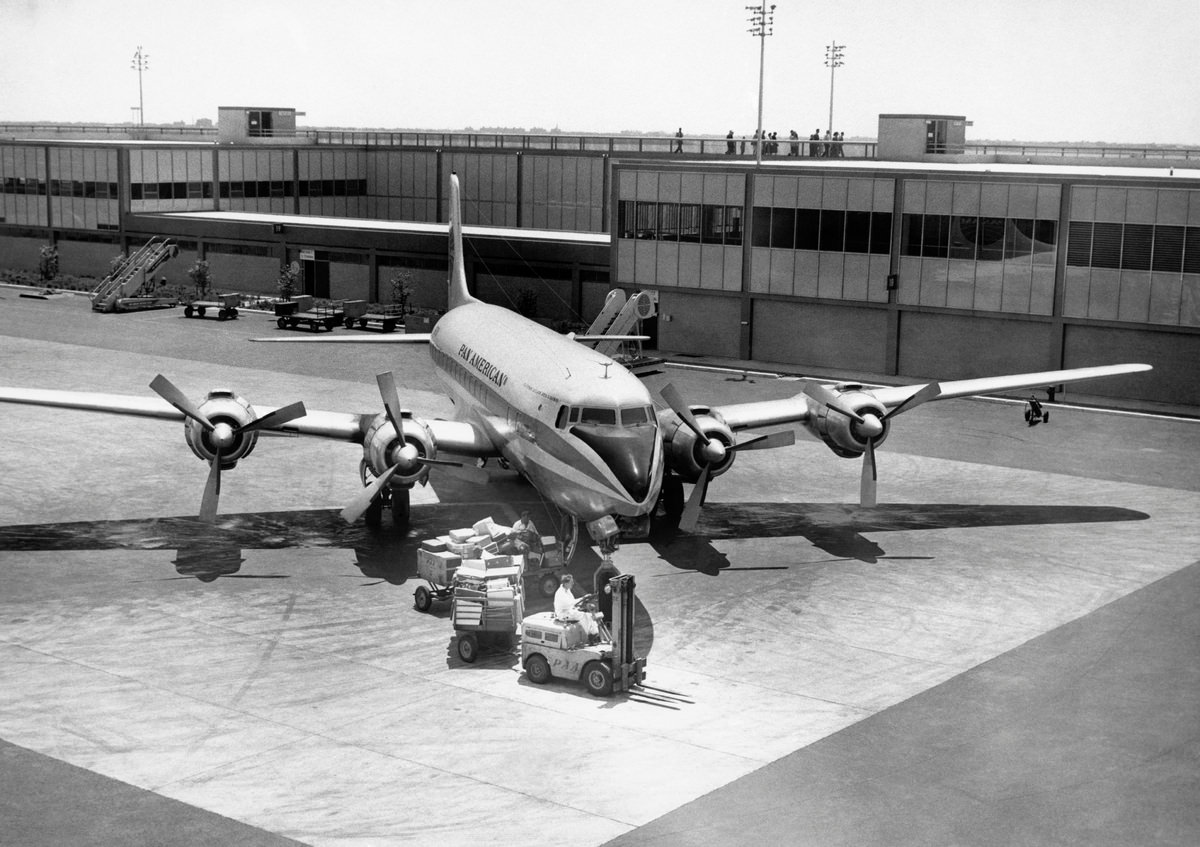
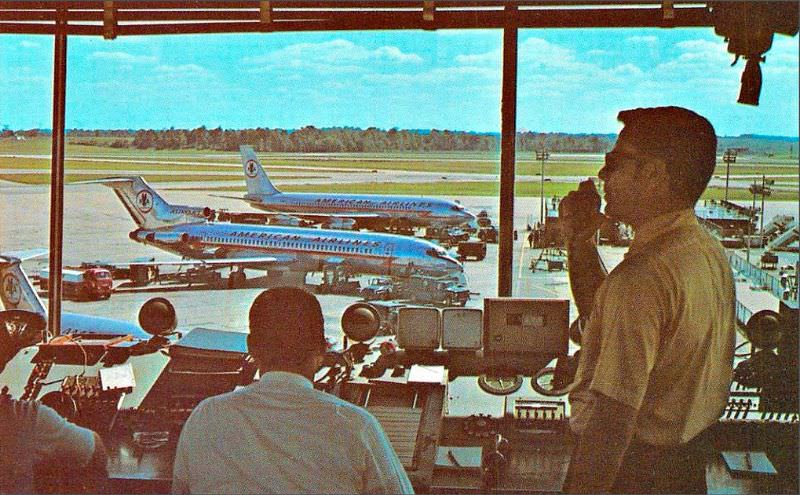
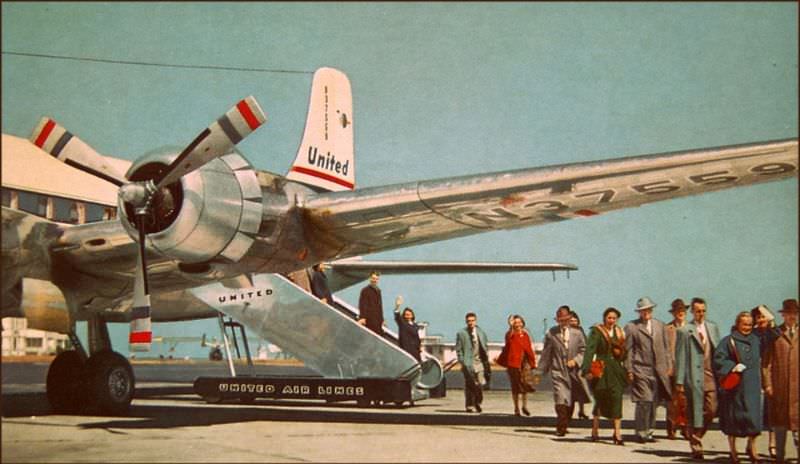
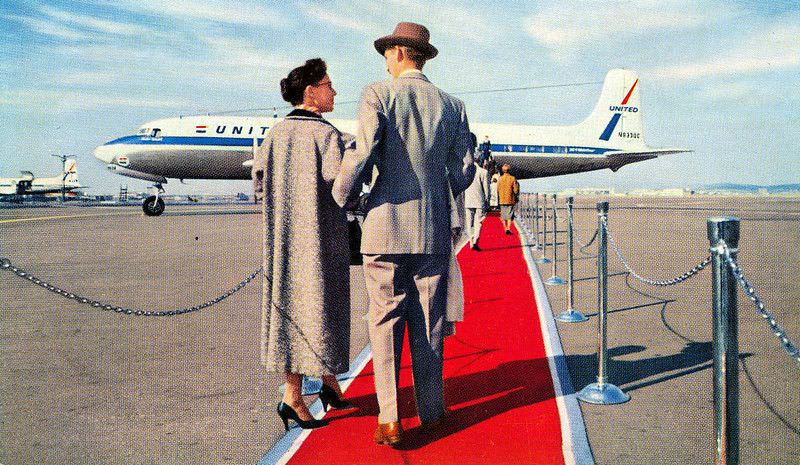
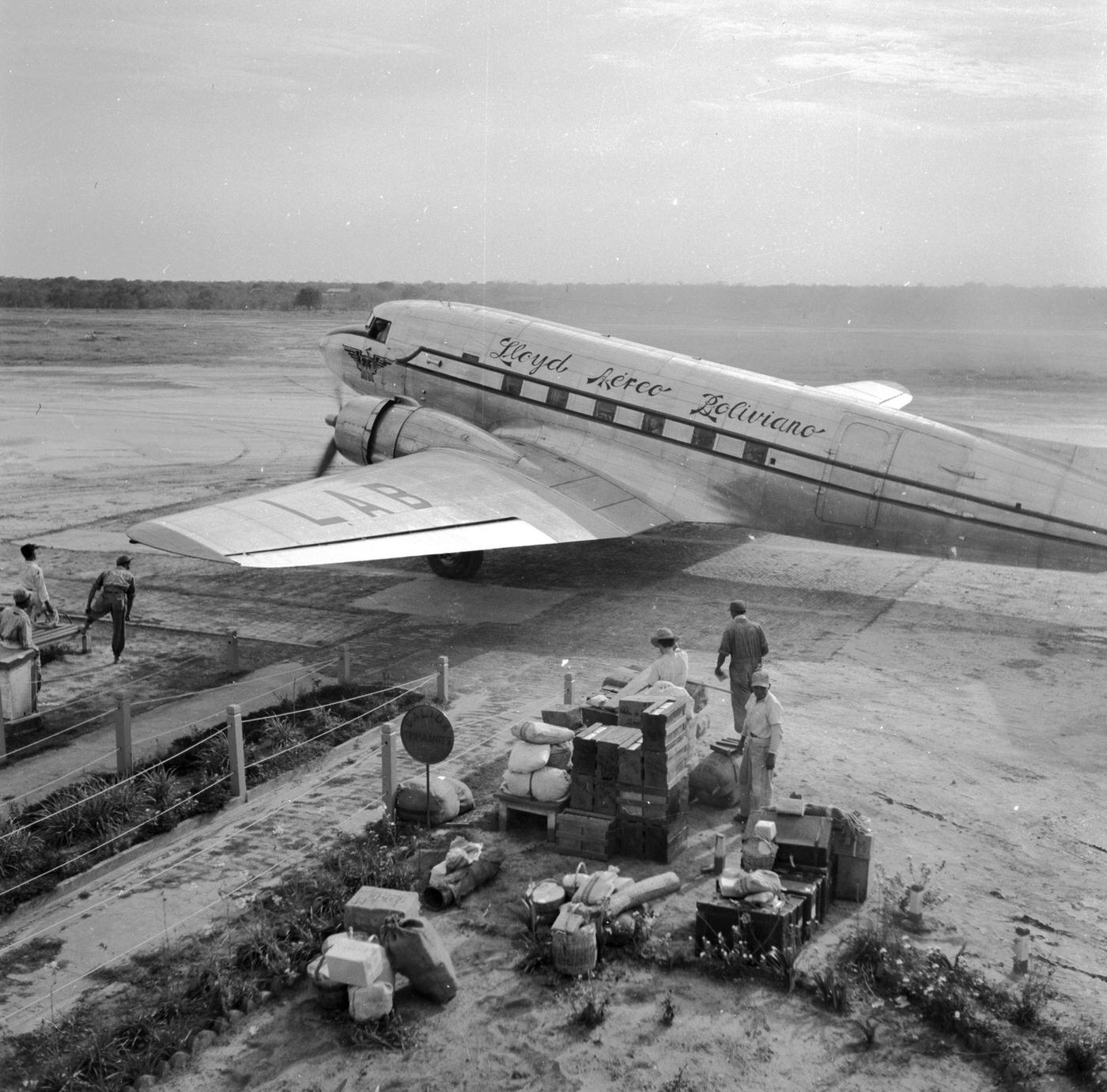
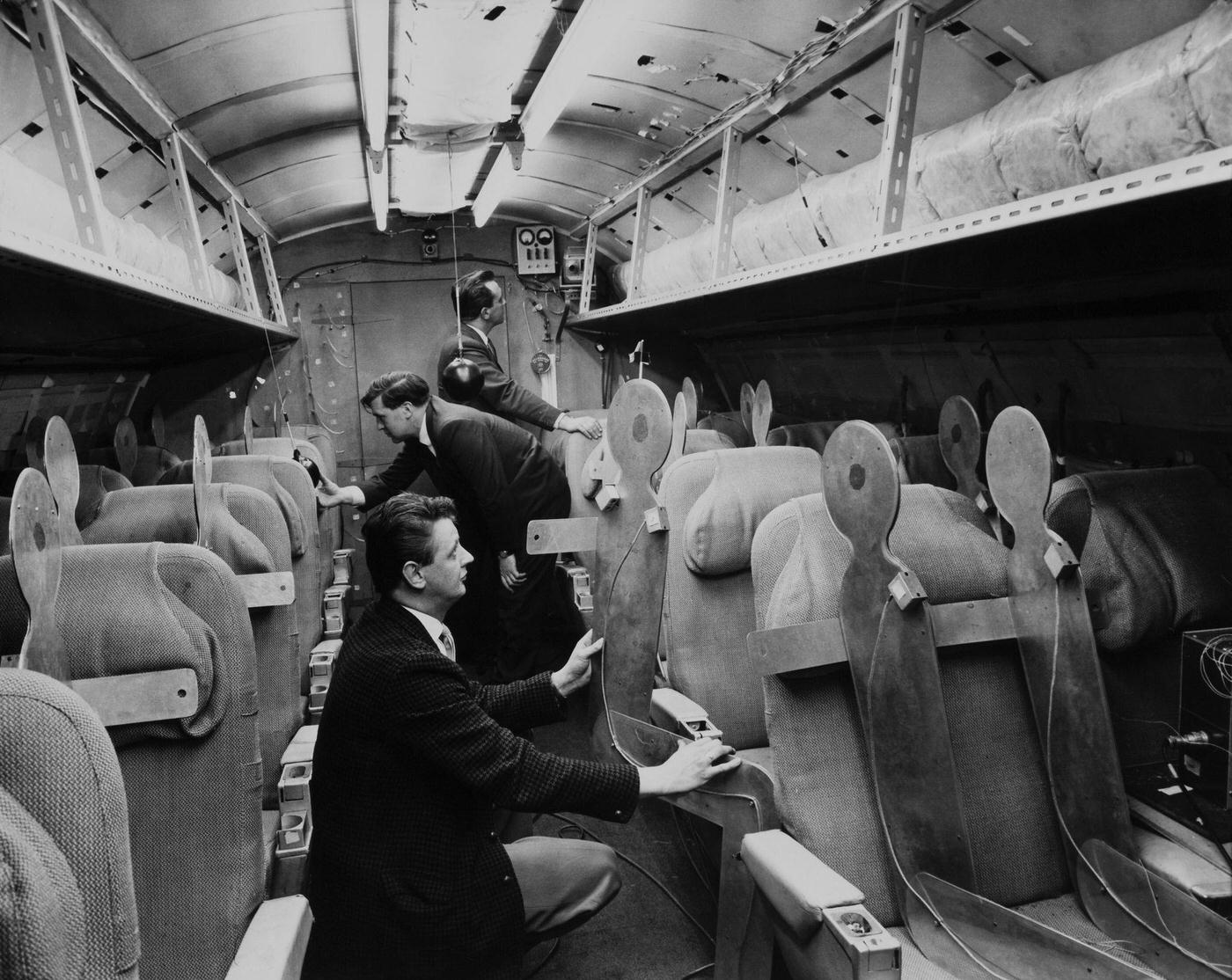
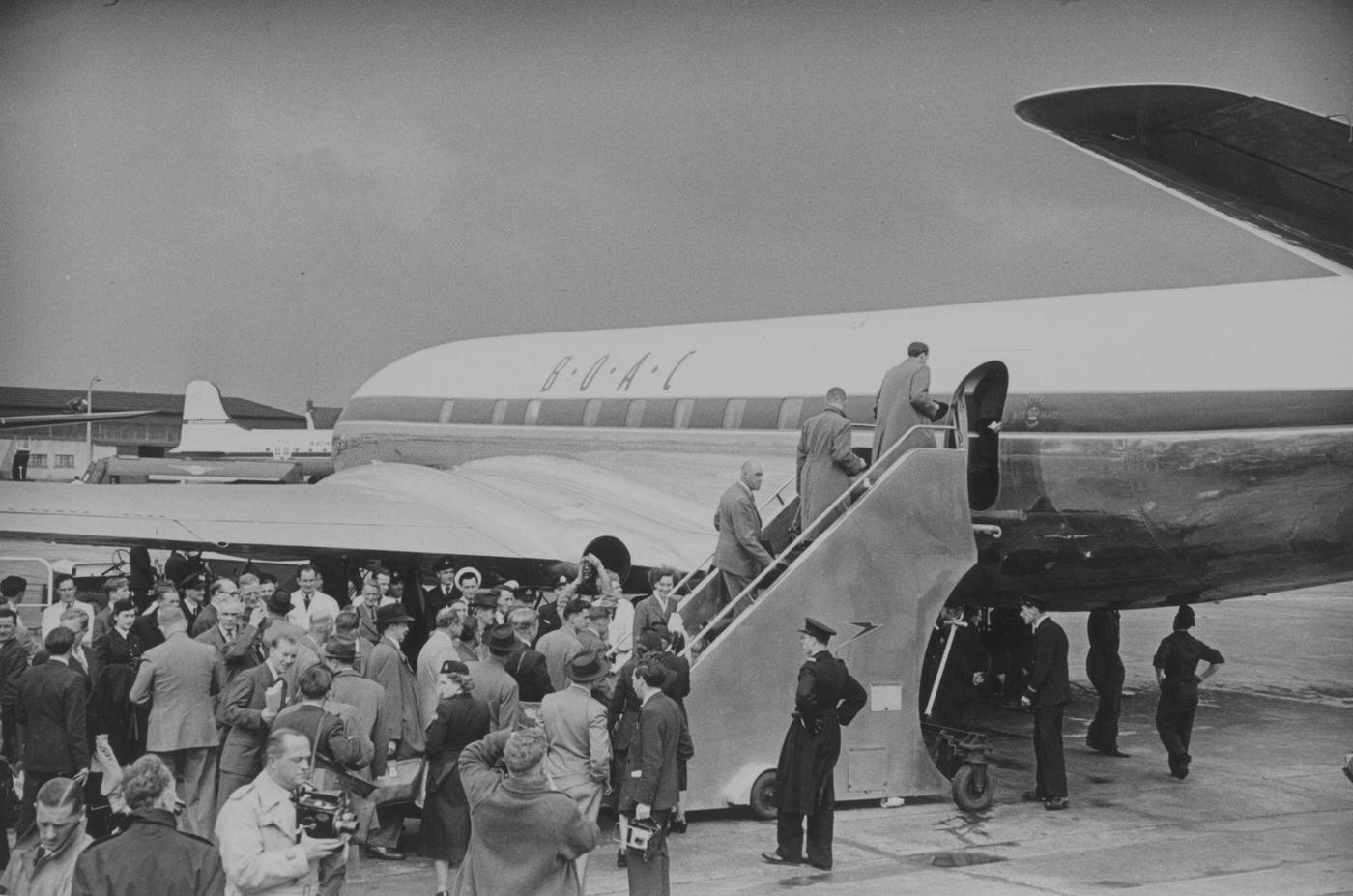
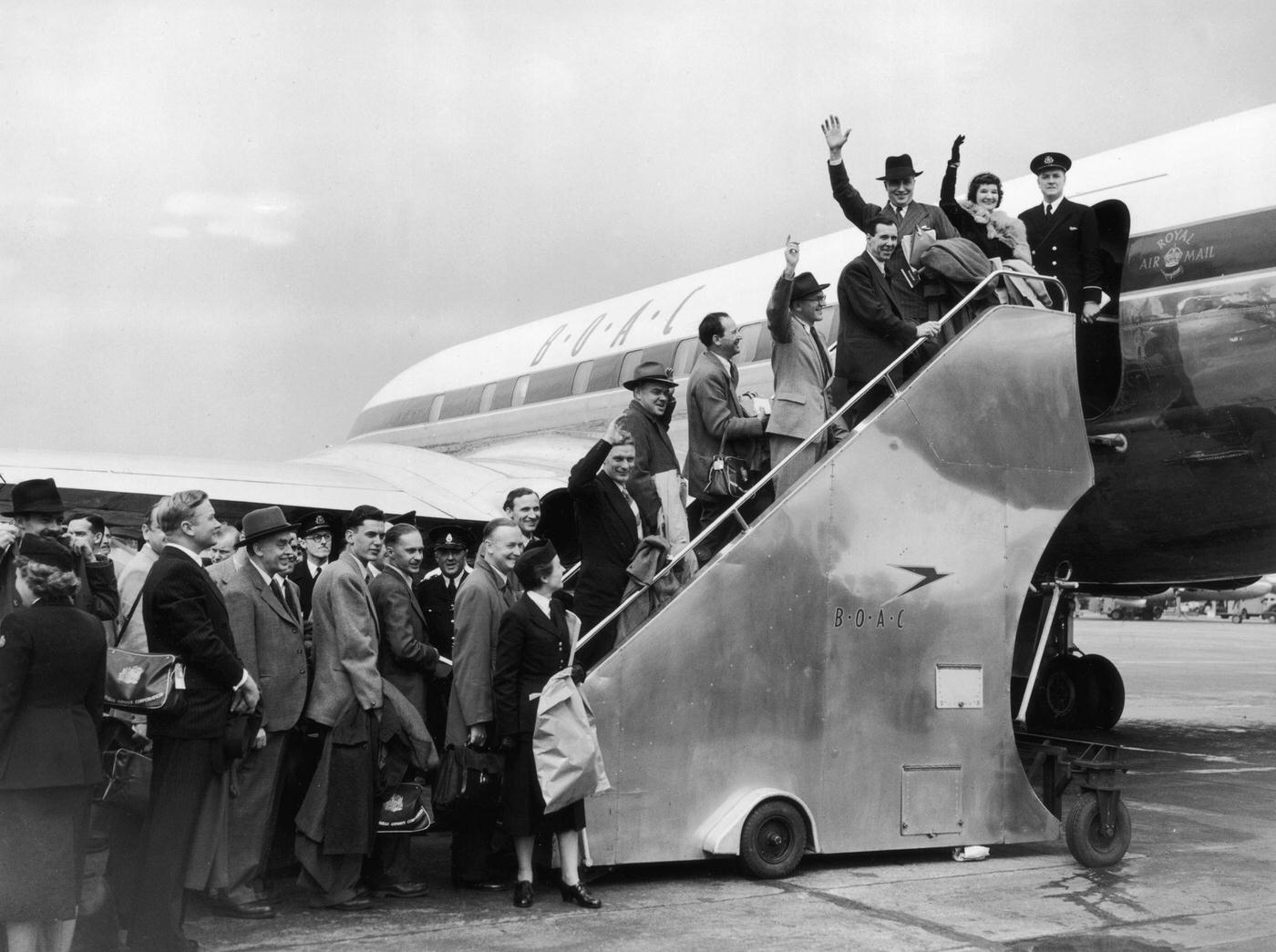
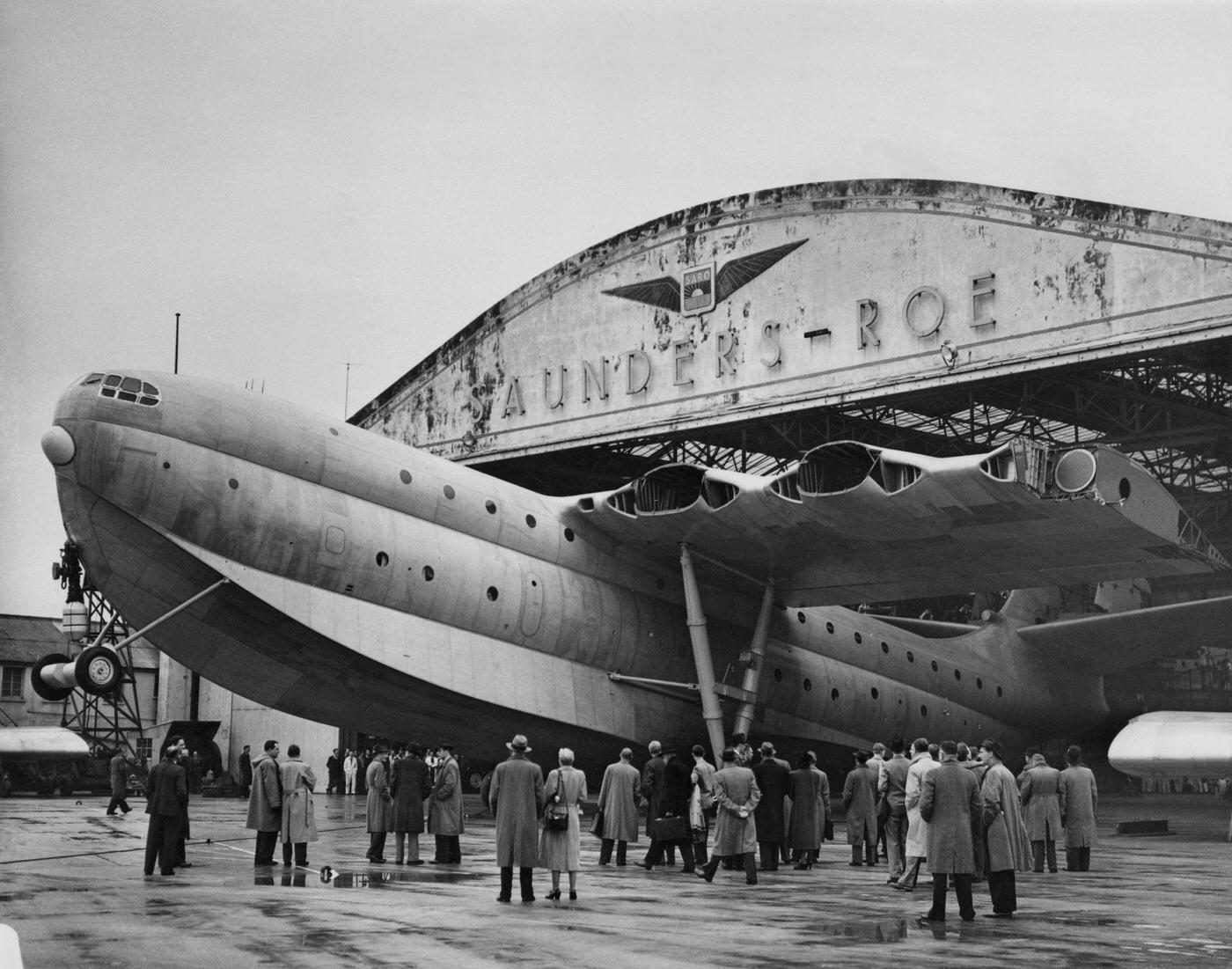
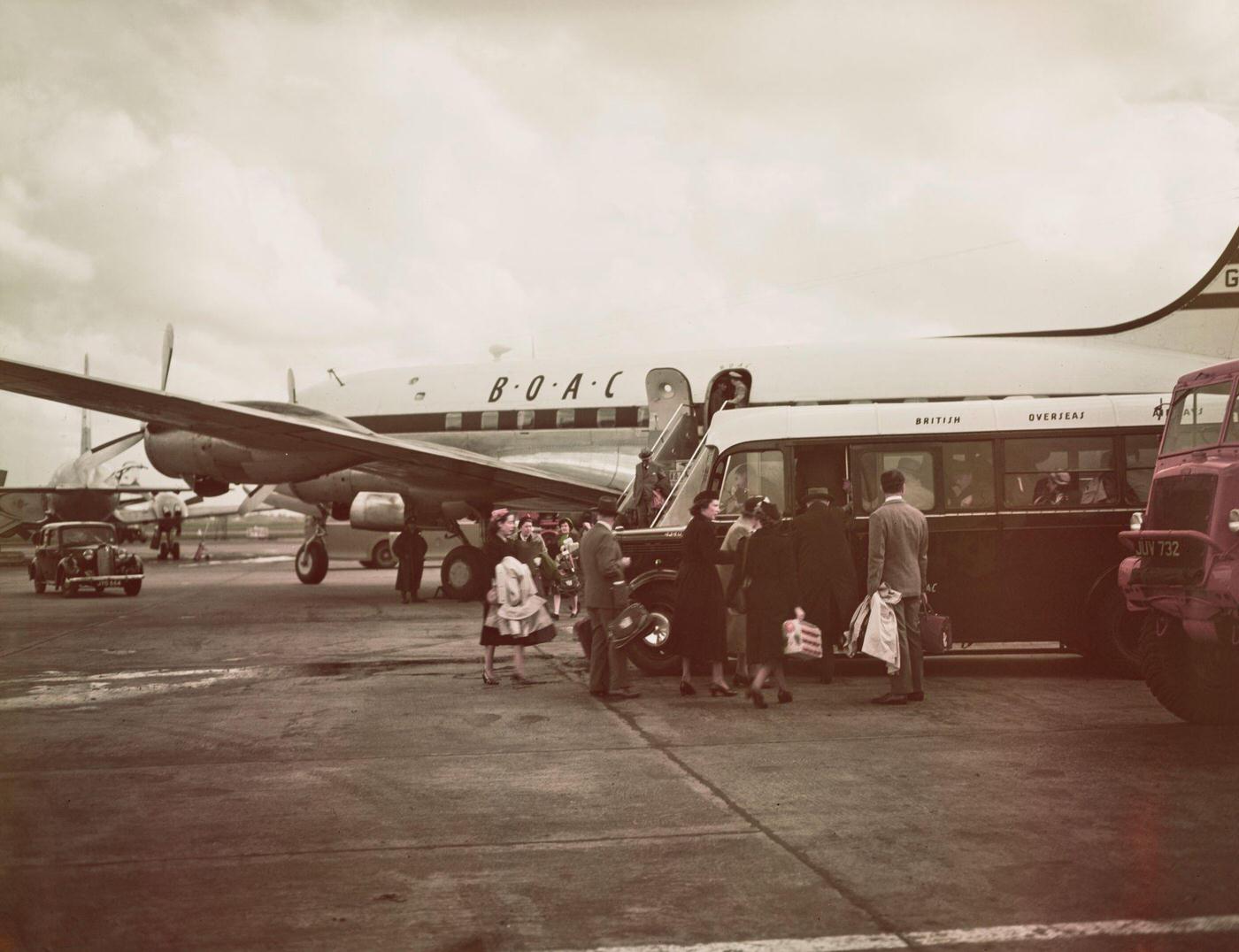
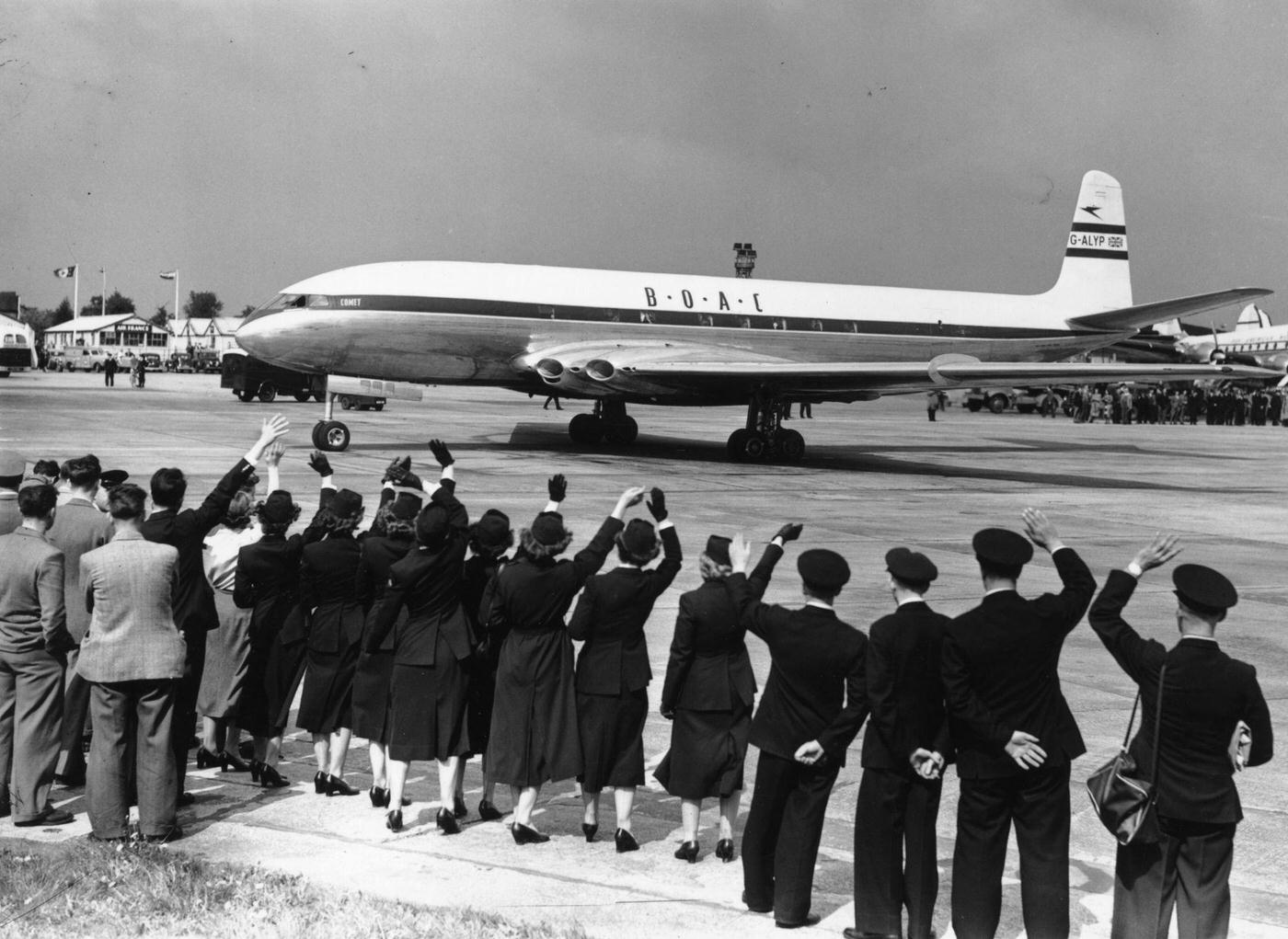
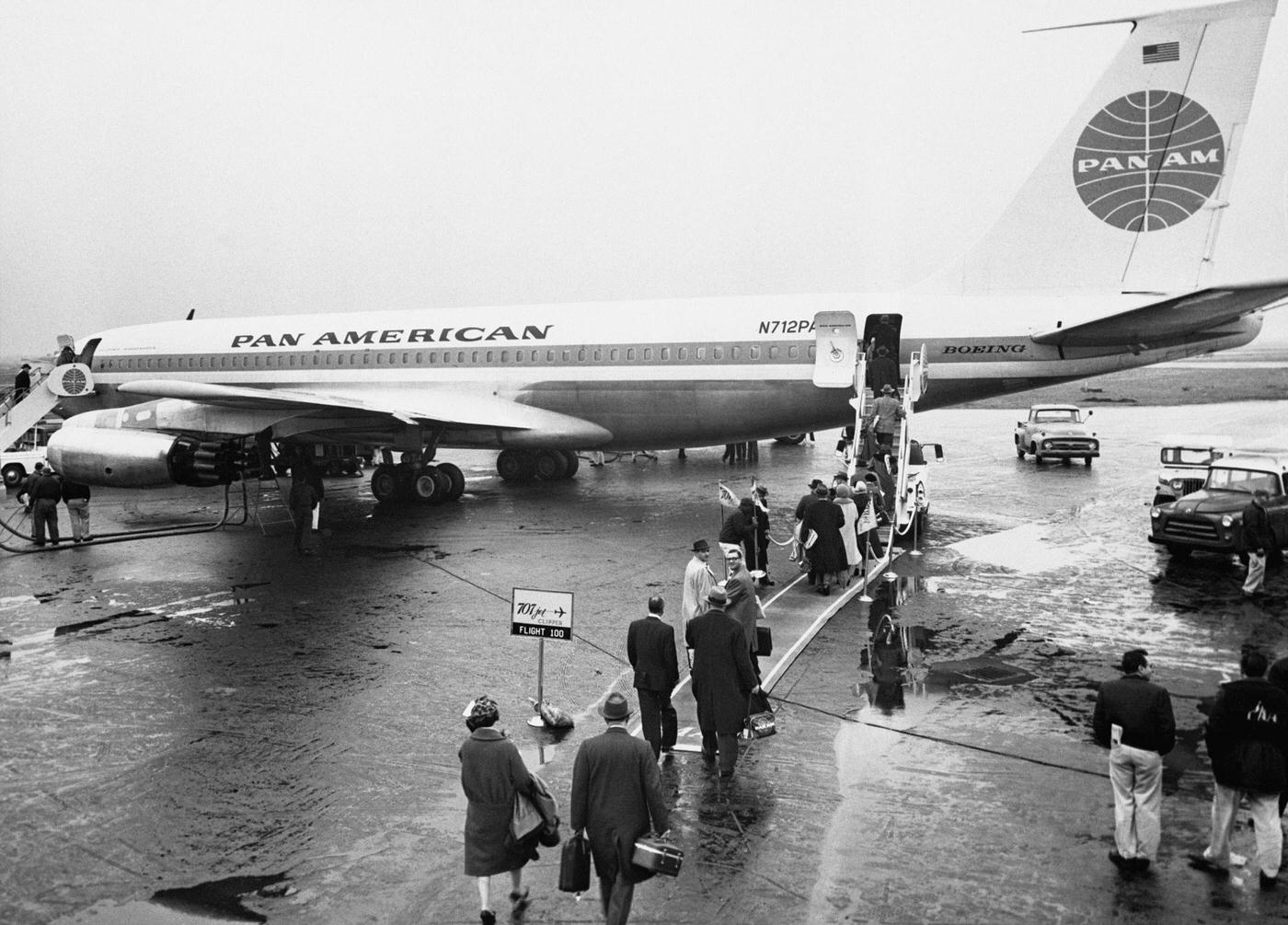
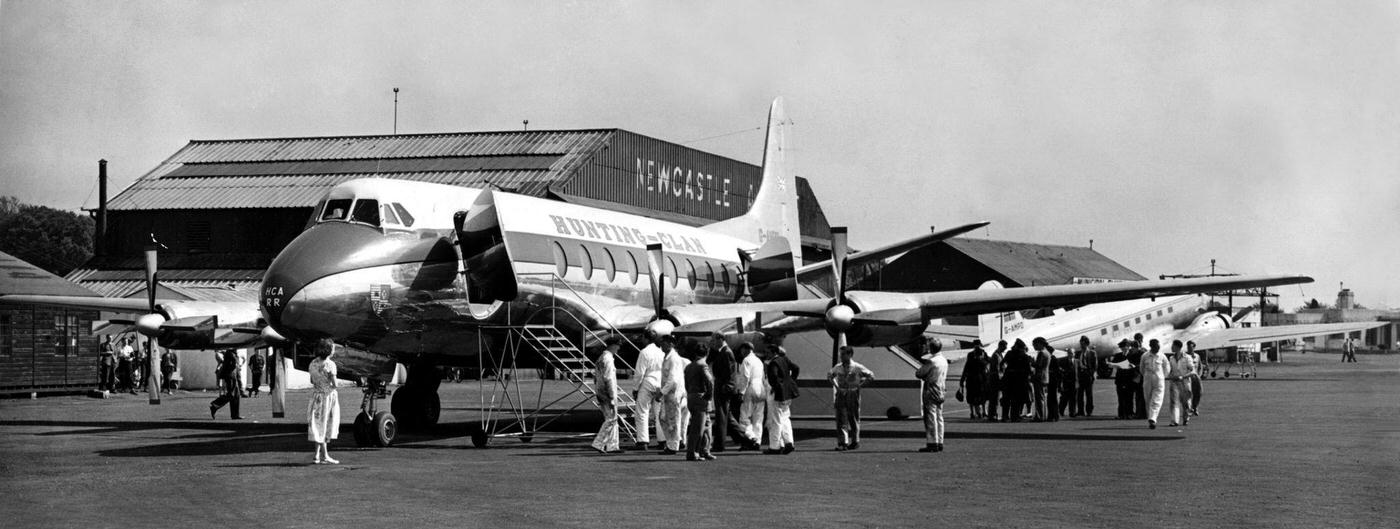
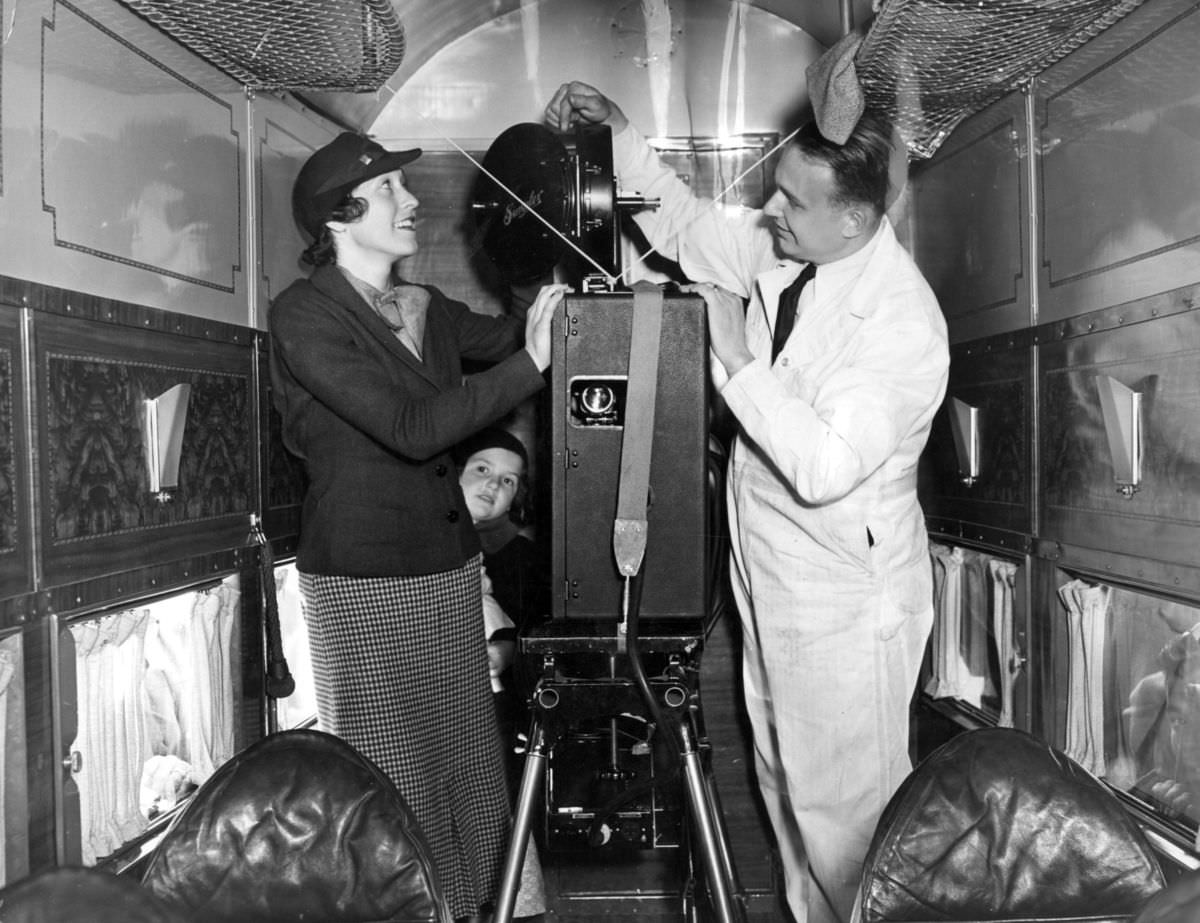
Air travel in the 1950s was marked by a significant increase in the number of people flying, as well as advancements in aircraft technology and infrastructure. The decade saw the introduction of jet airliners, which greatly increased the speed and efficiency of air travel. The first commercial jet airliner, the de Havilland Comet, was introduced in 1952, followed by the Boeing 707 and Douglas DC-8 in the late 1950s. These new jet airliners allowed airlines to offer faster, more comfortable, and more convenient flights, and they quickly became popular with passengers.
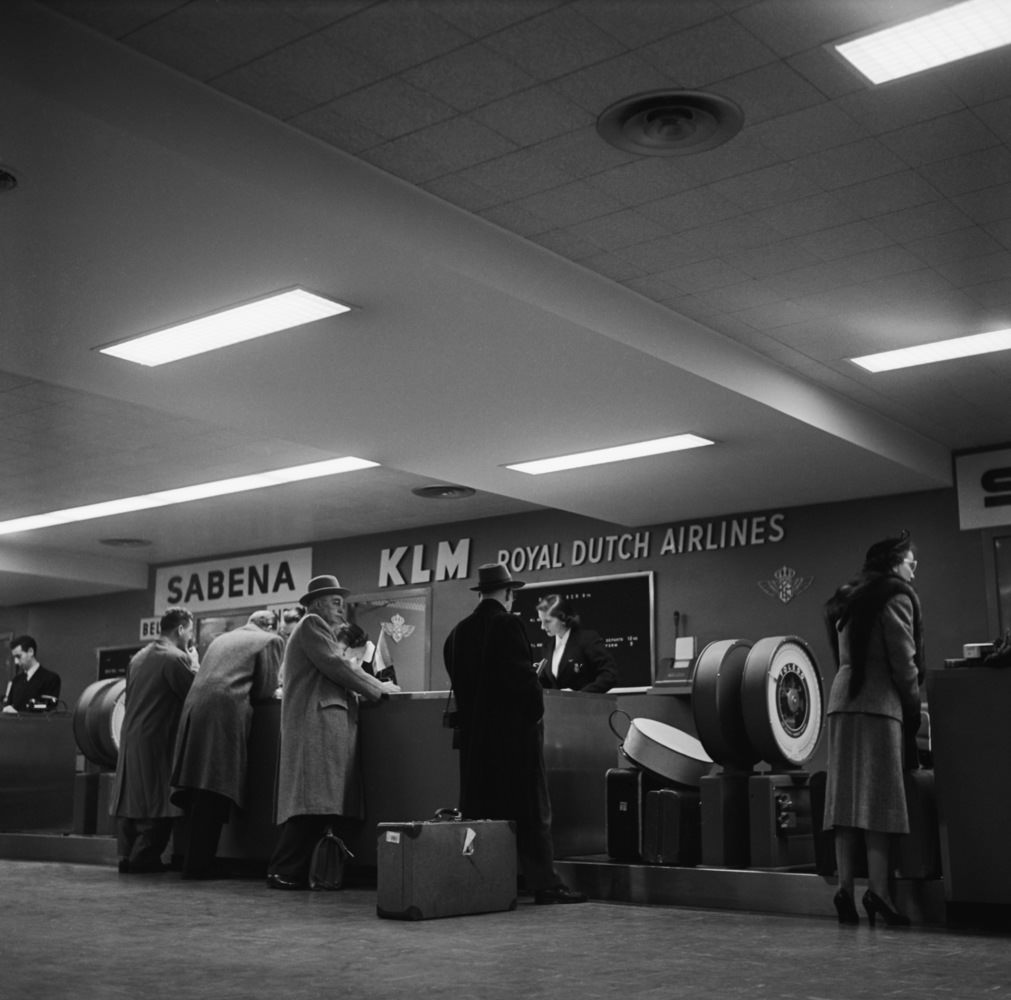
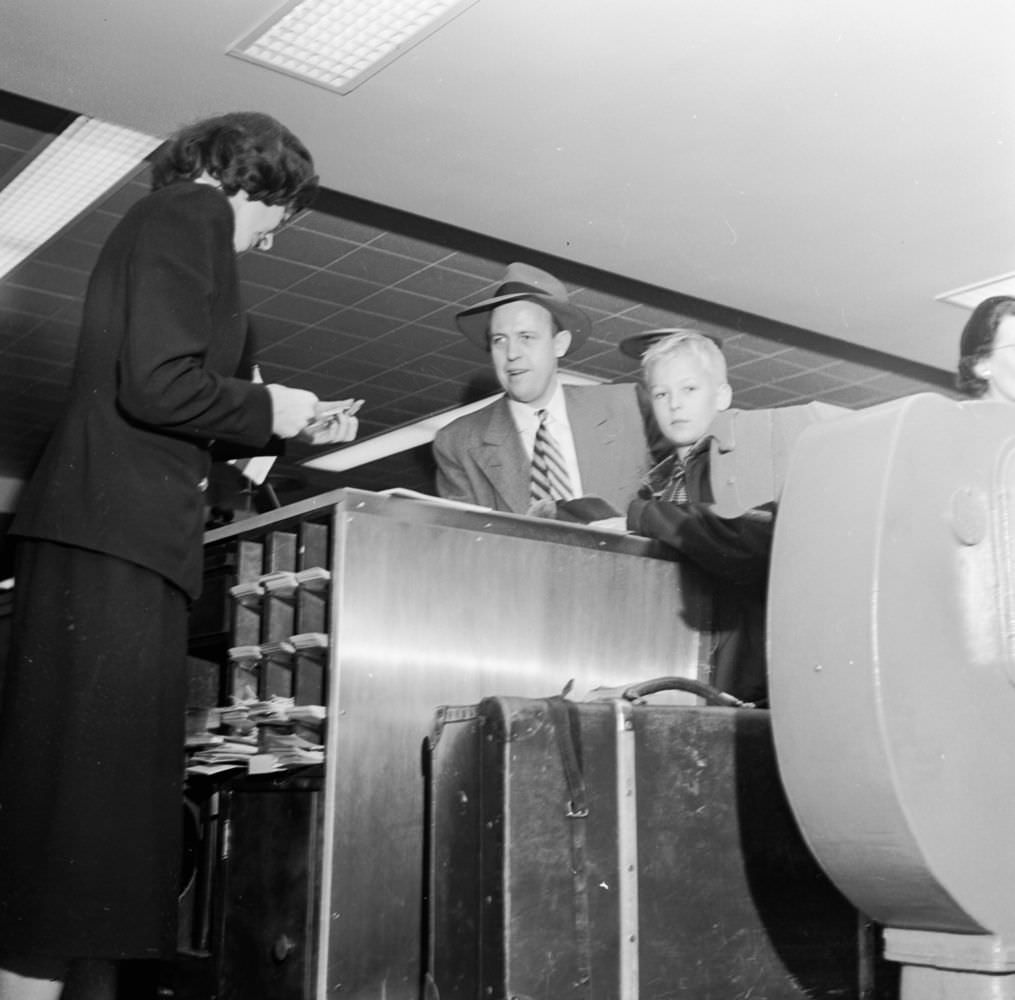
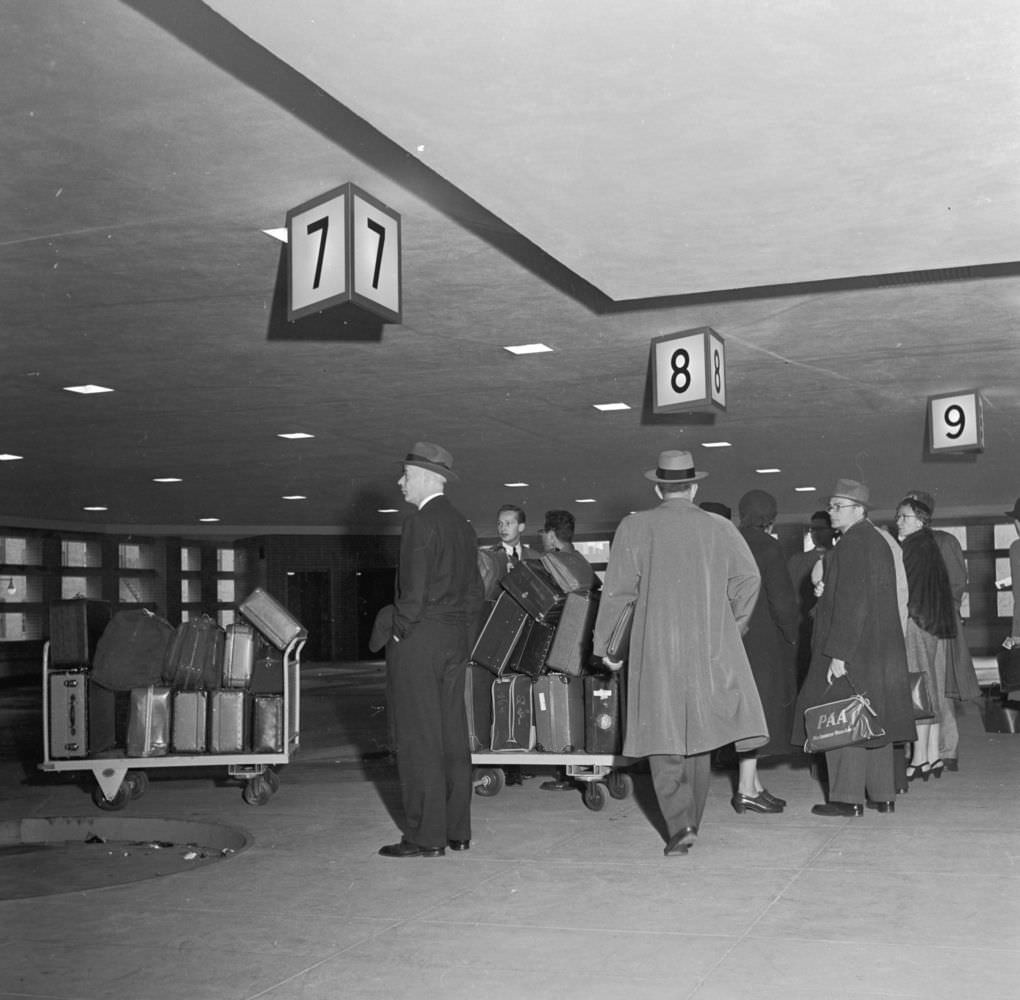
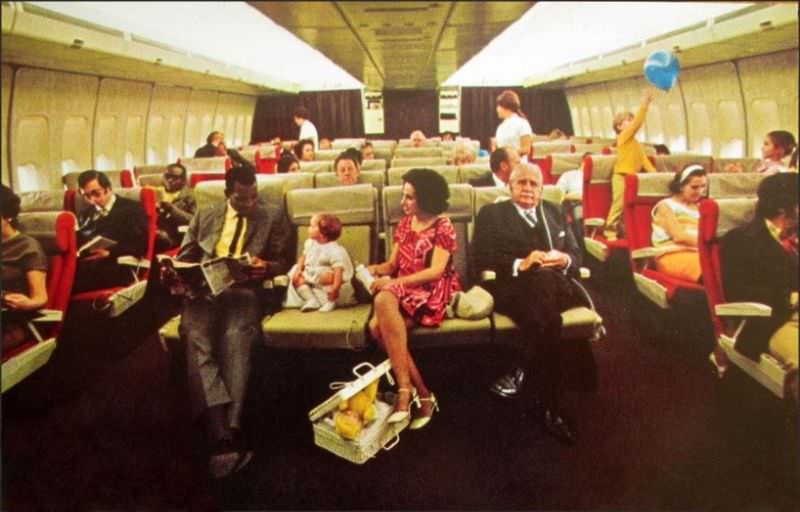
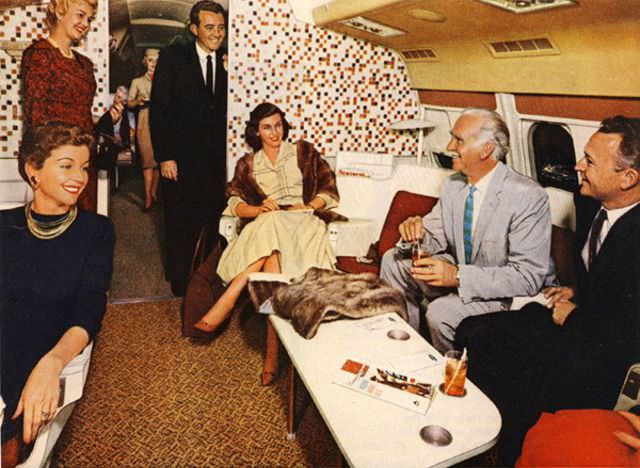
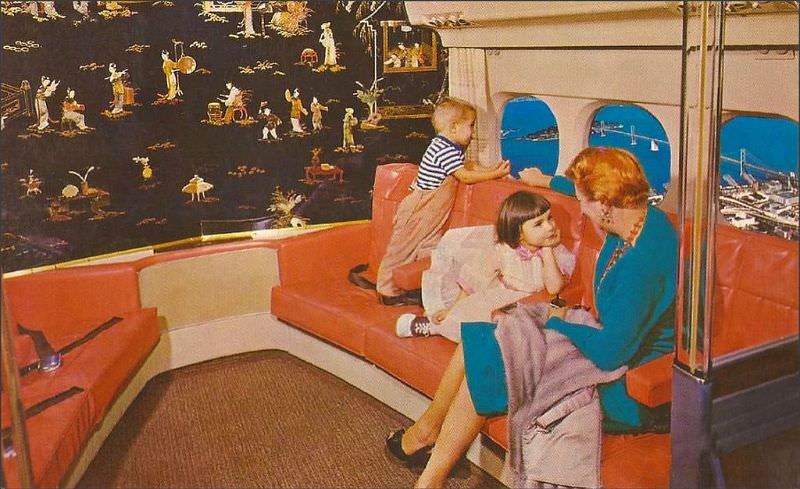
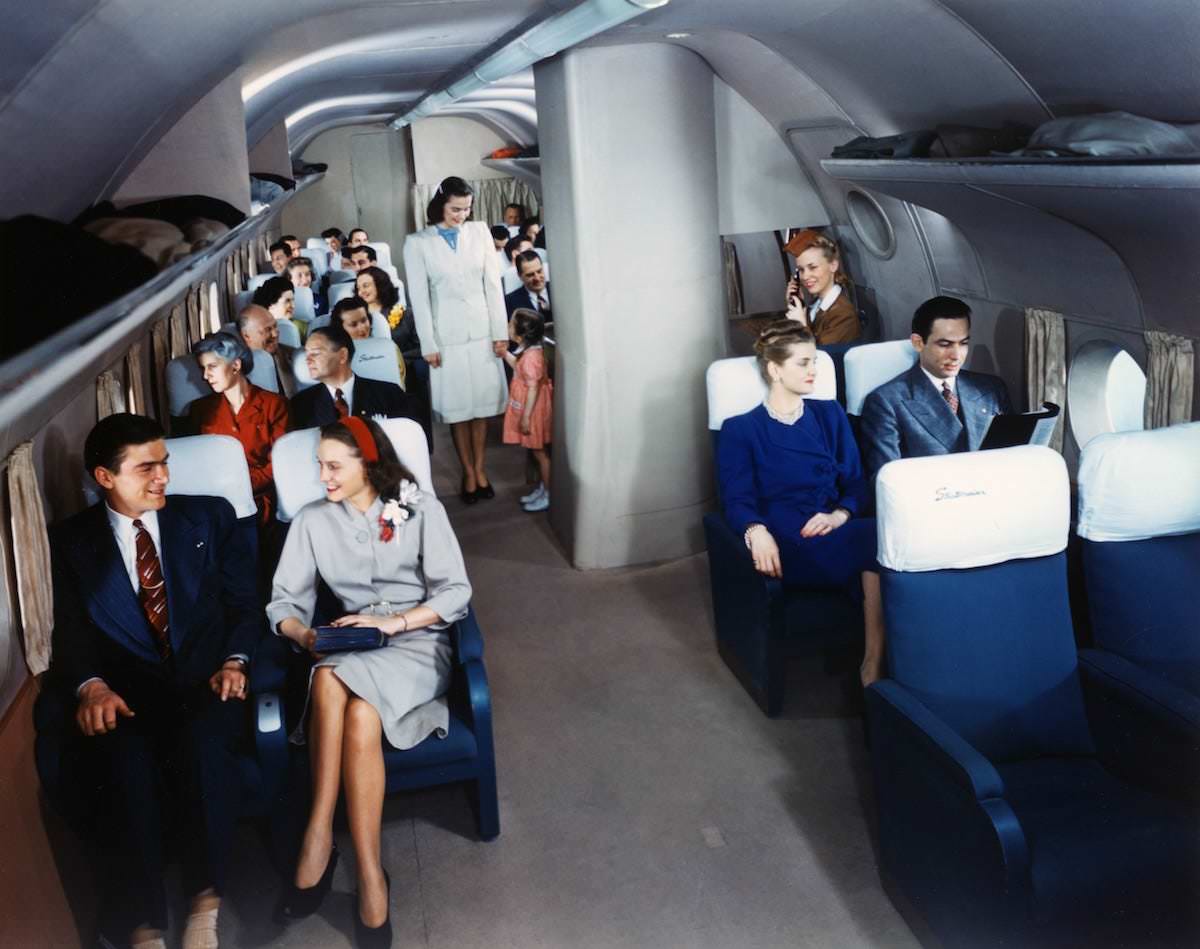
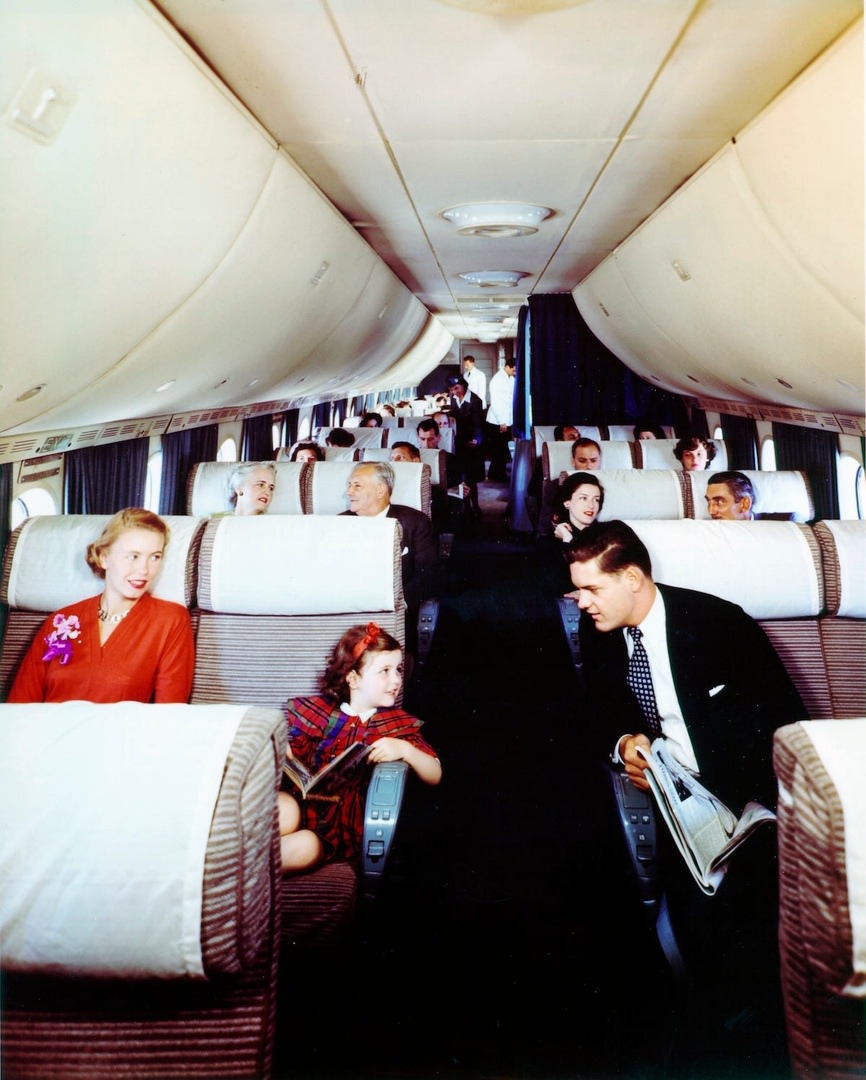
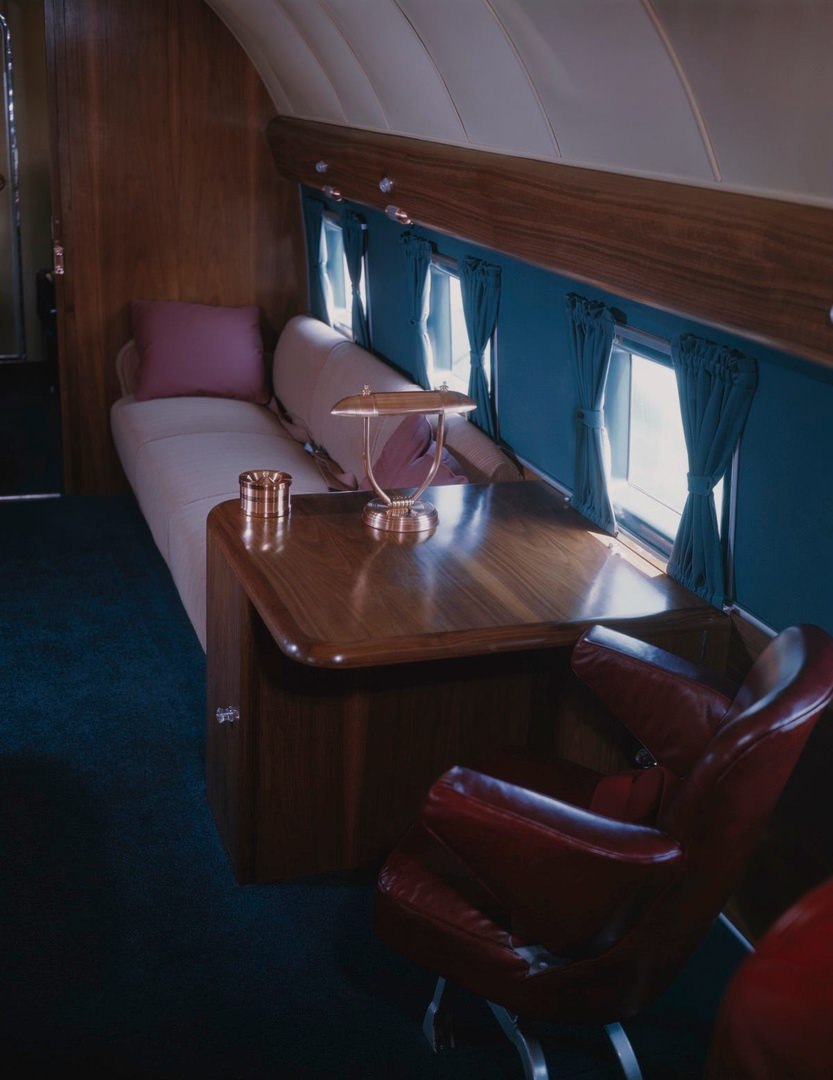
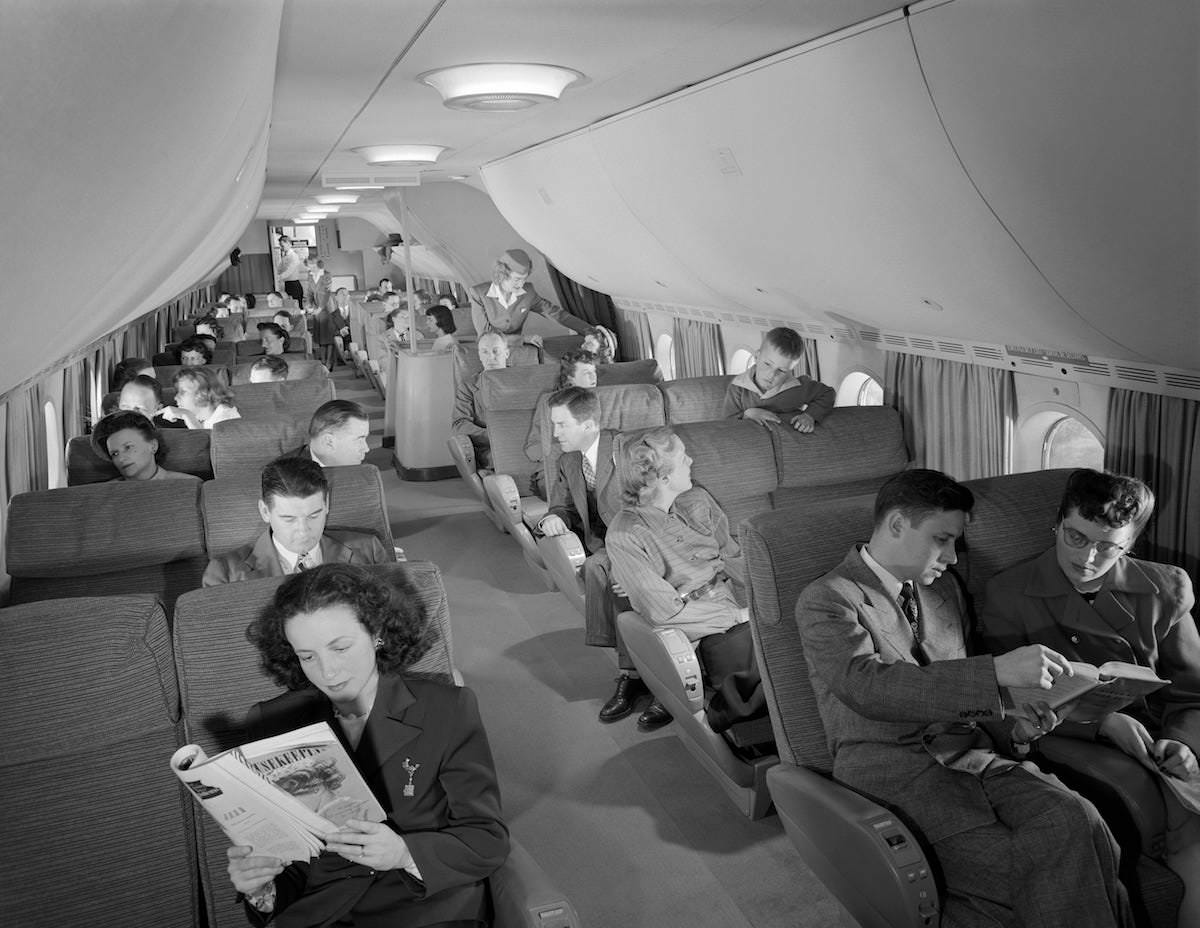
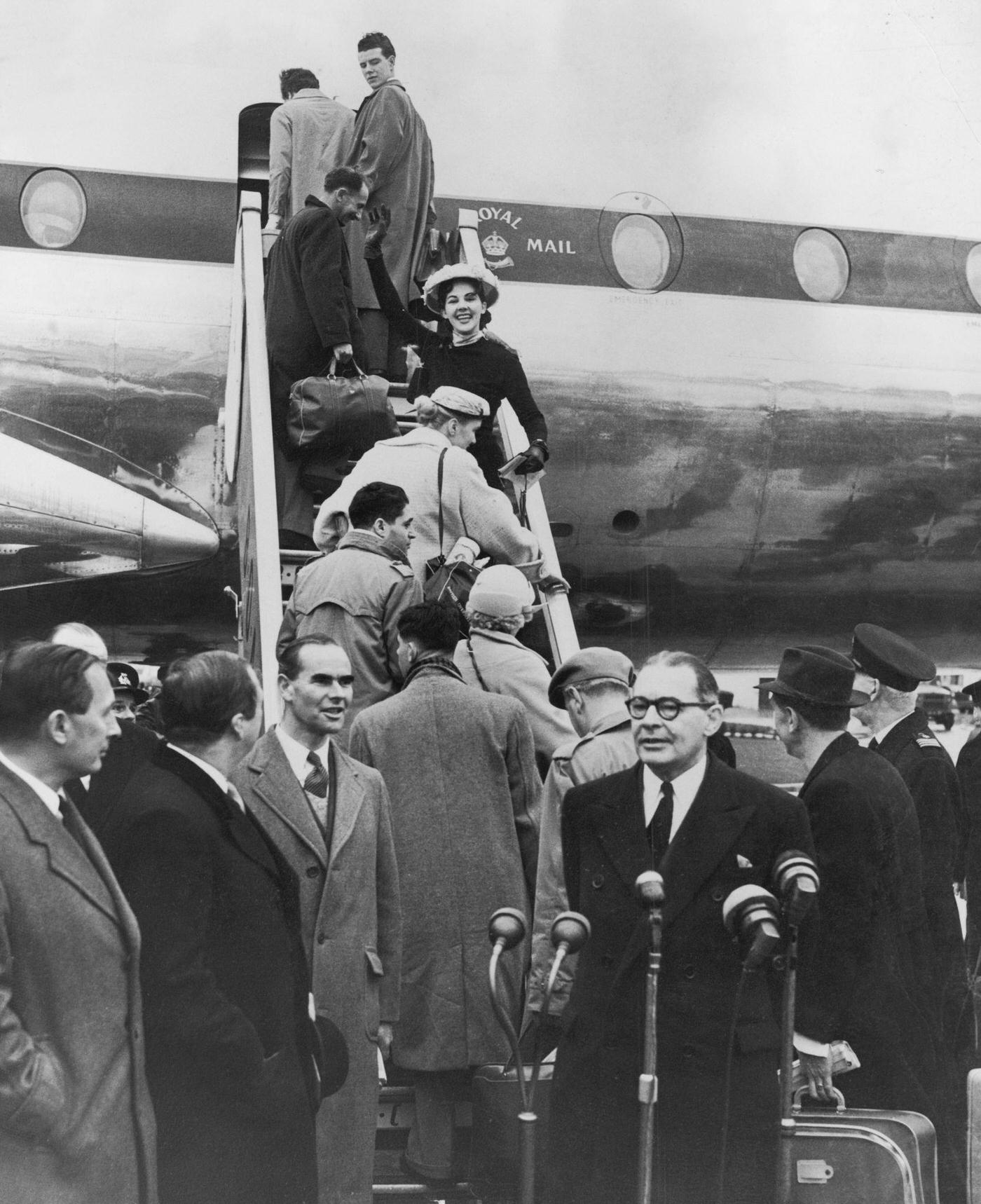
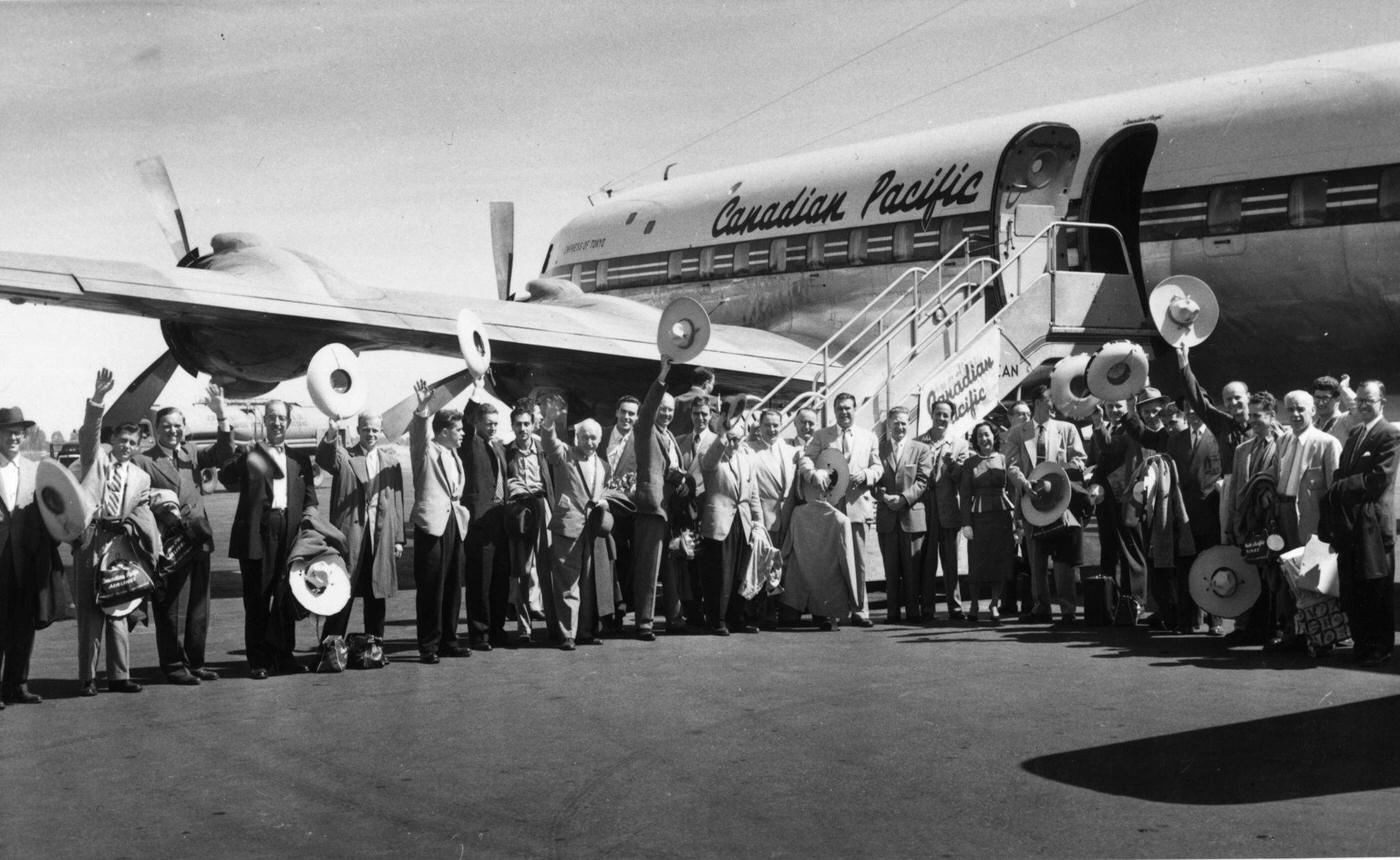
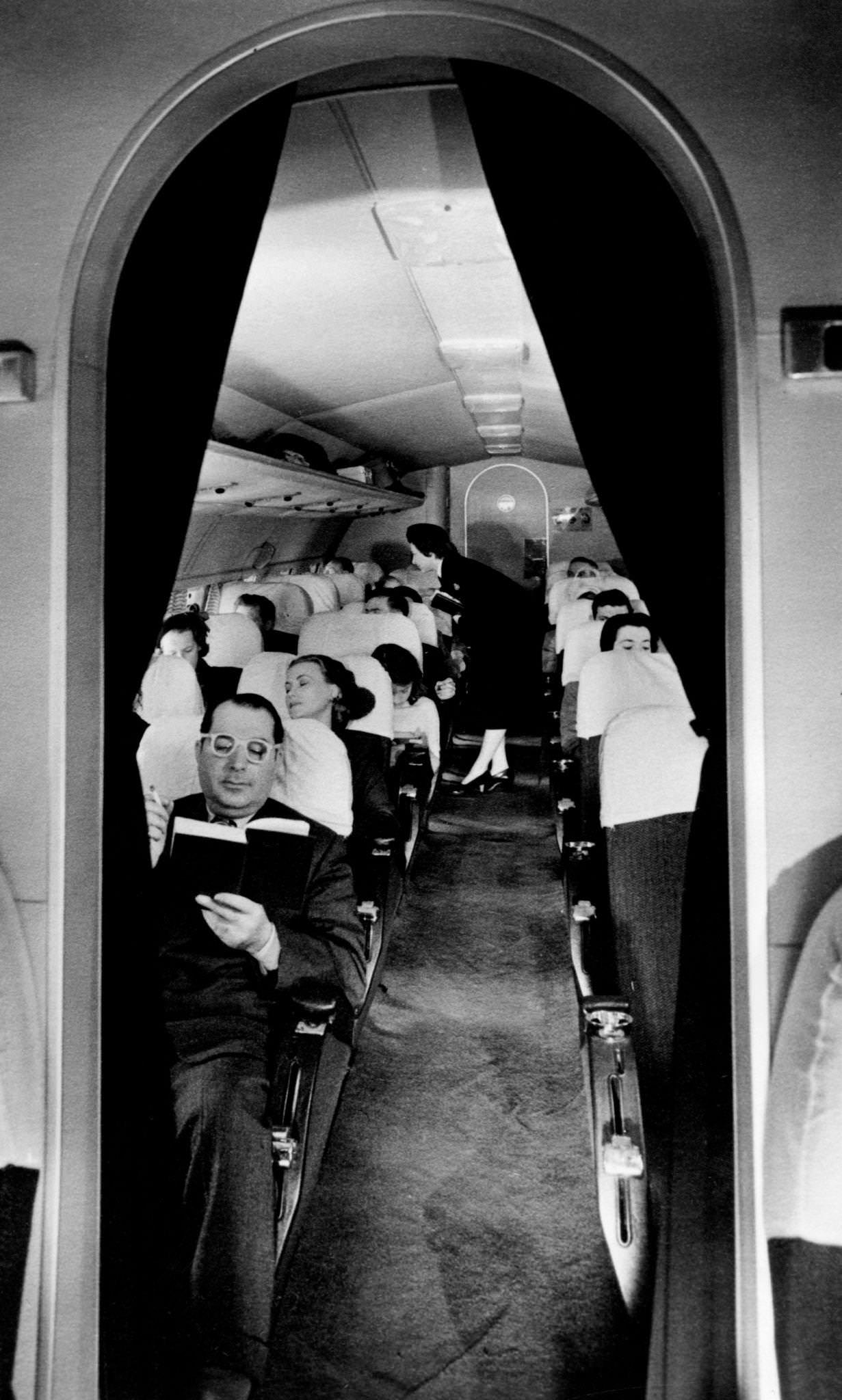
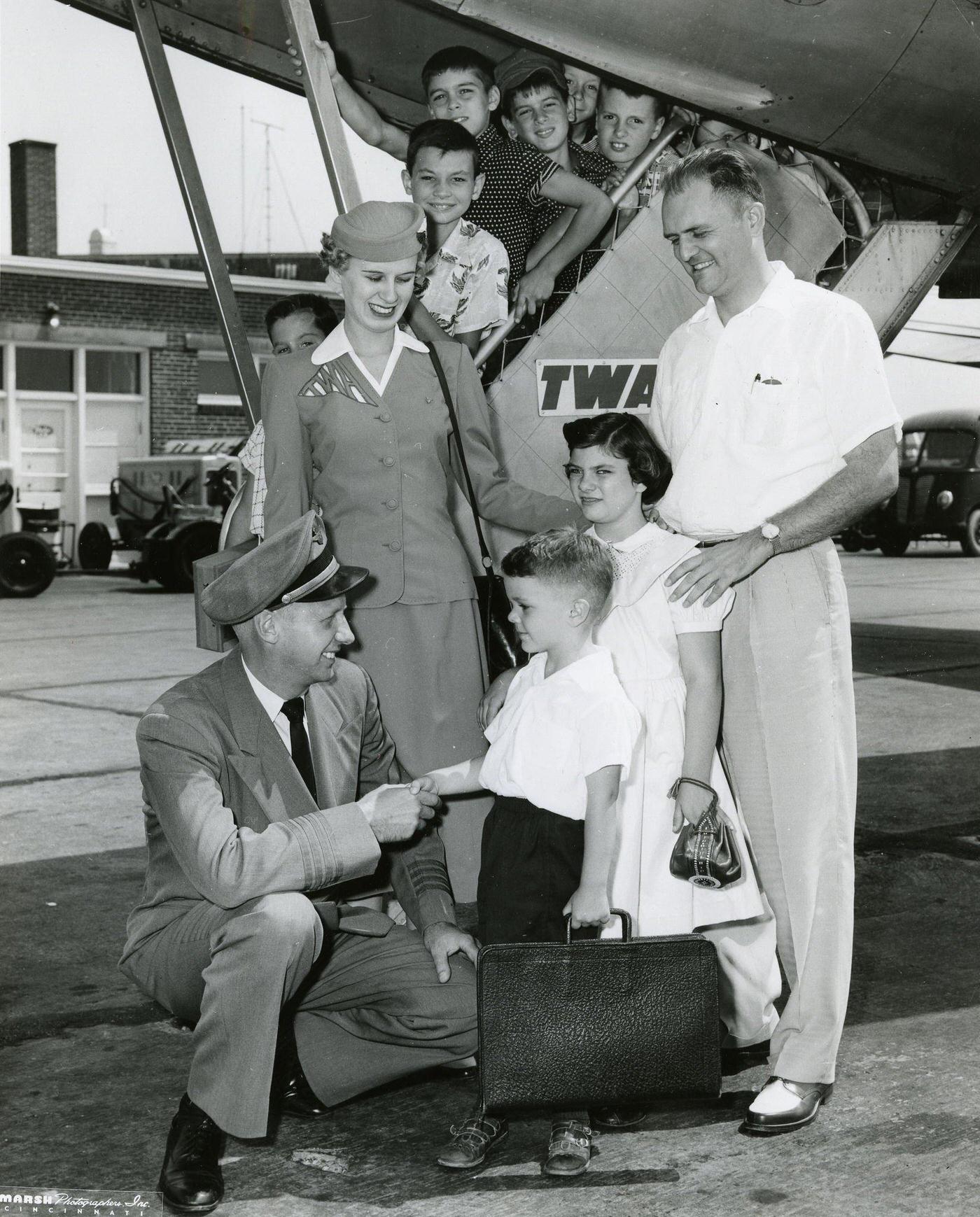
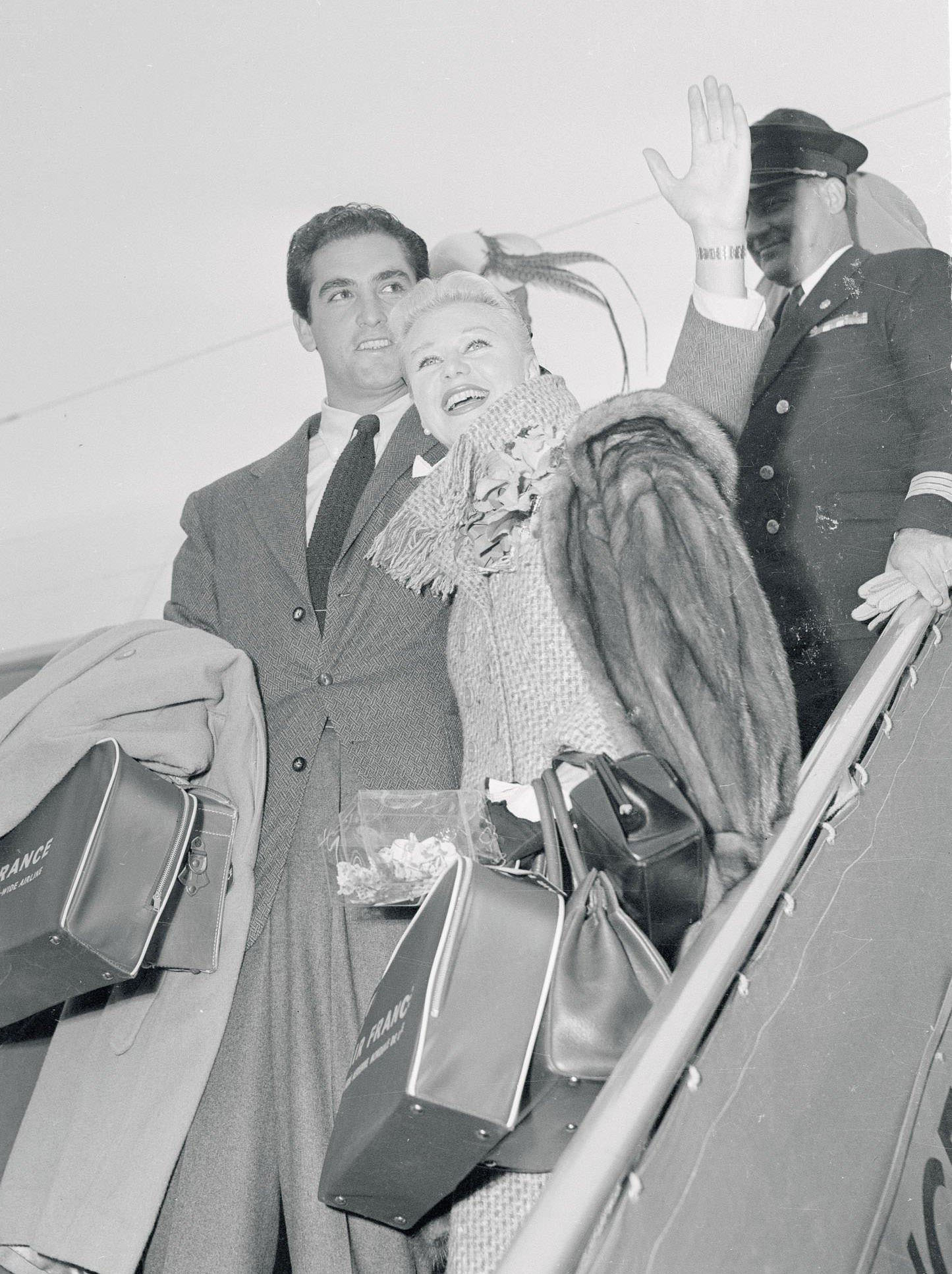
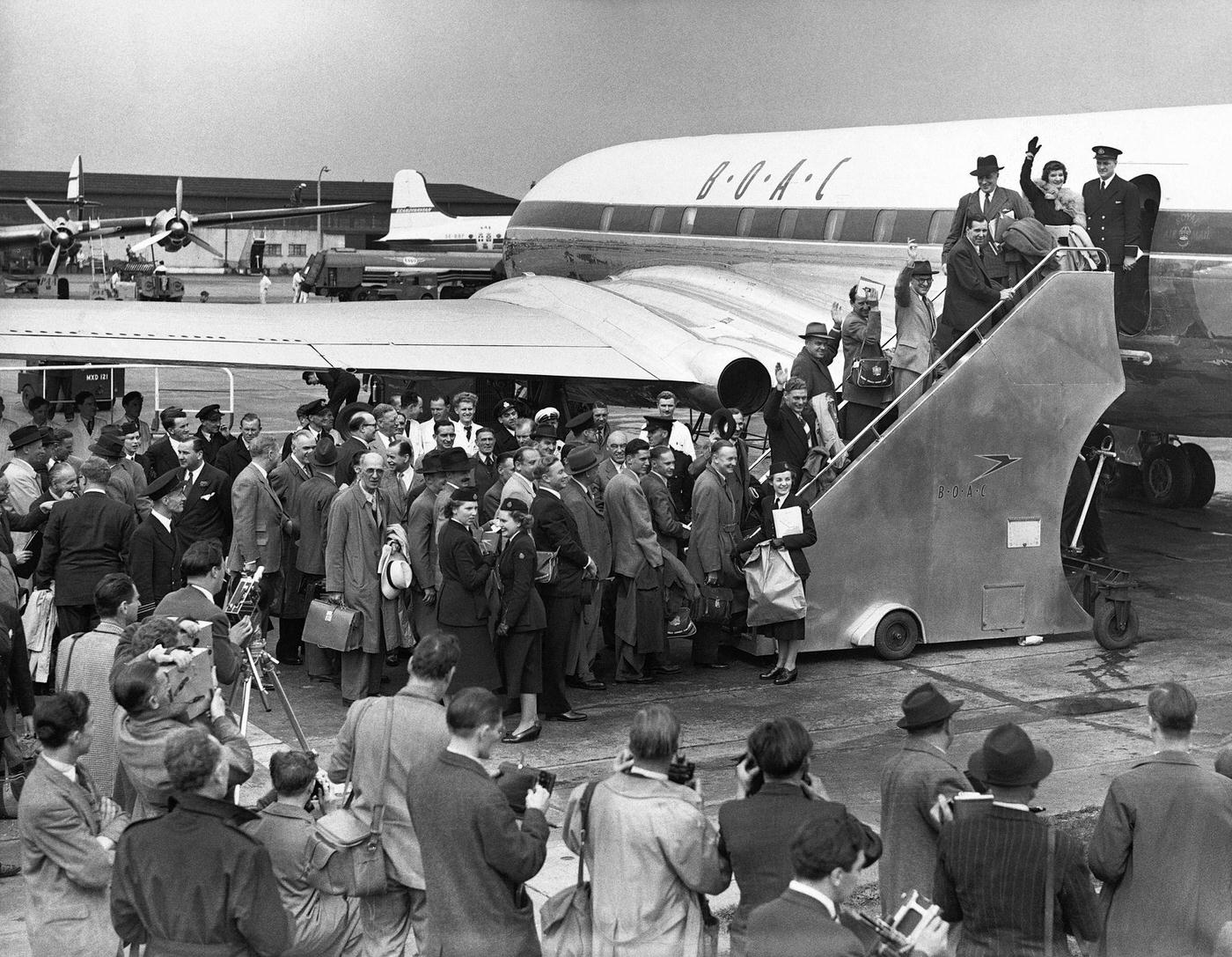
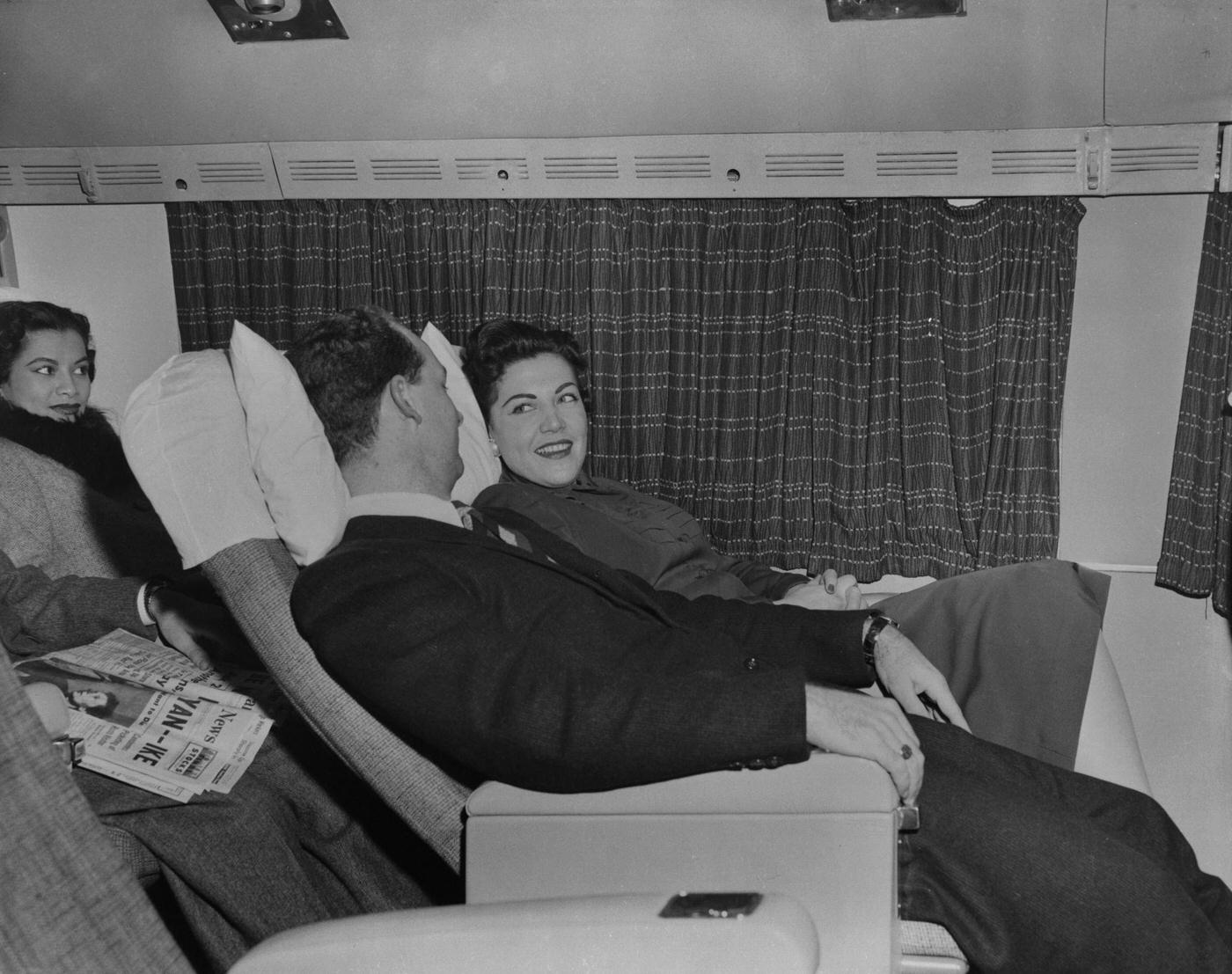
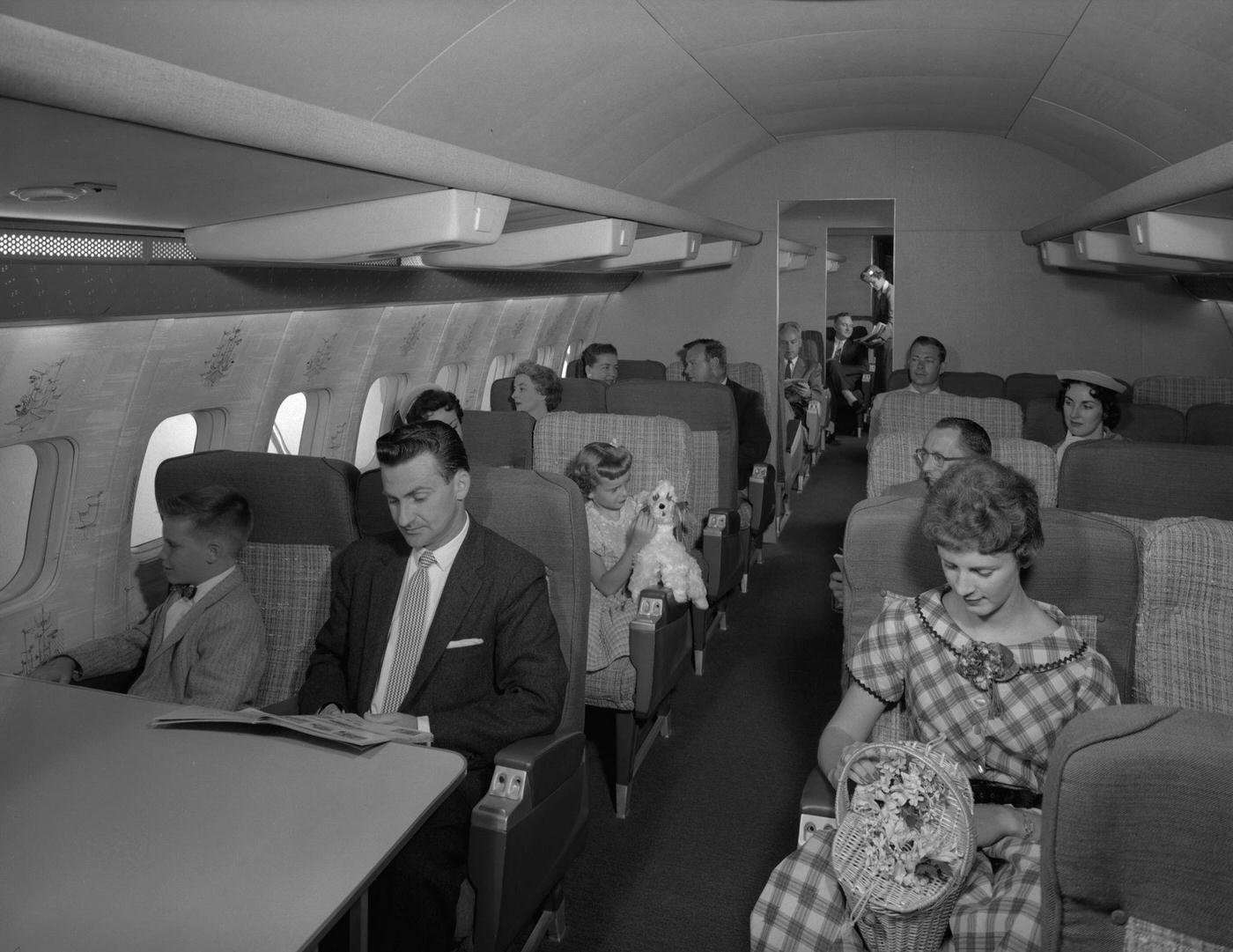
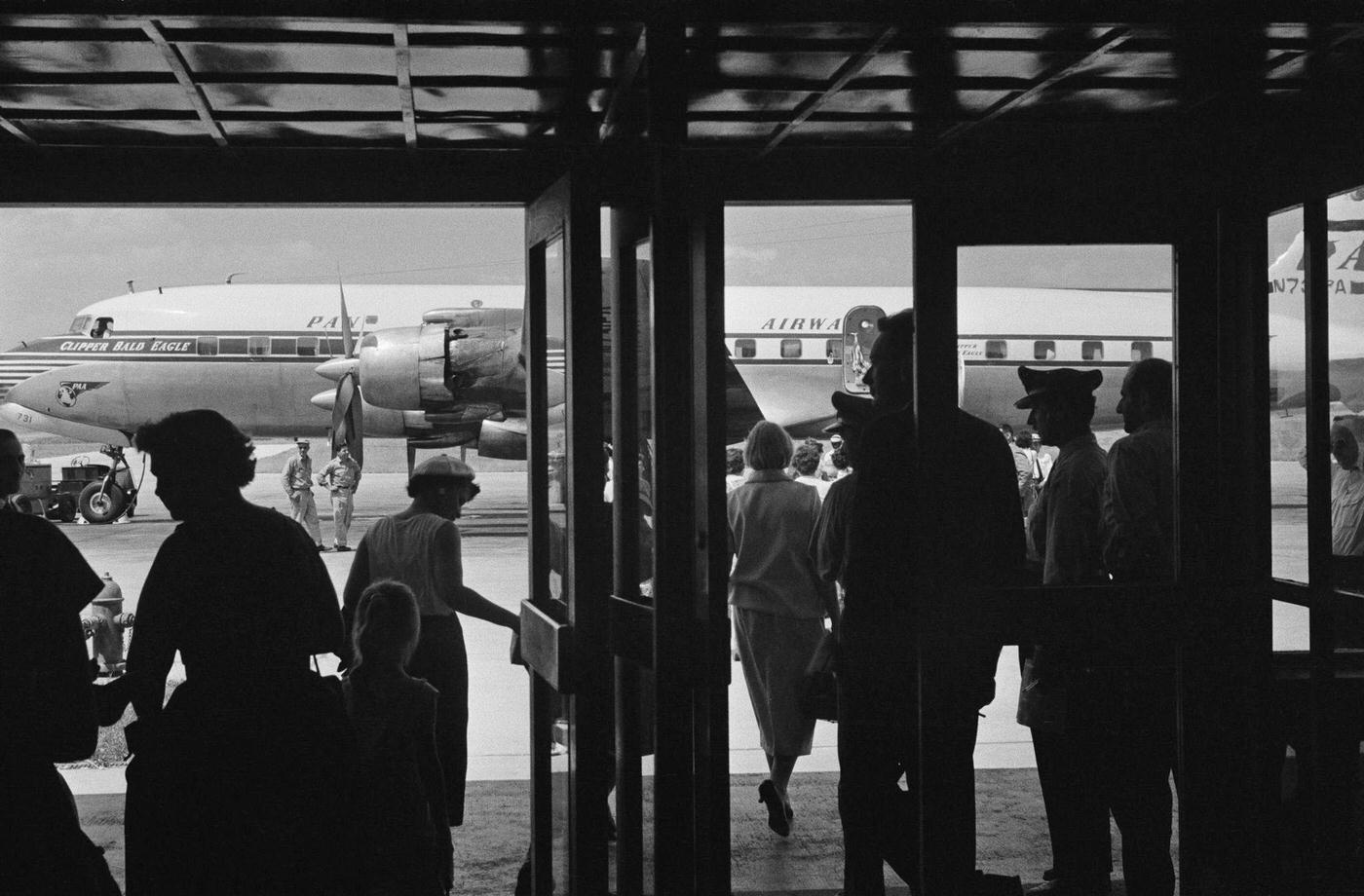
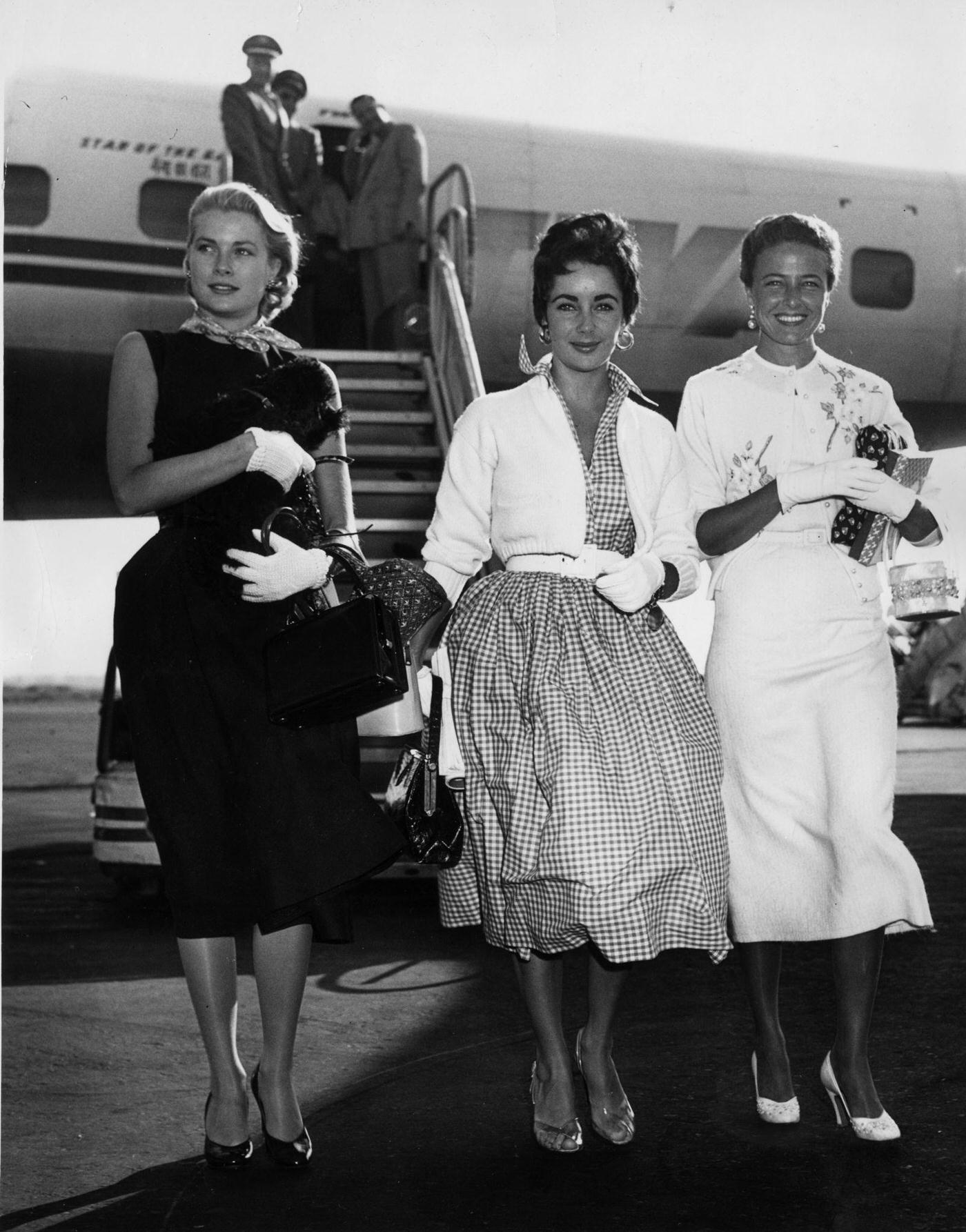
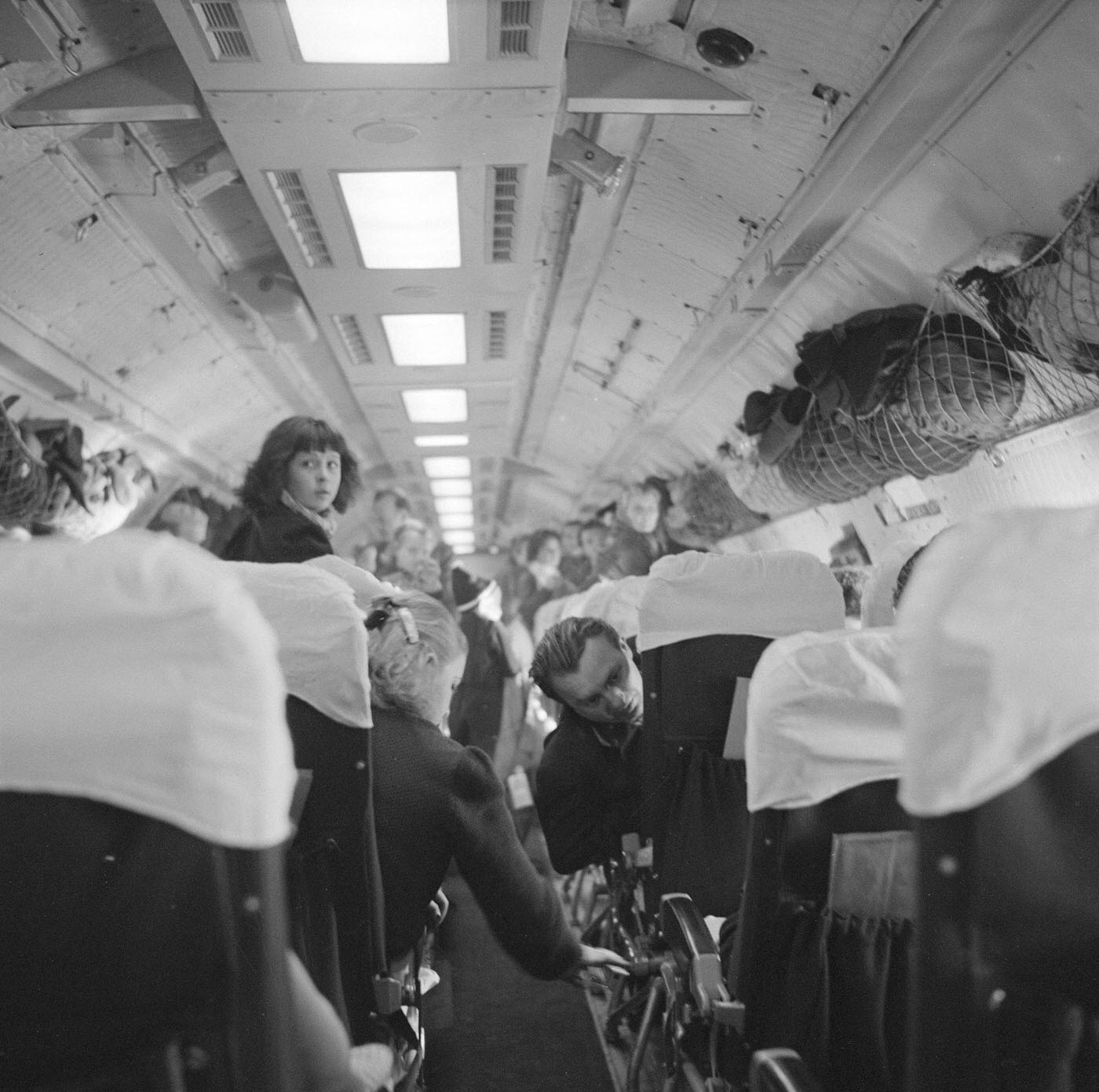
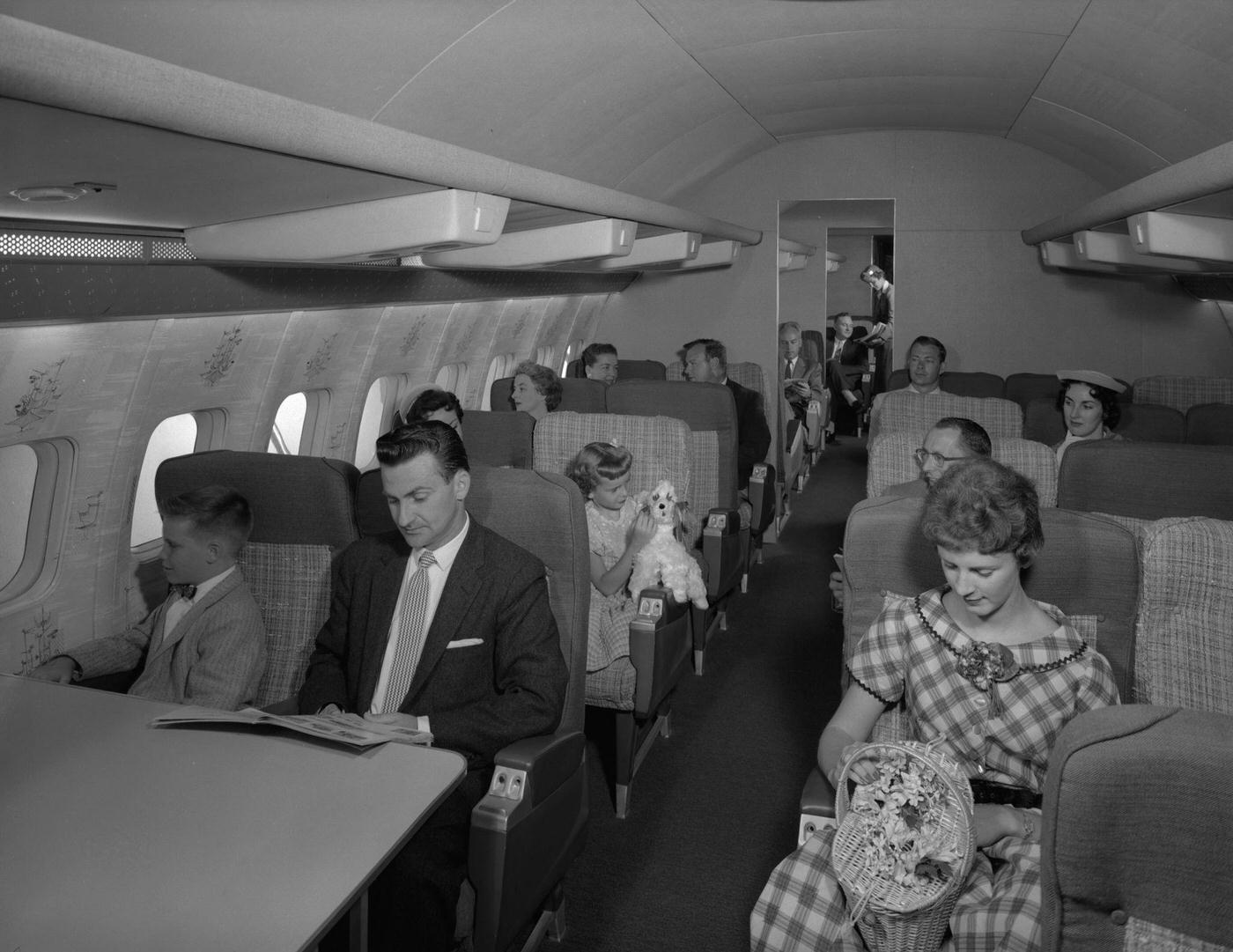
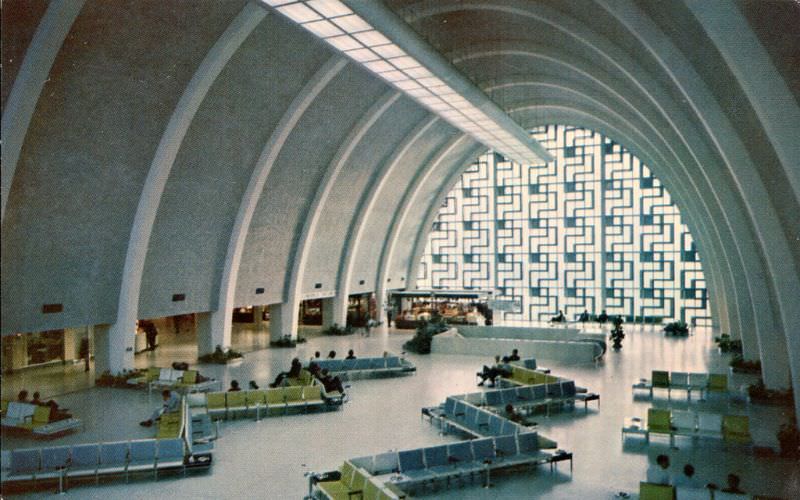
During the 1950s, air travel was still considered a luxury, but it was becoming more affordable and accessible to the general public. Airlines offered more flights and destinations than ever before, and air travel was becoming more common for both business and leisure. Many airlines also began to offer vacation packages, which included airfare, accommodations, and activities, making it even easier for people to travel.
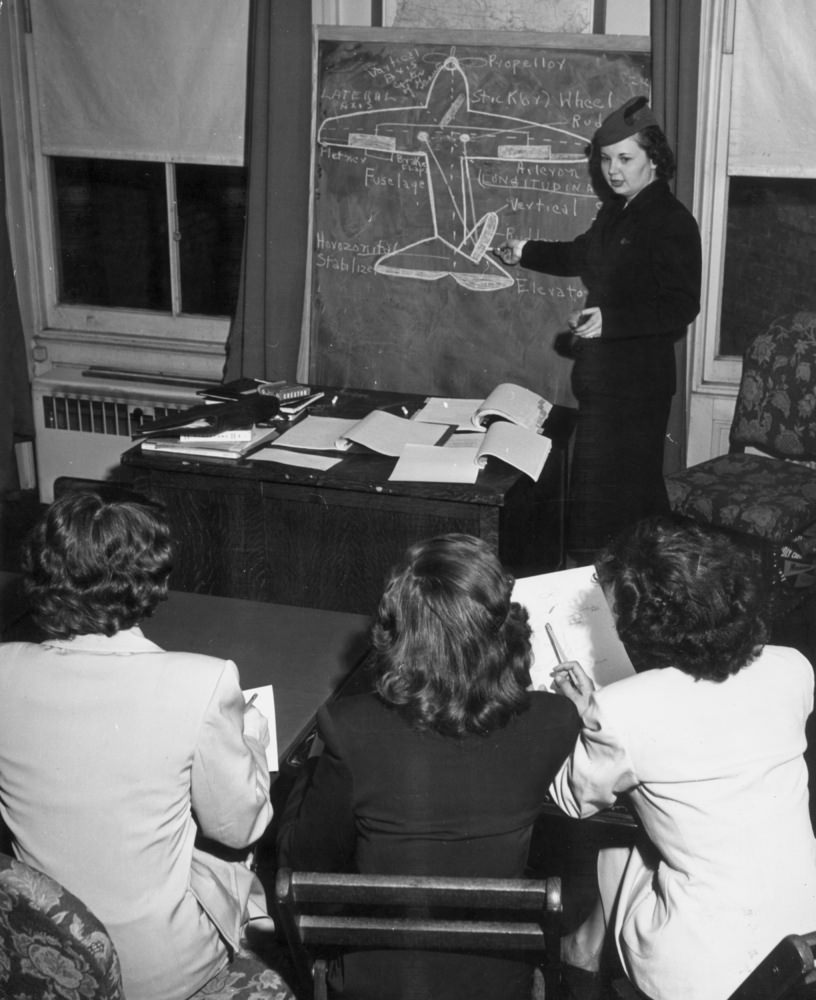
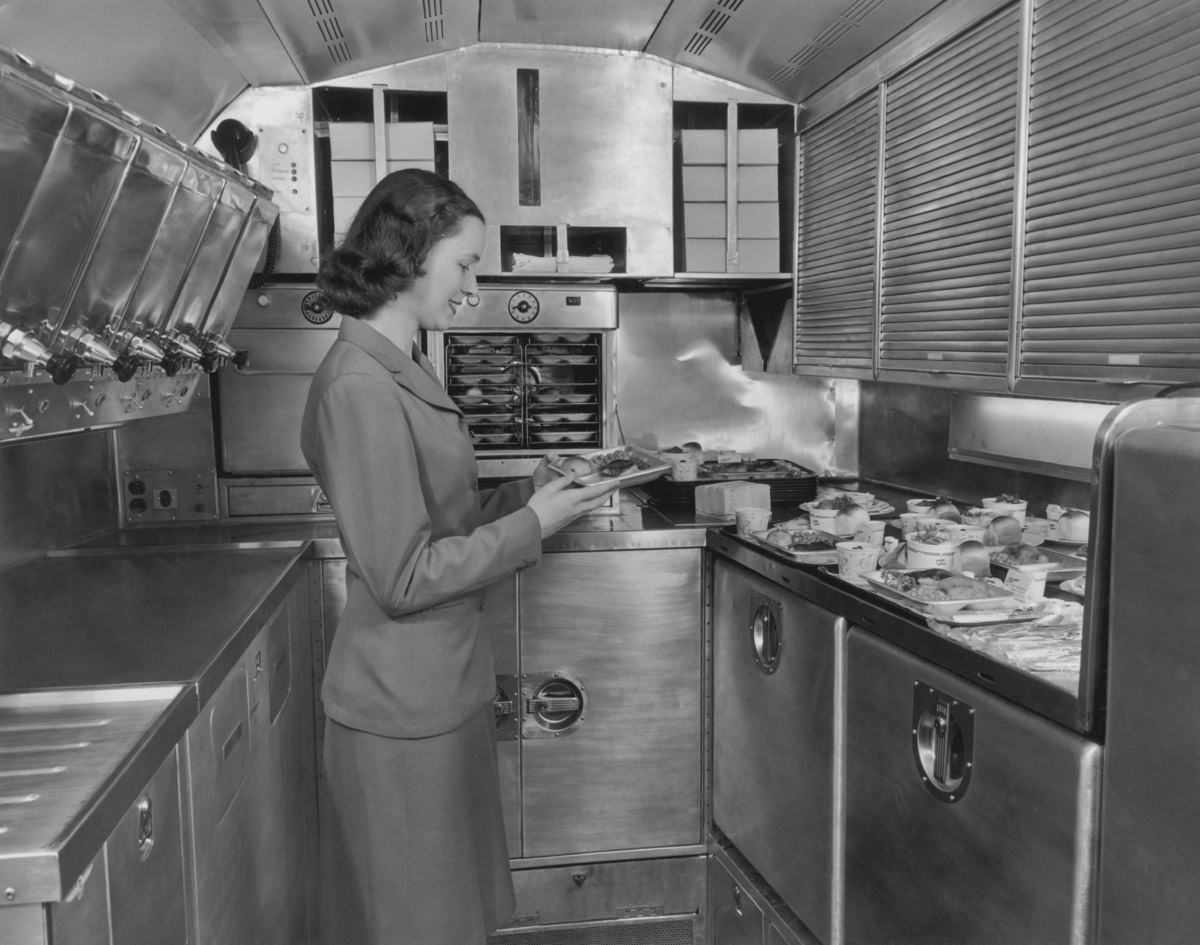
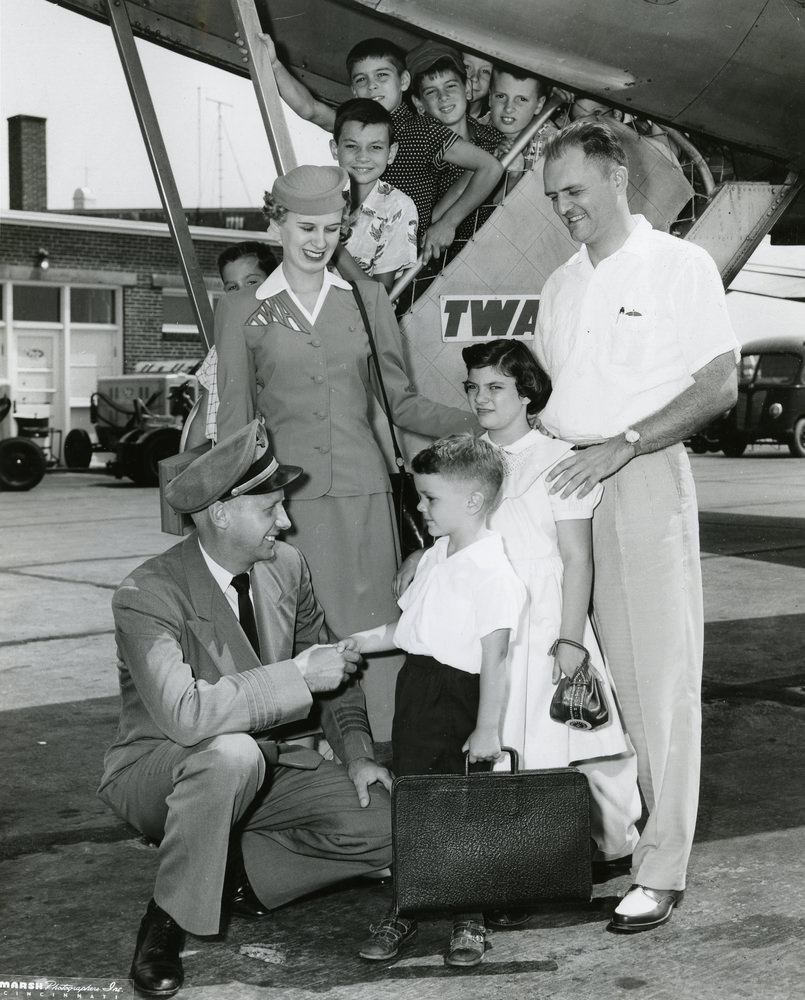
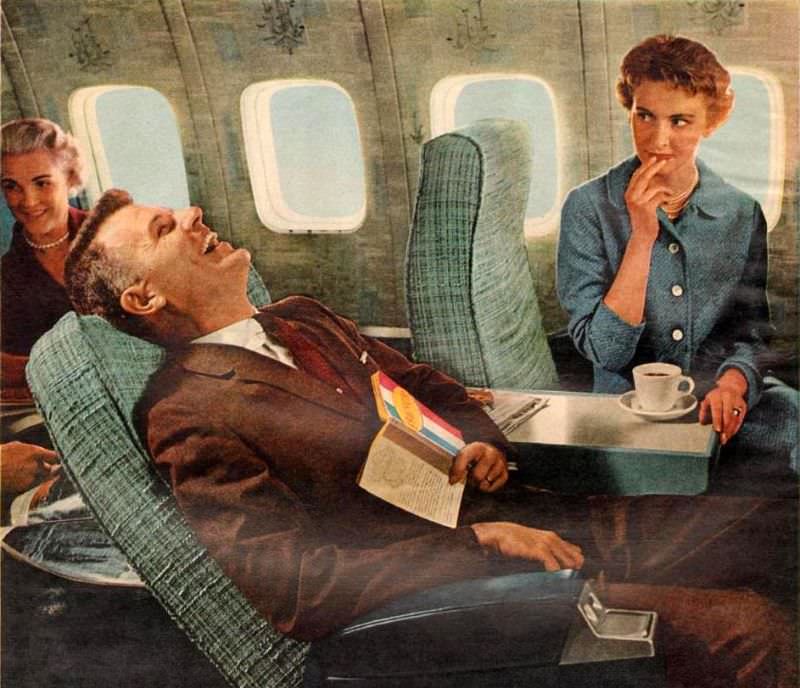
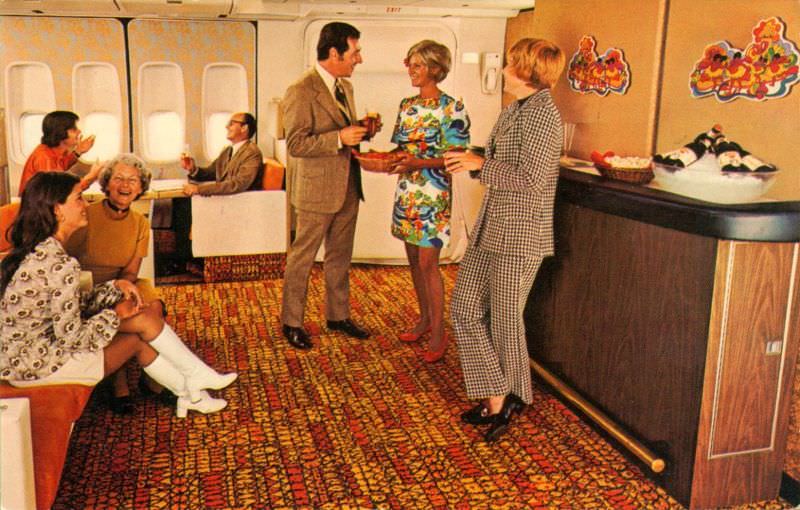
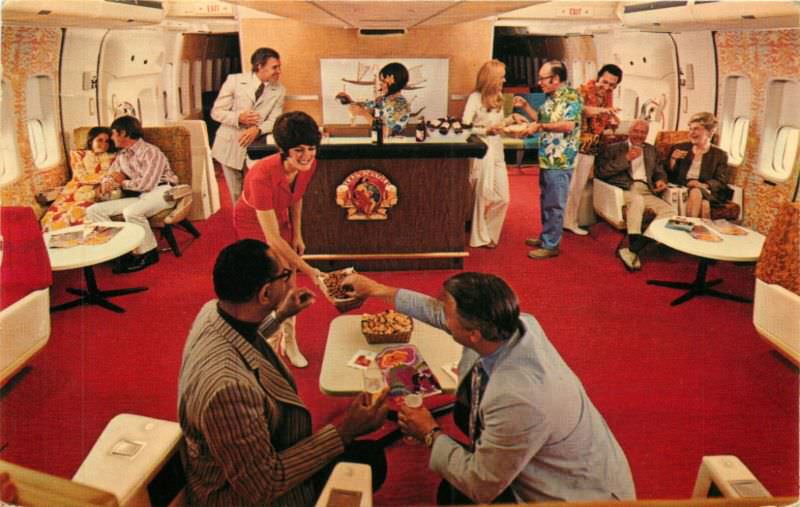
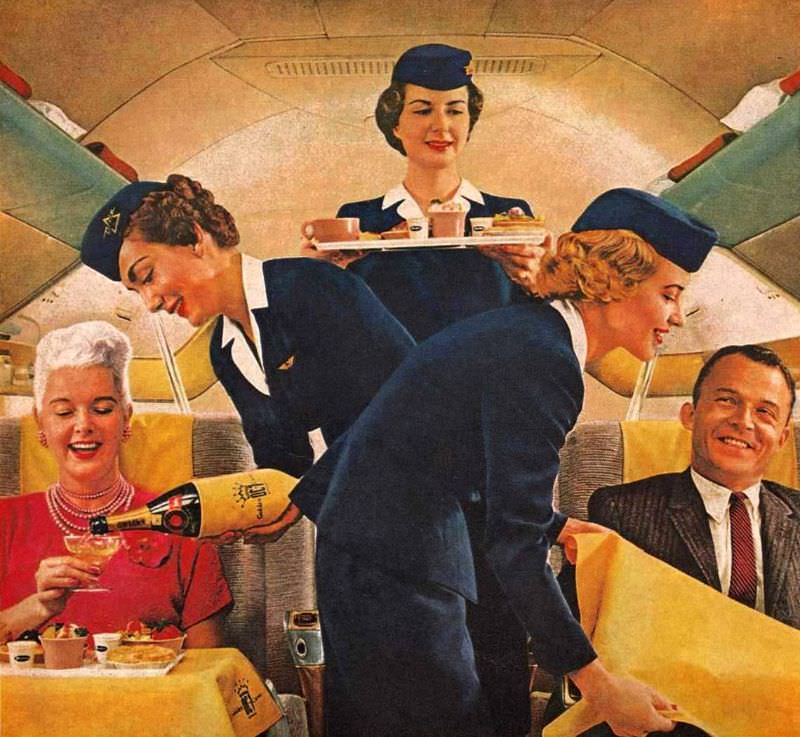
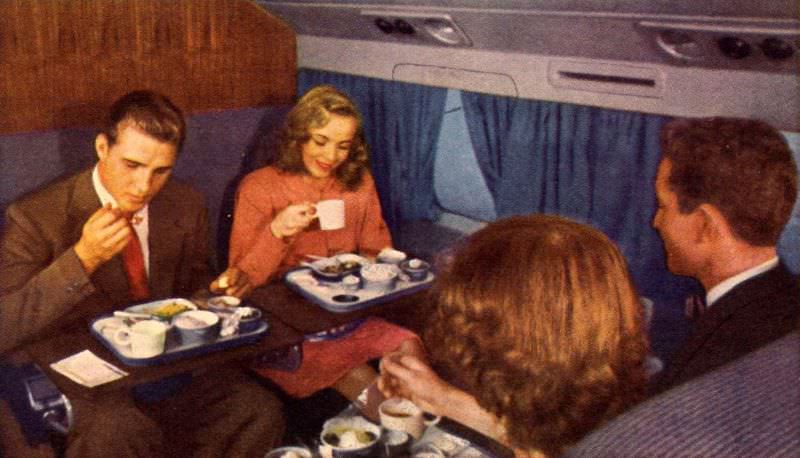
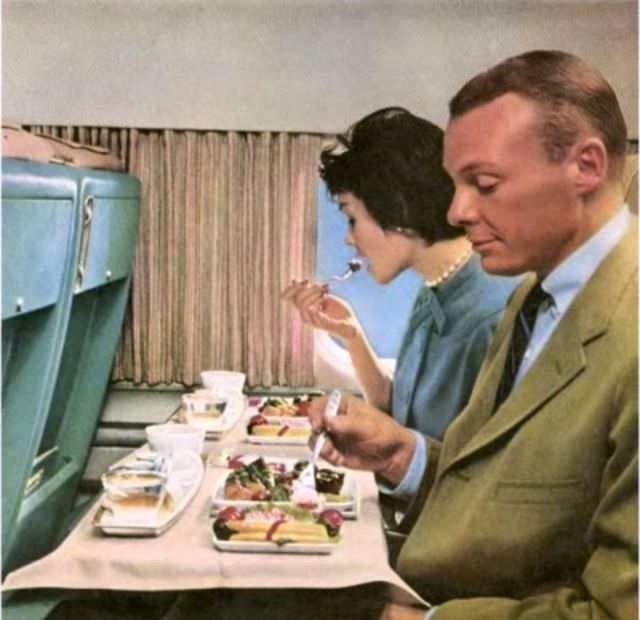
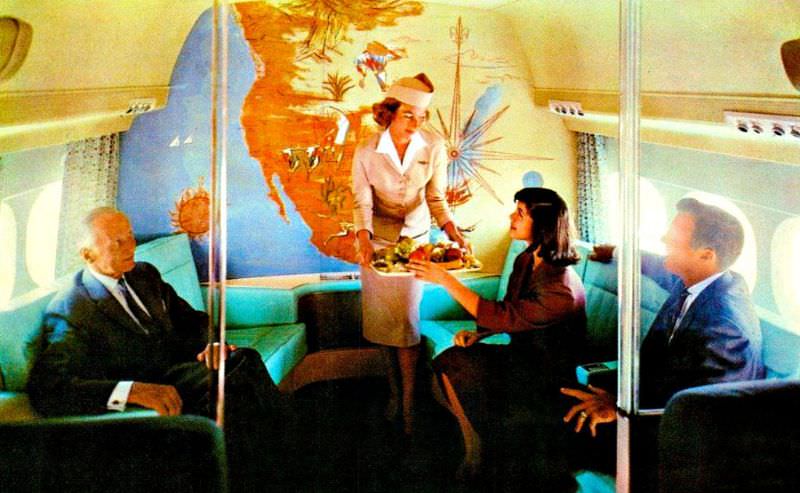
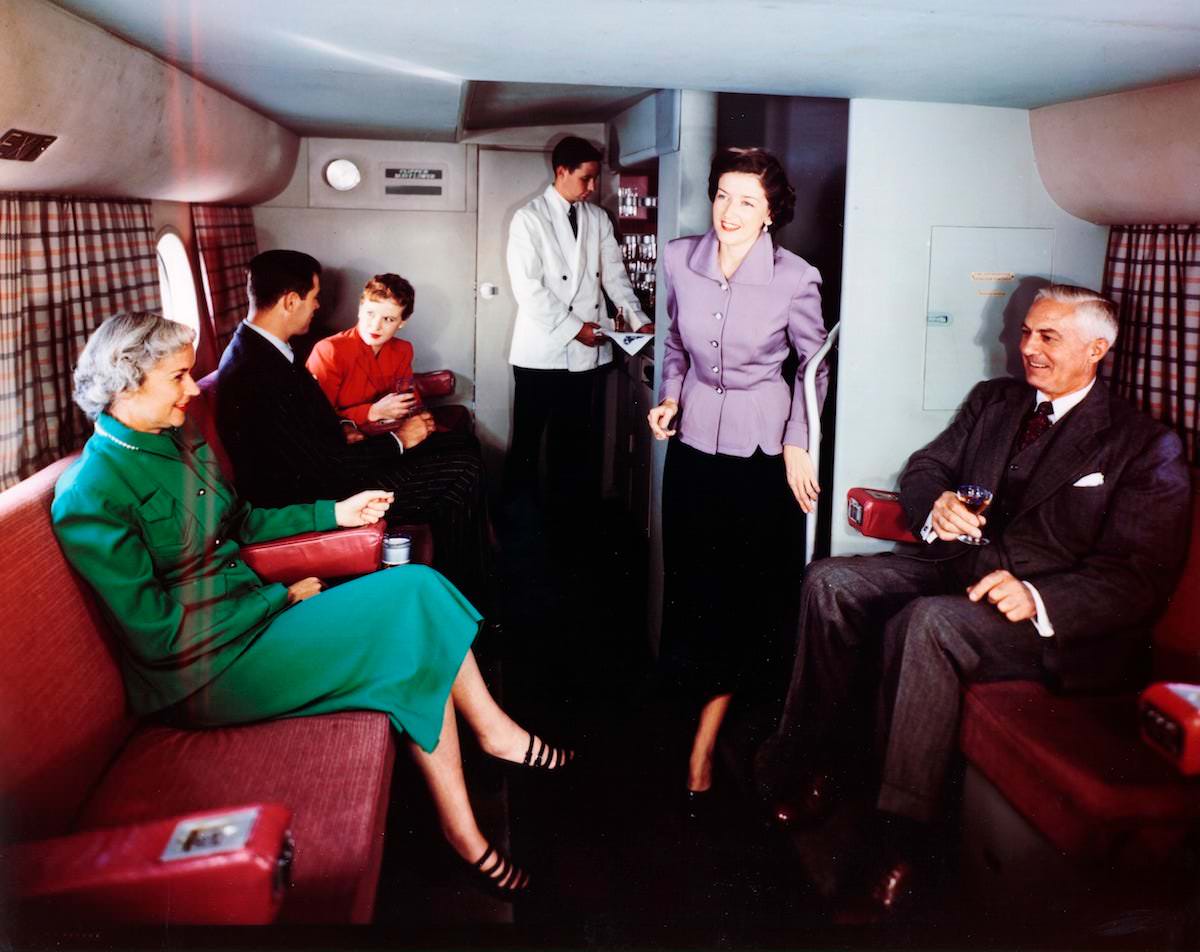
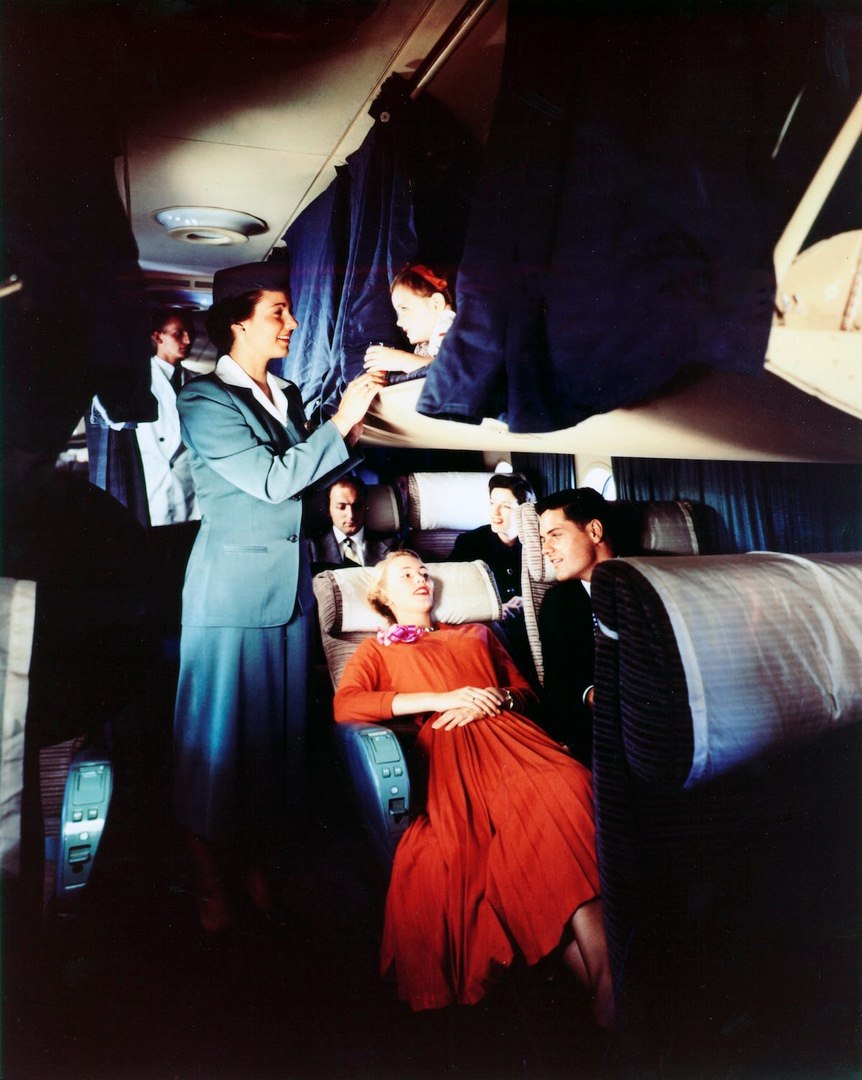
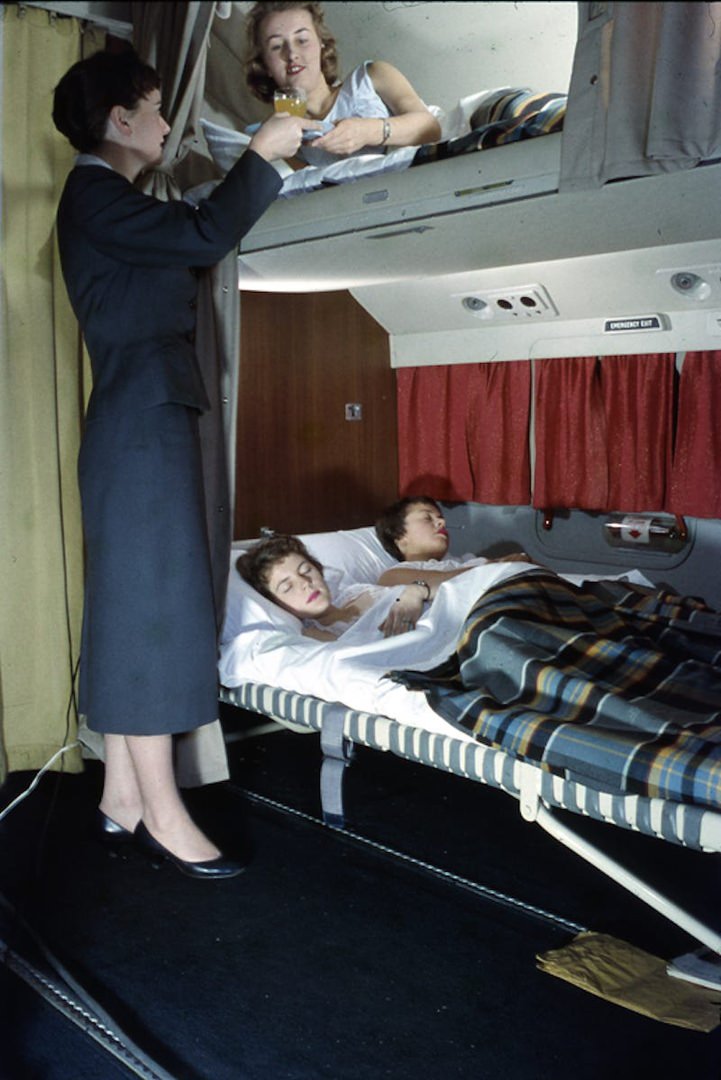
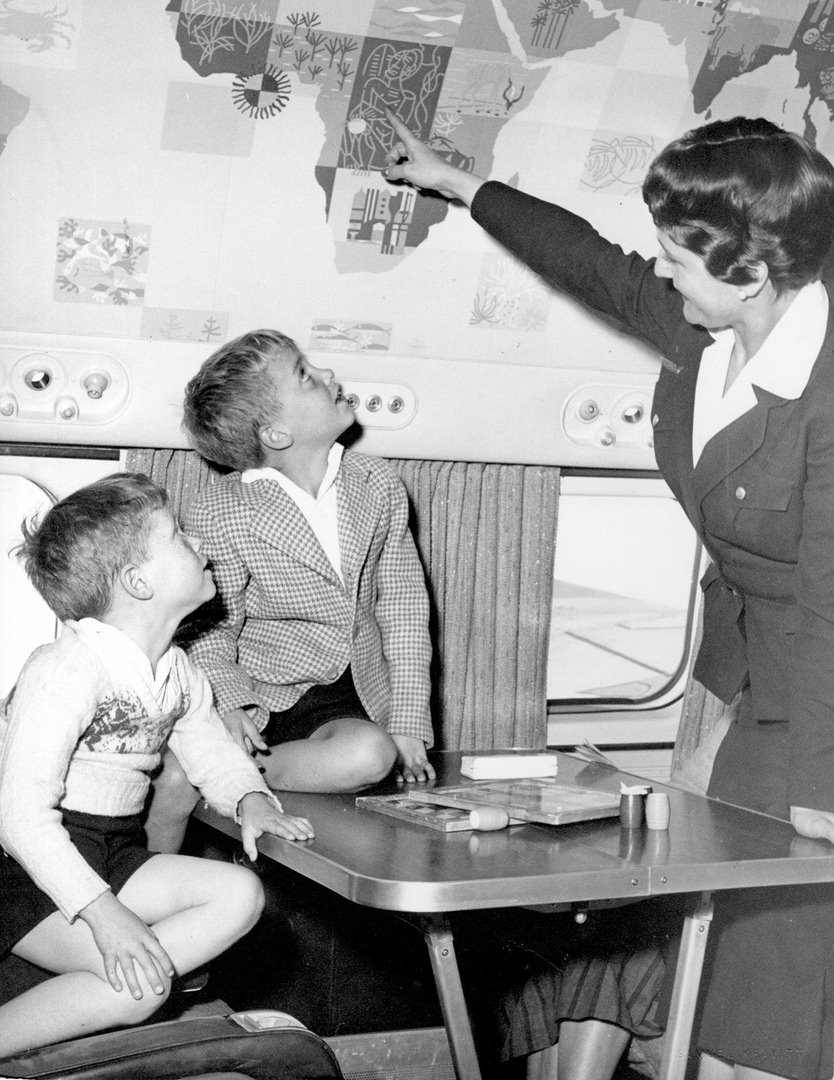
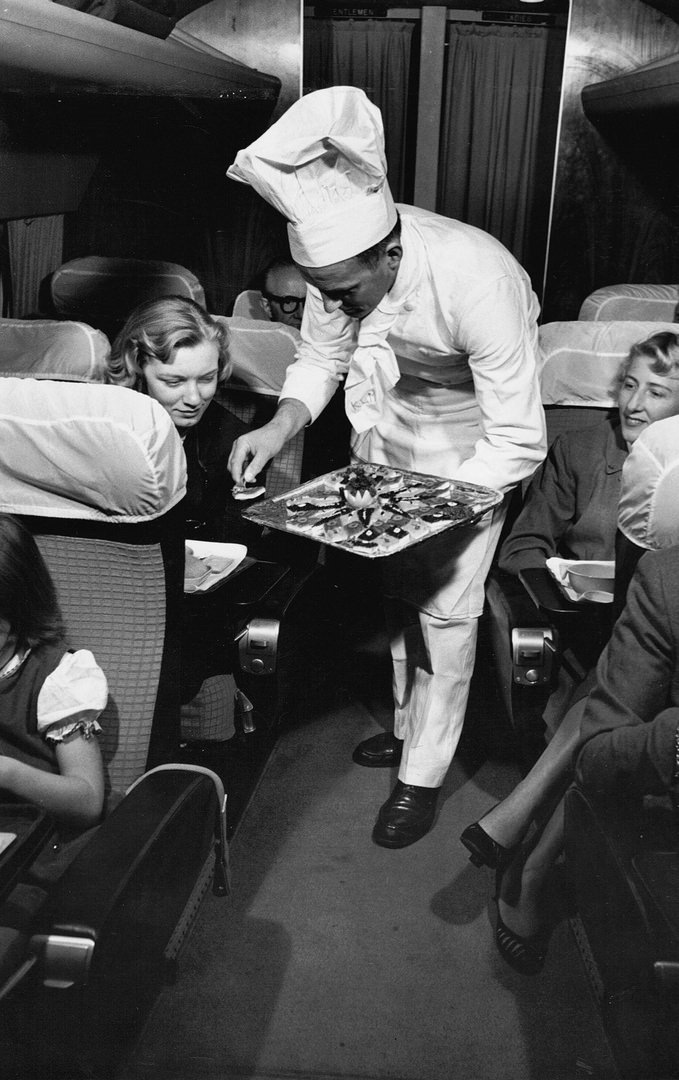
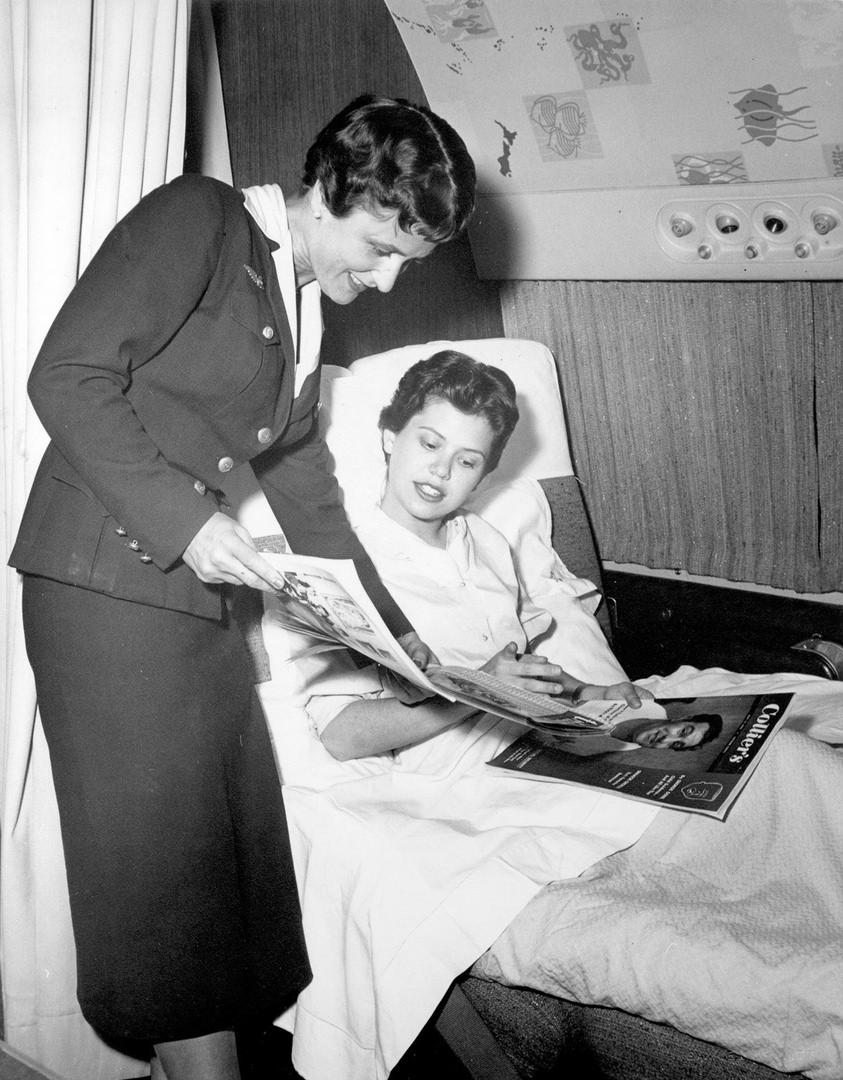
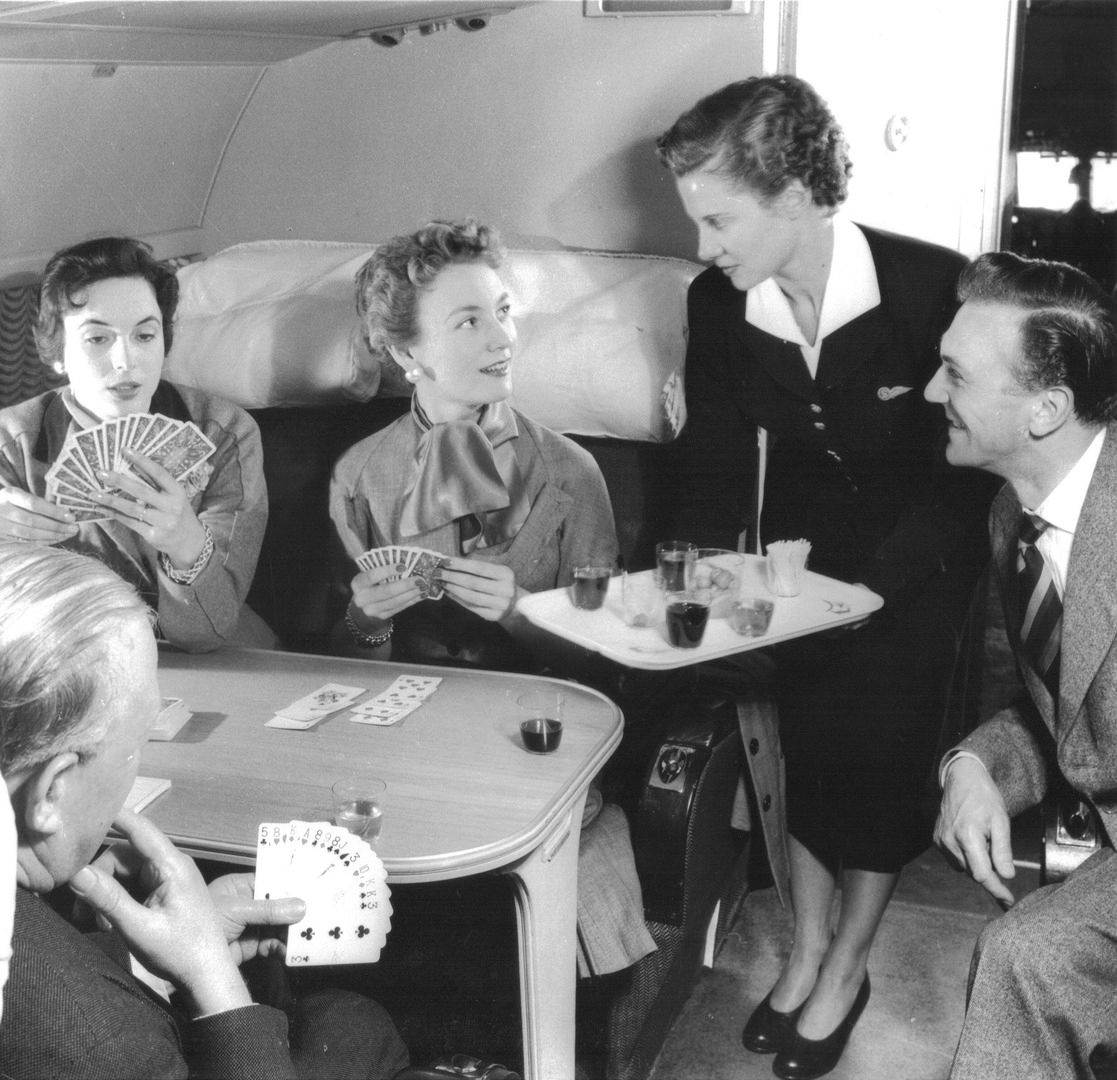
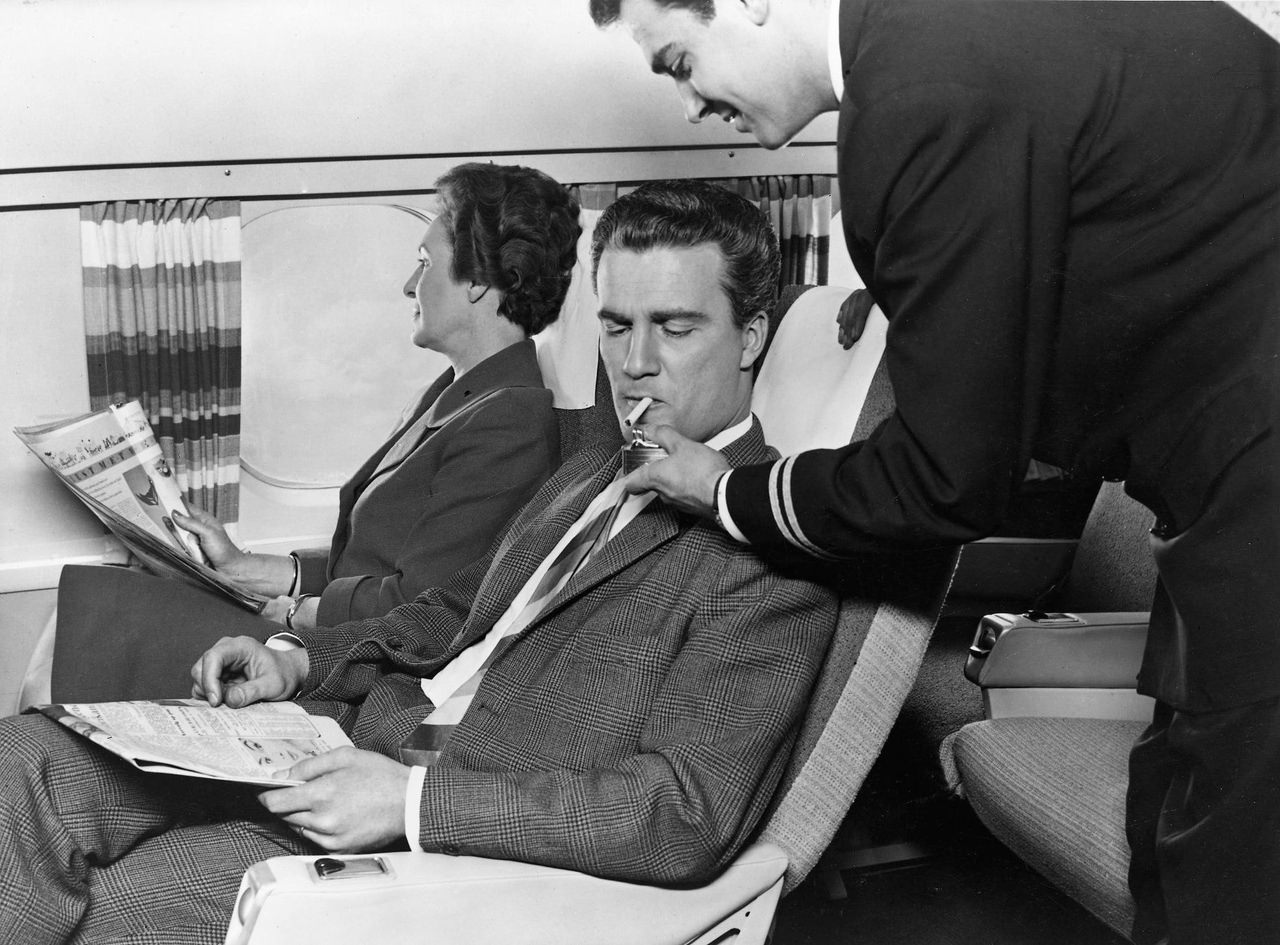
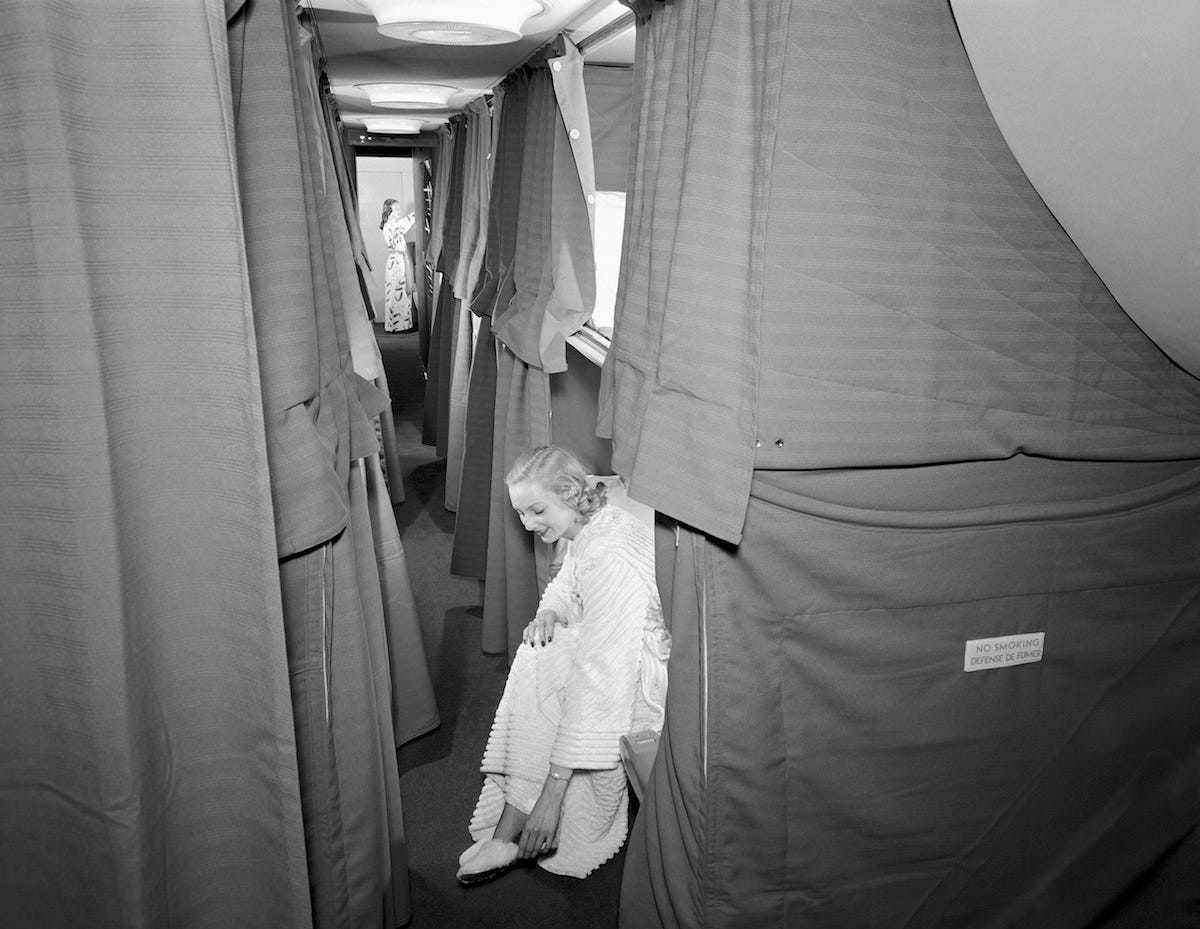
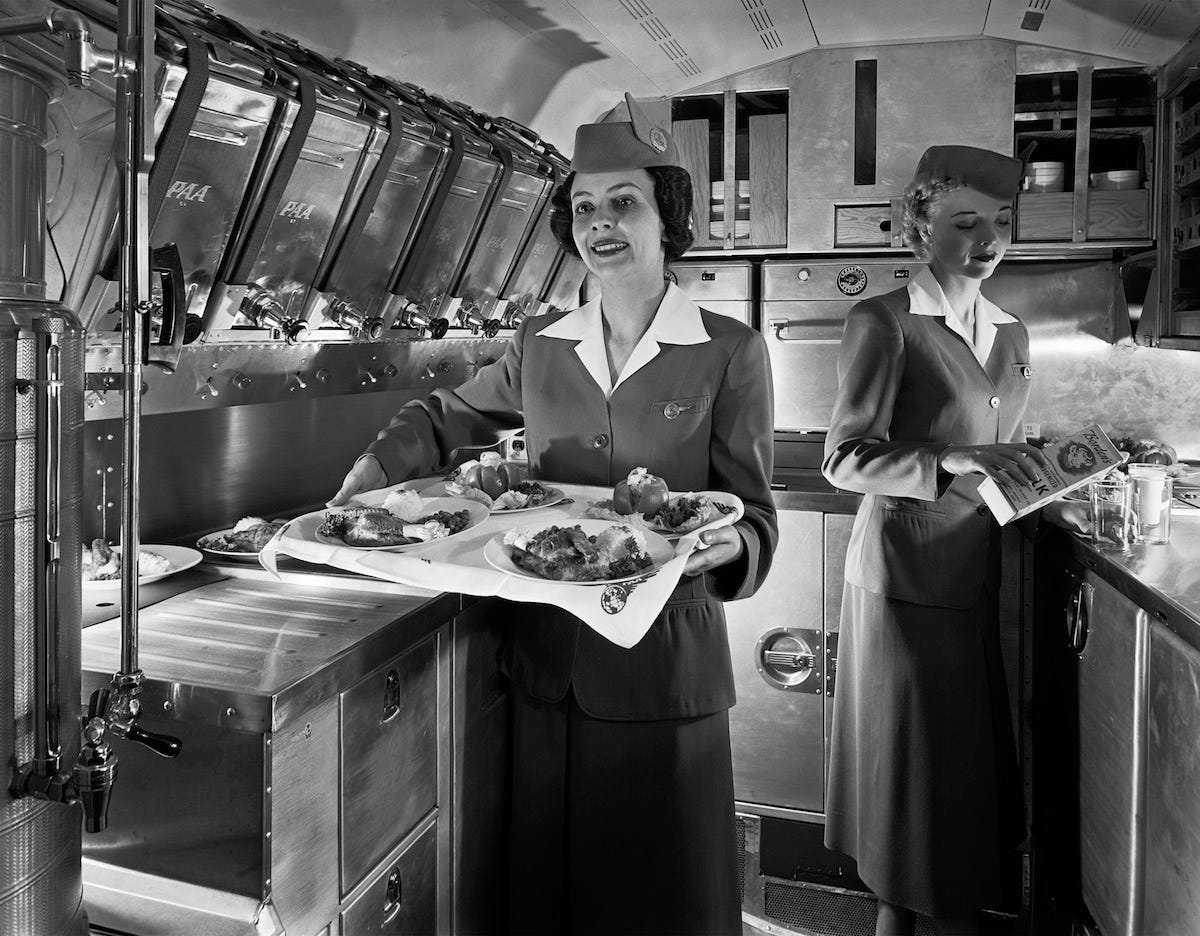
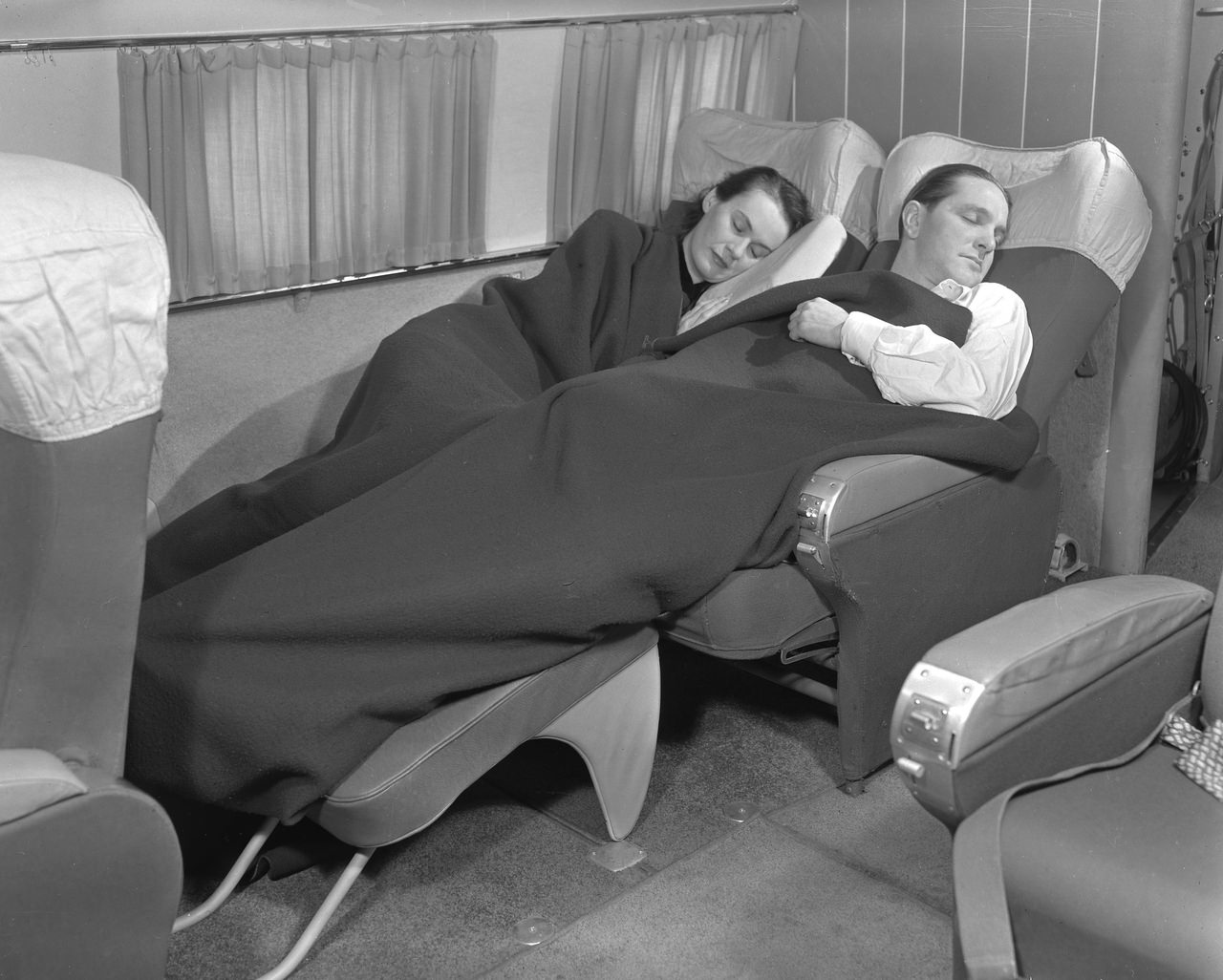
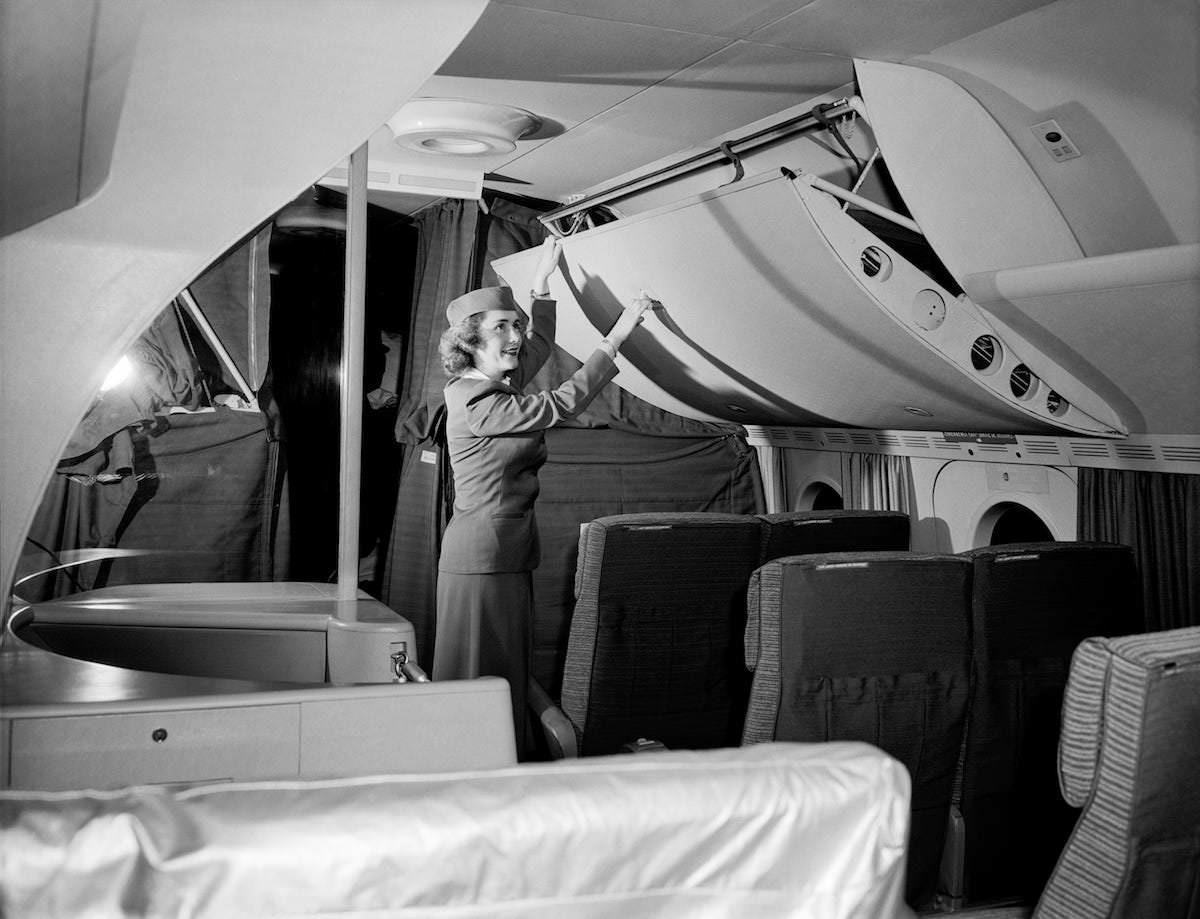
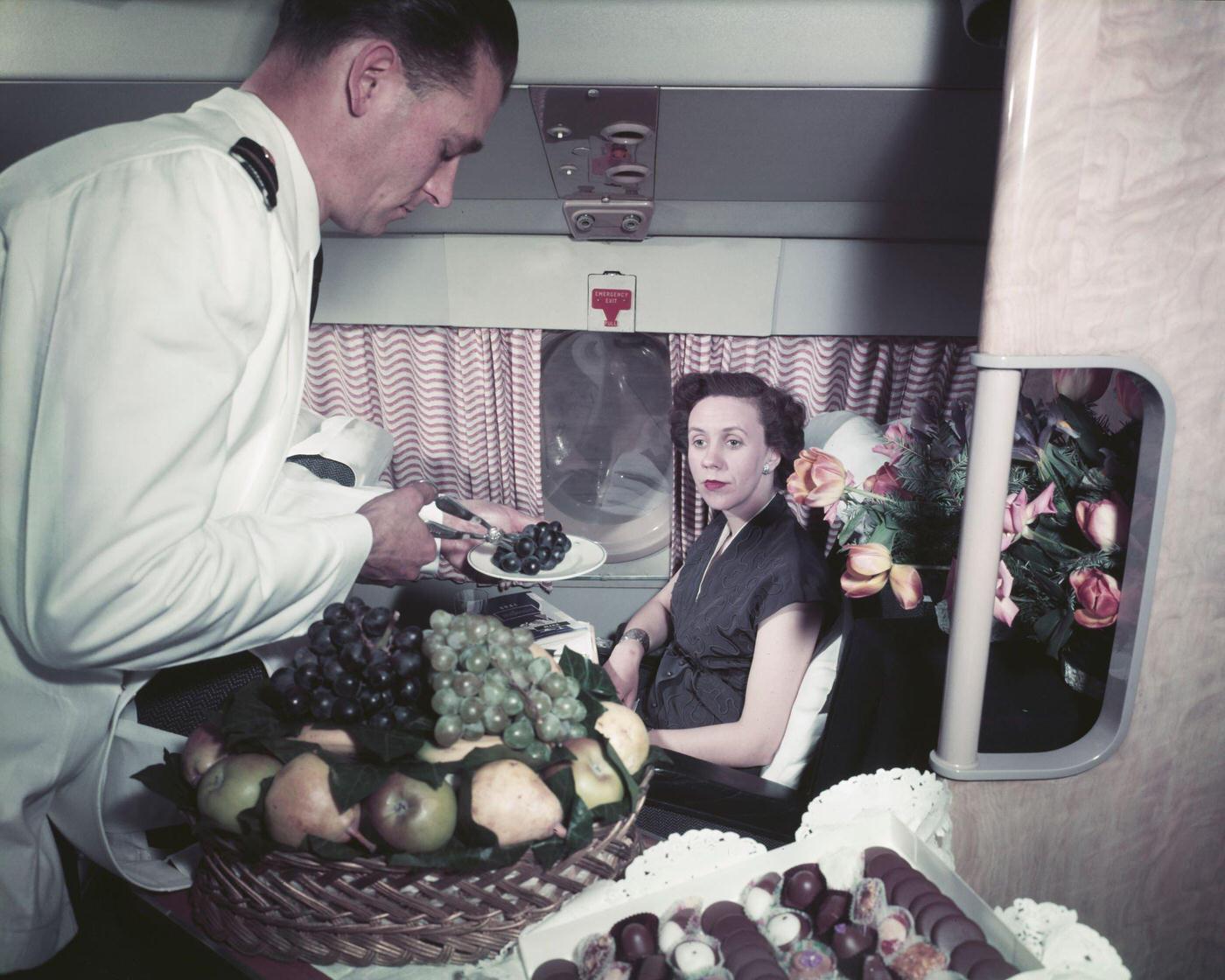
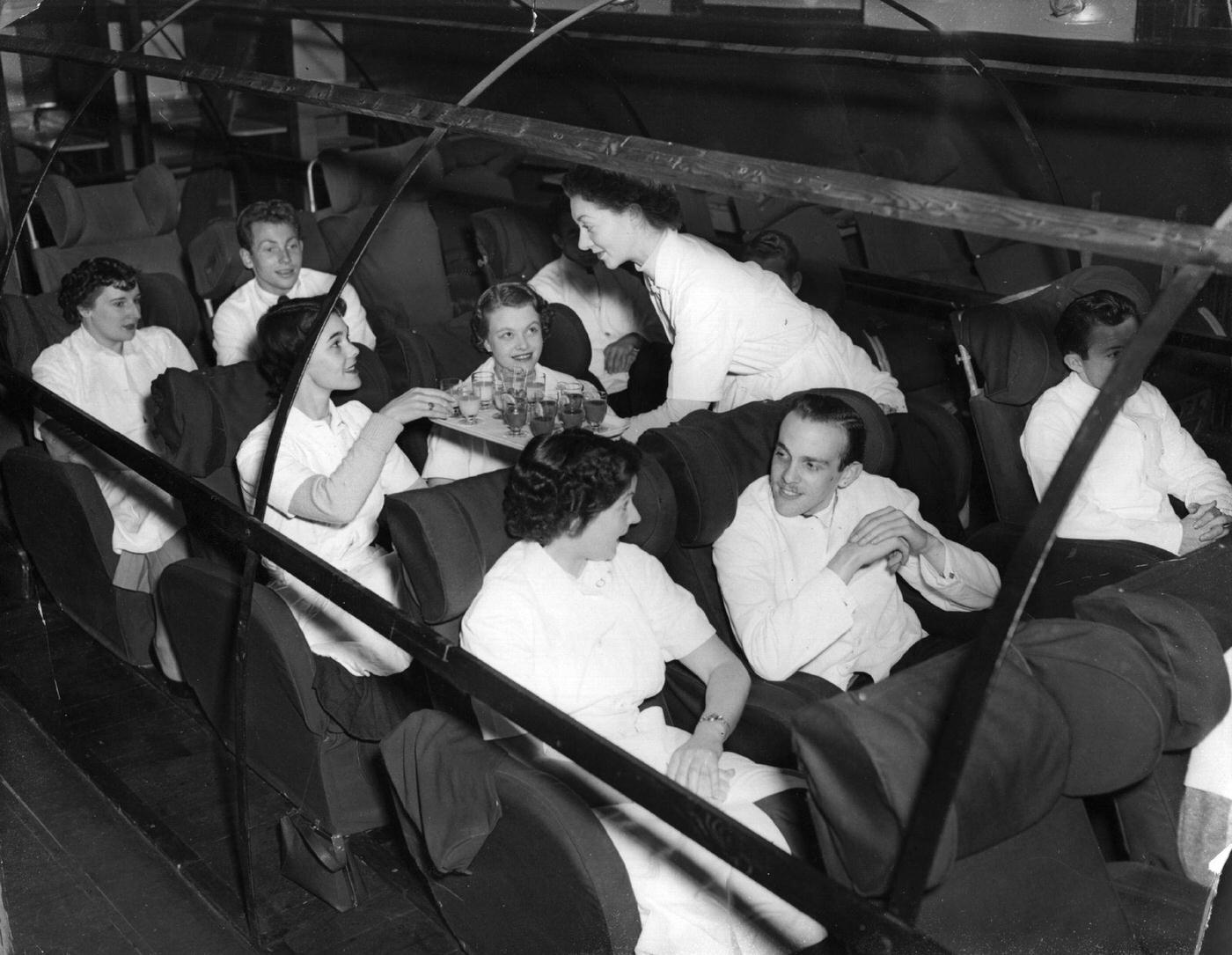
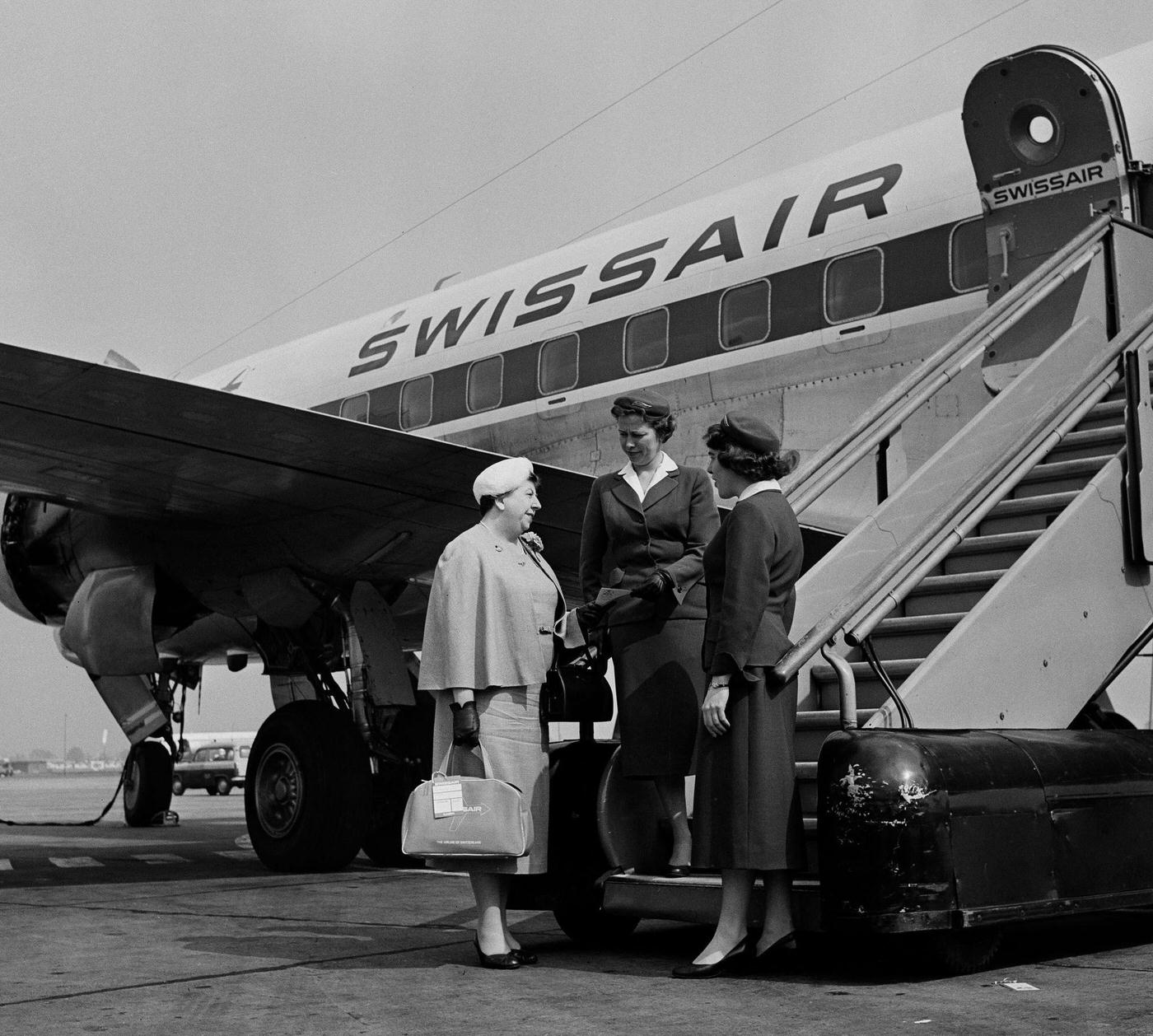
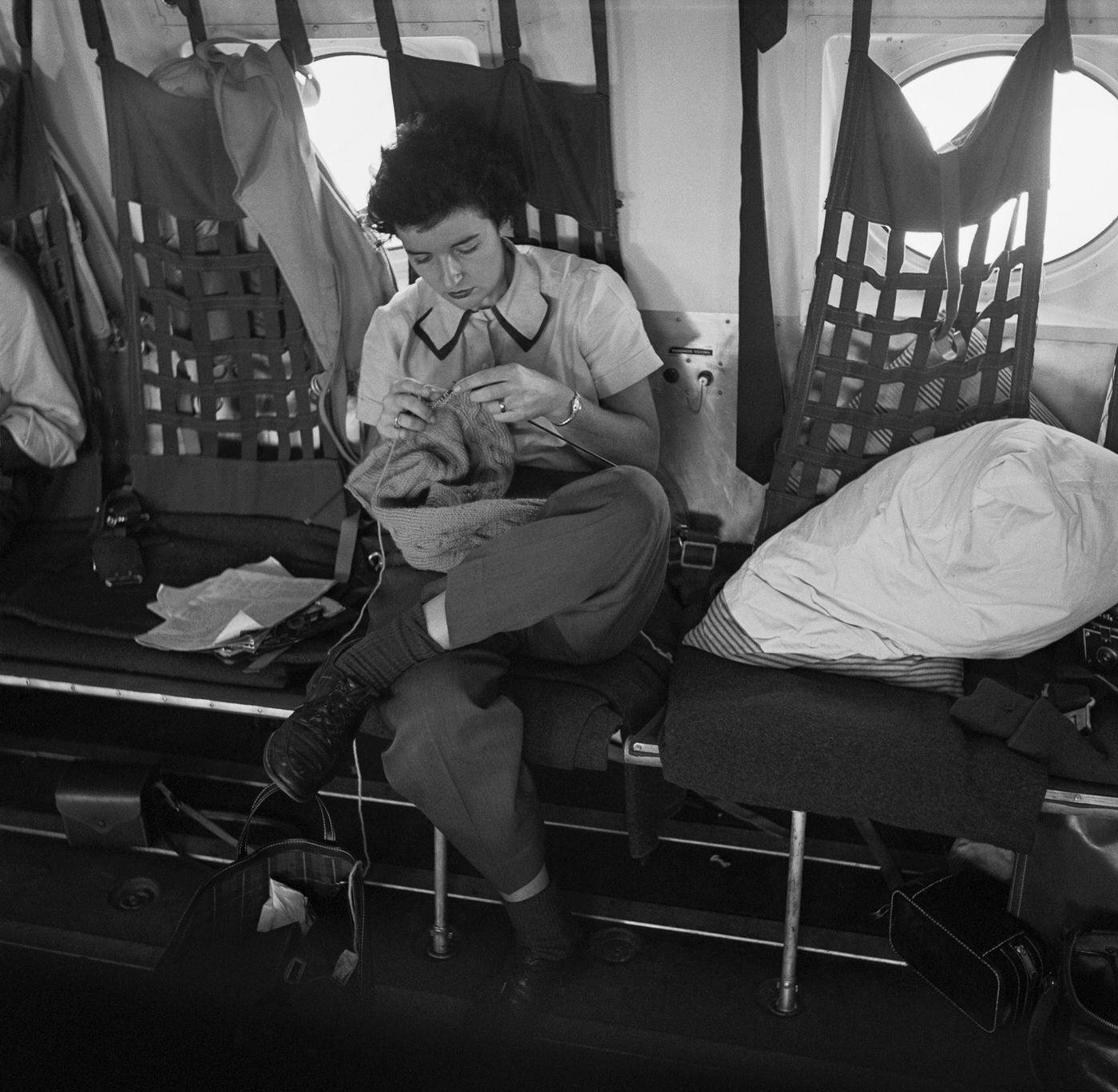
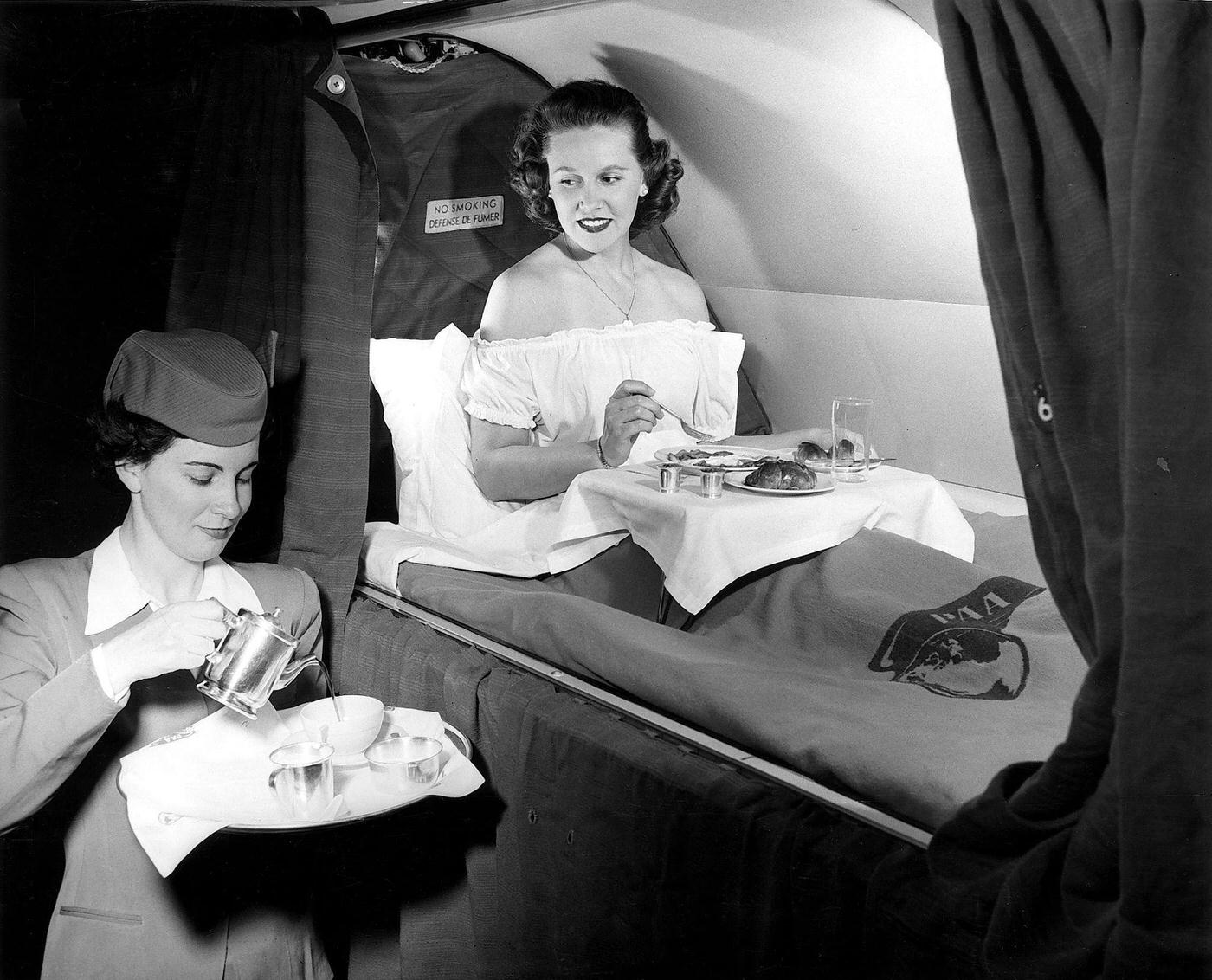
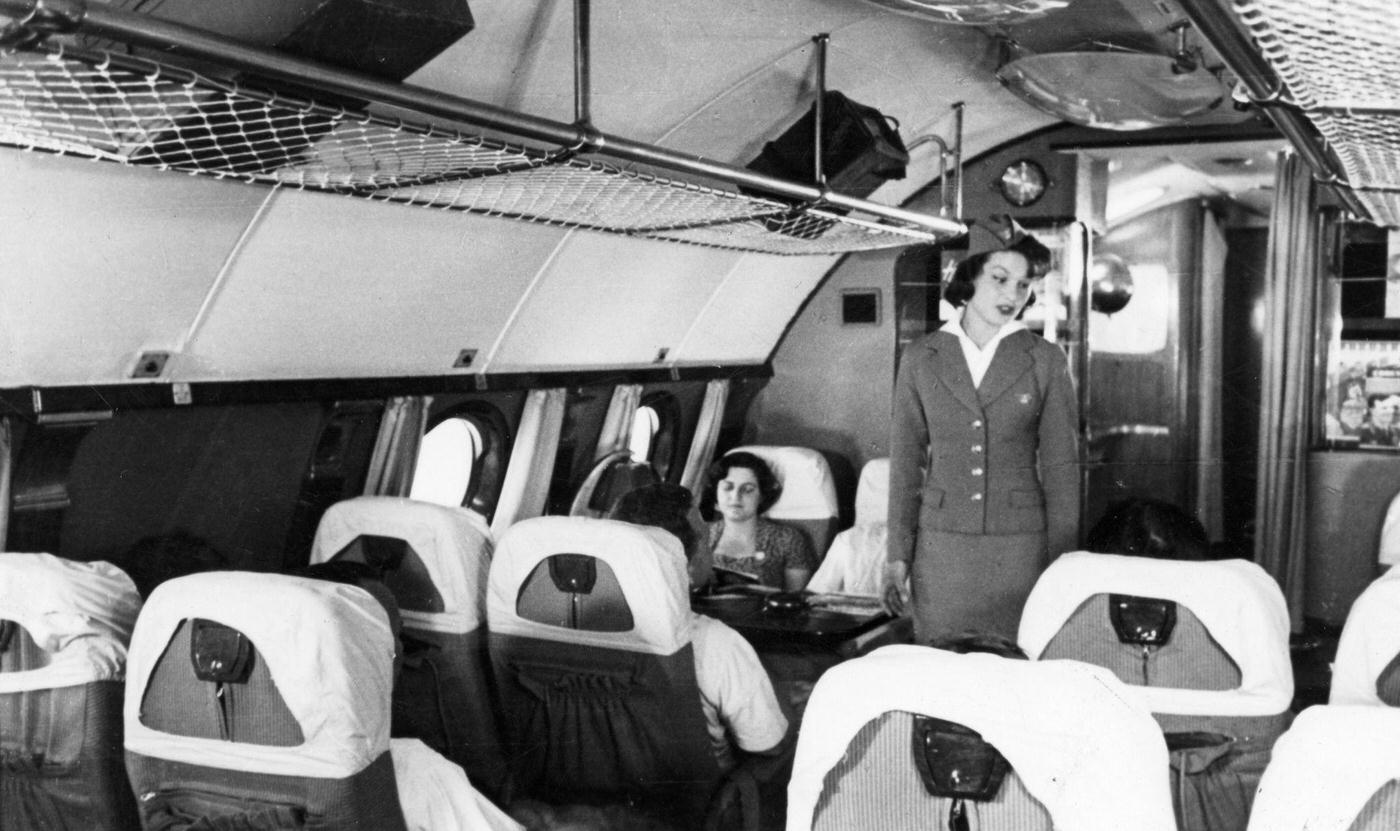
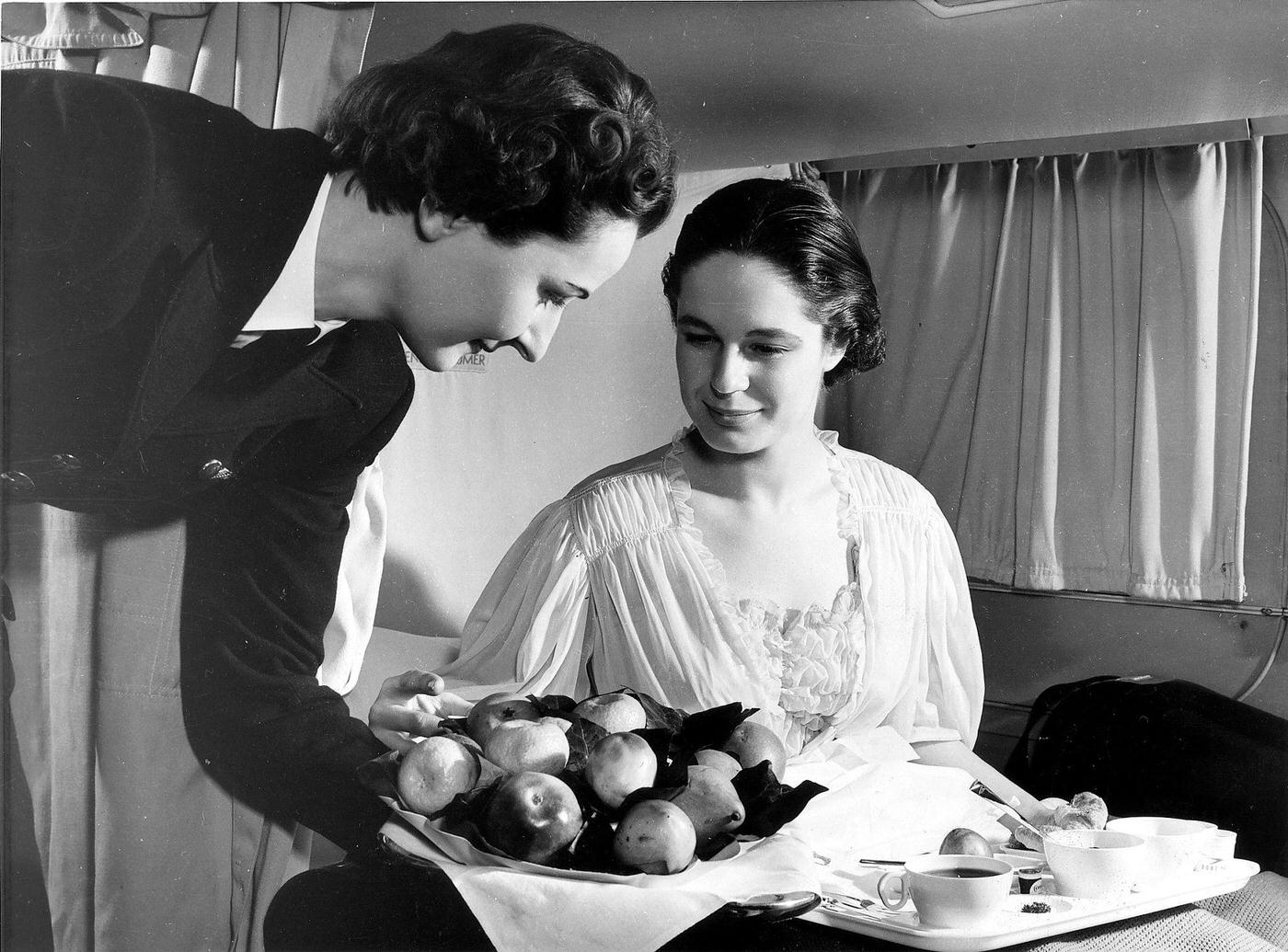
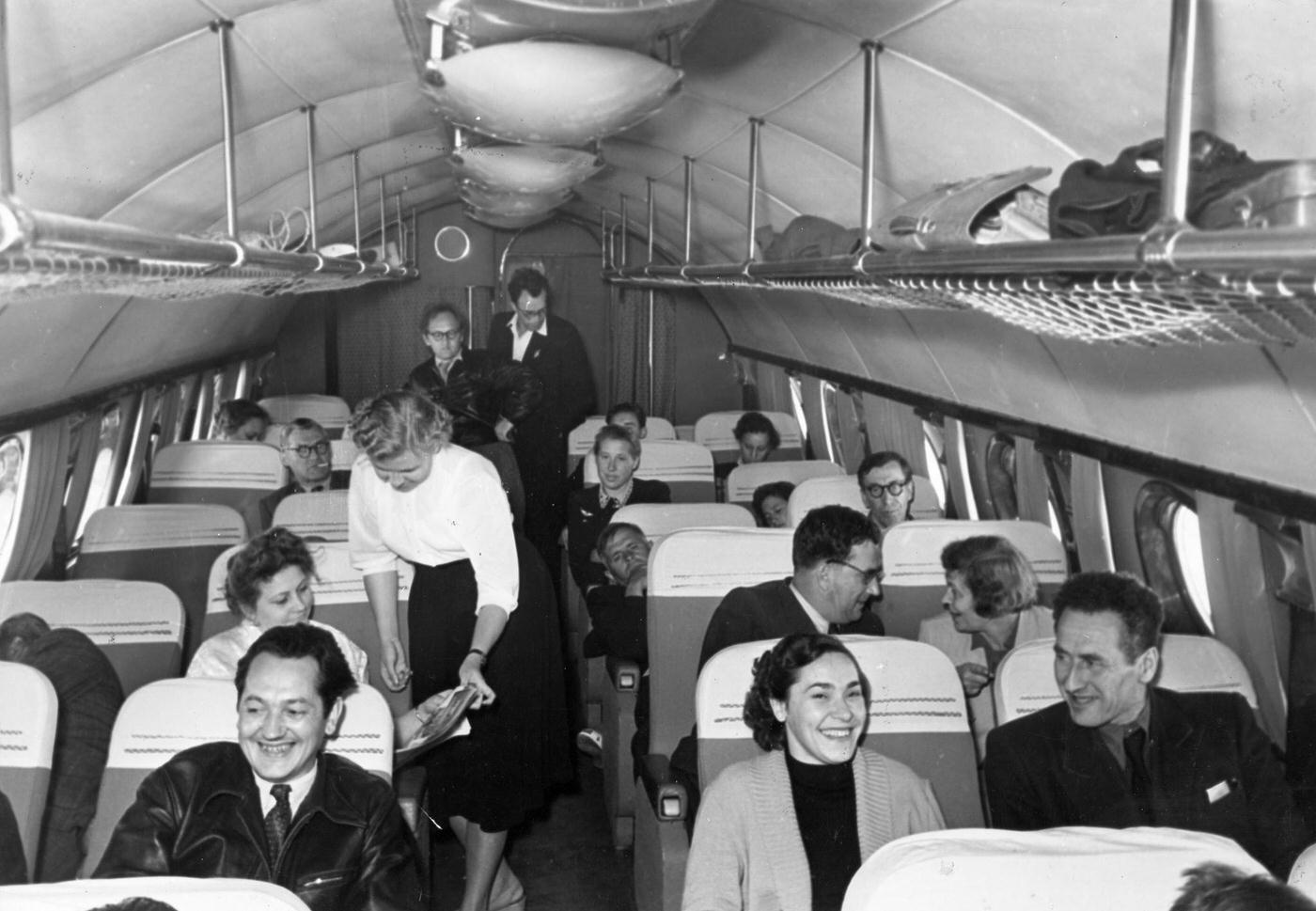
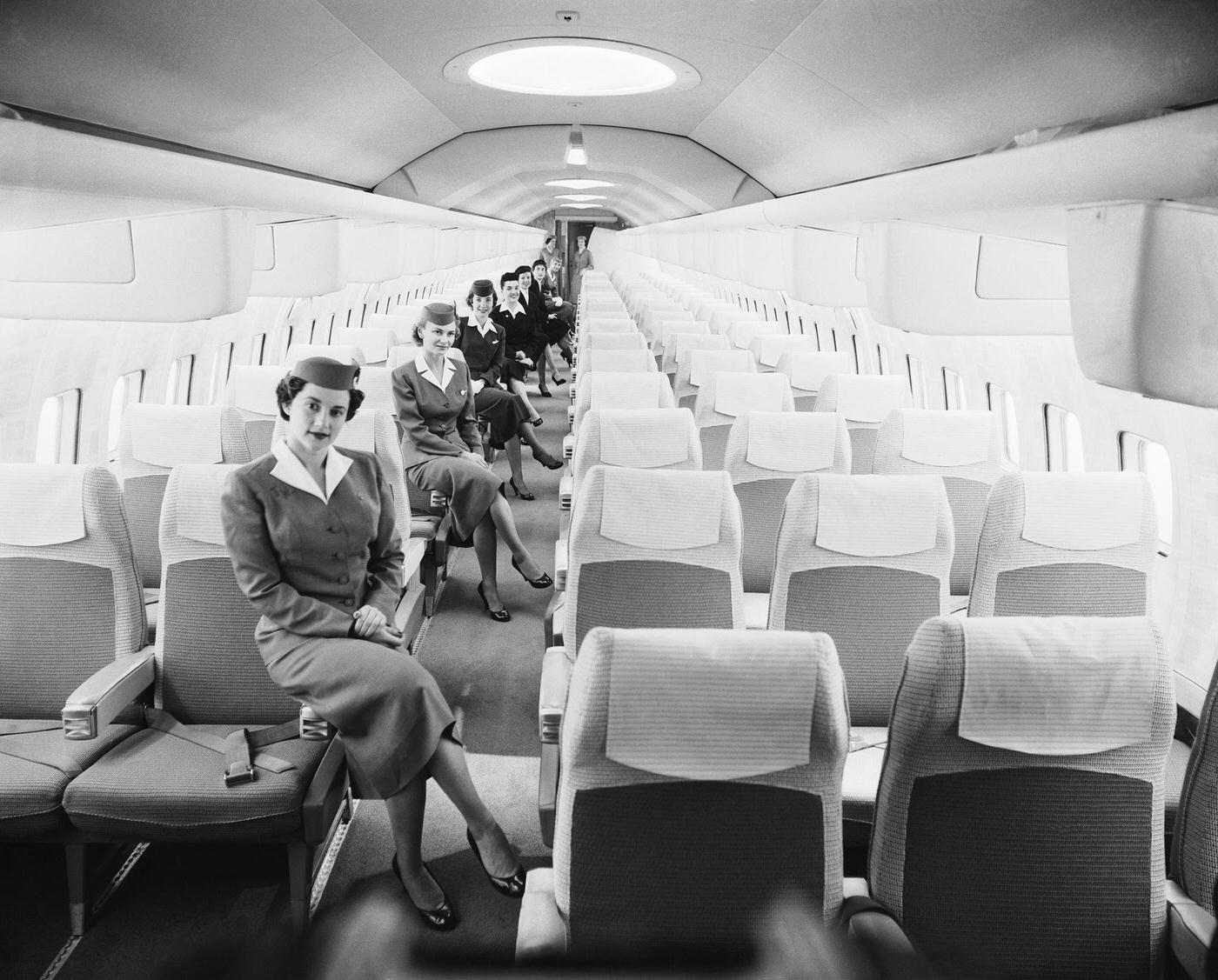
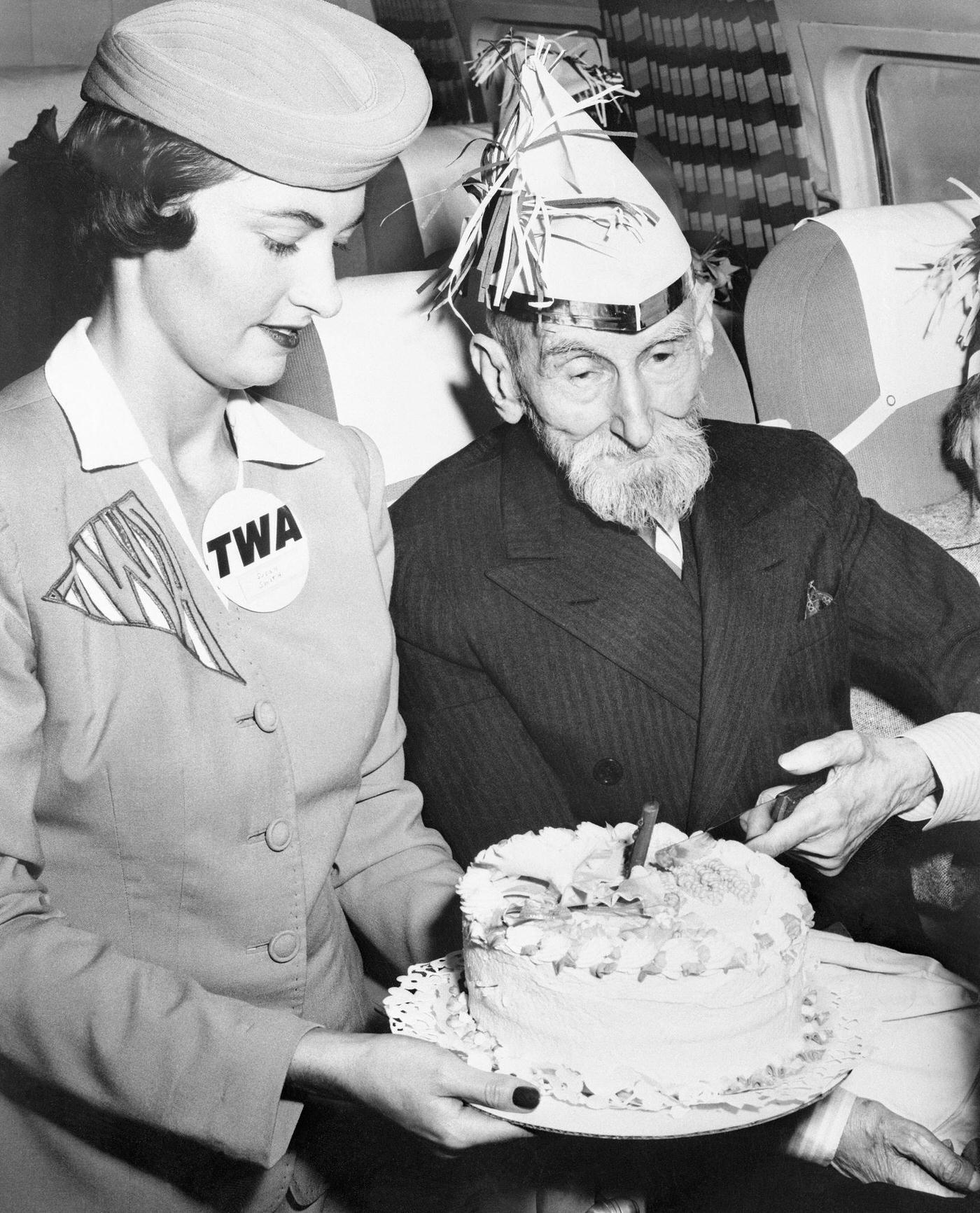
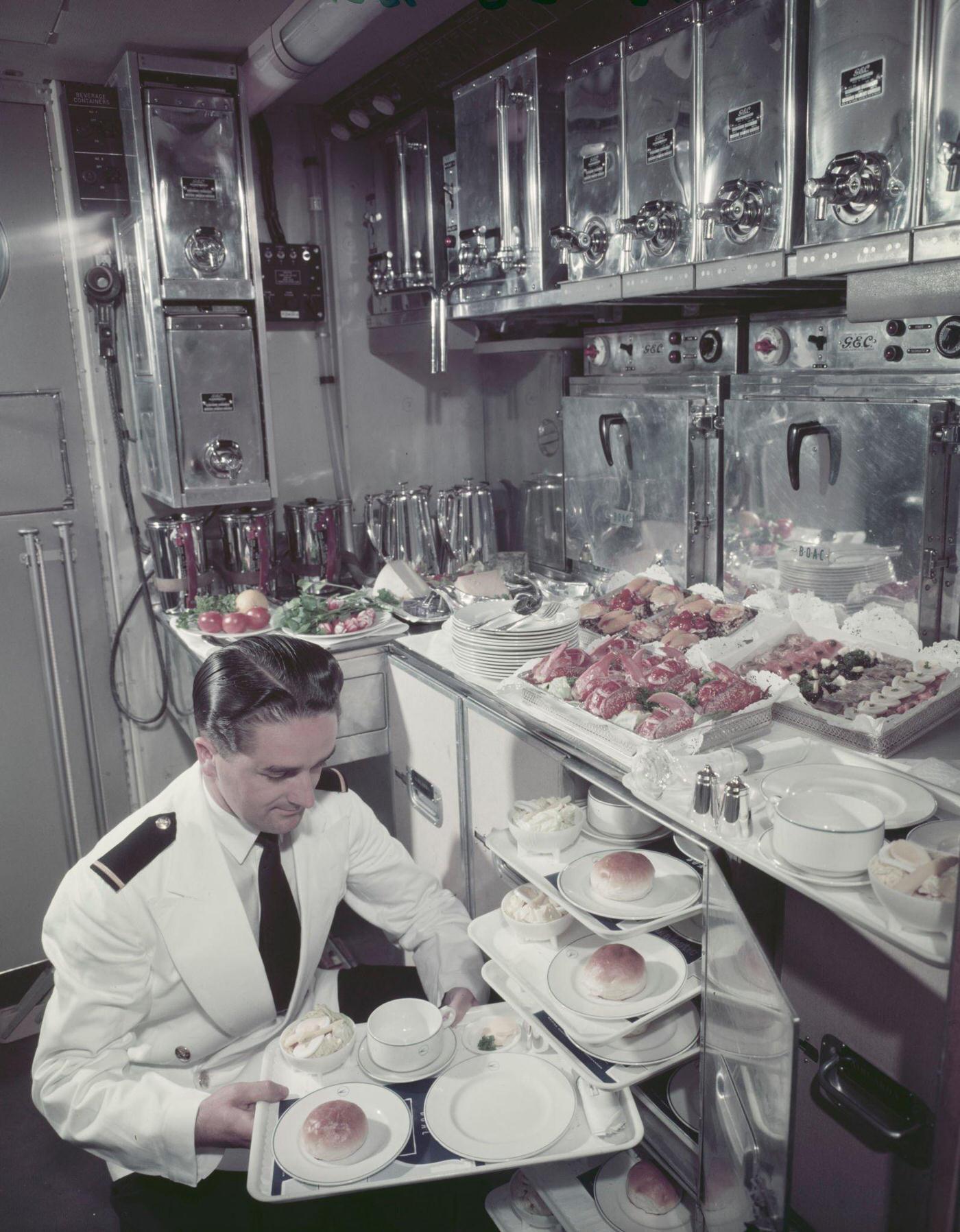
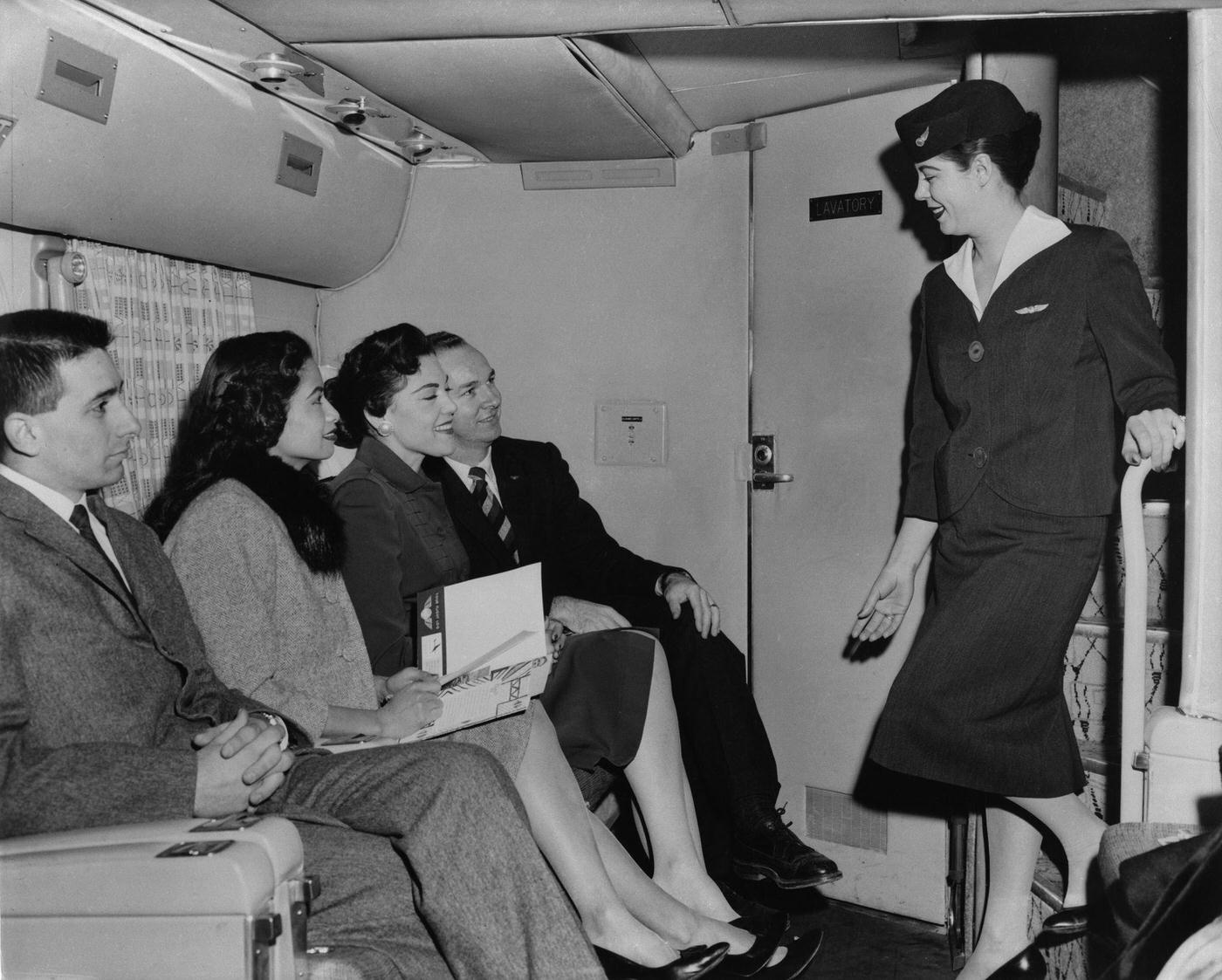
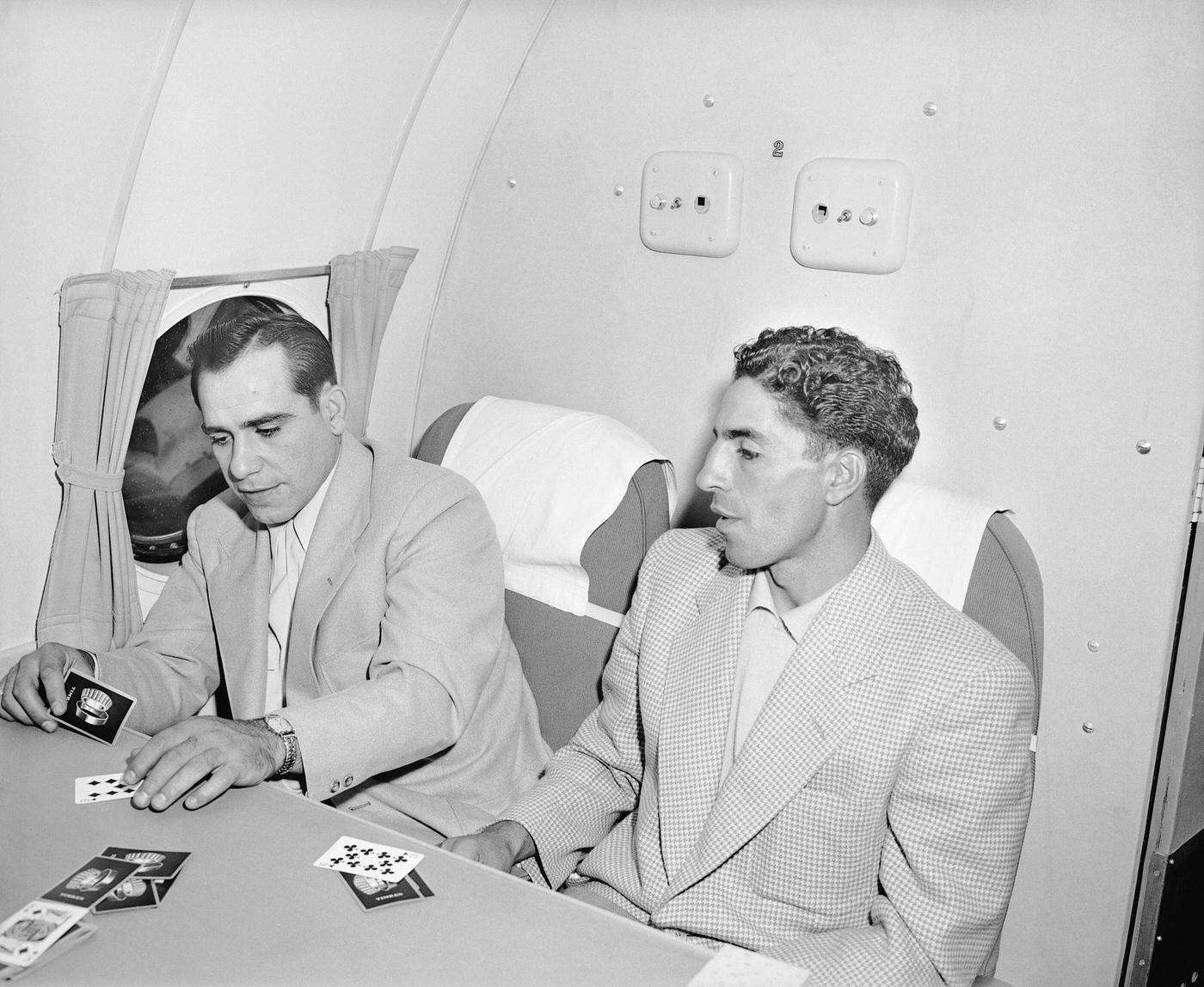
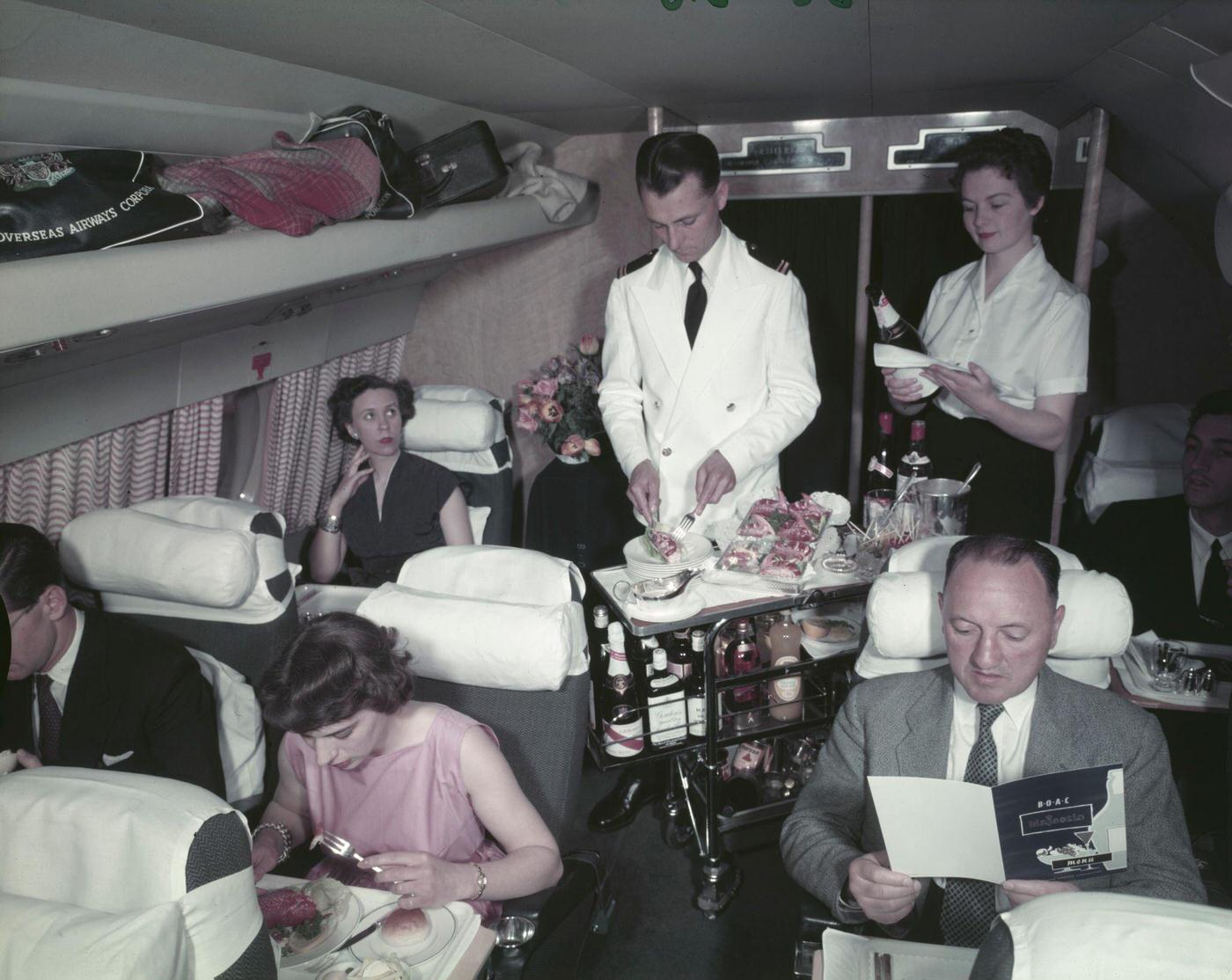
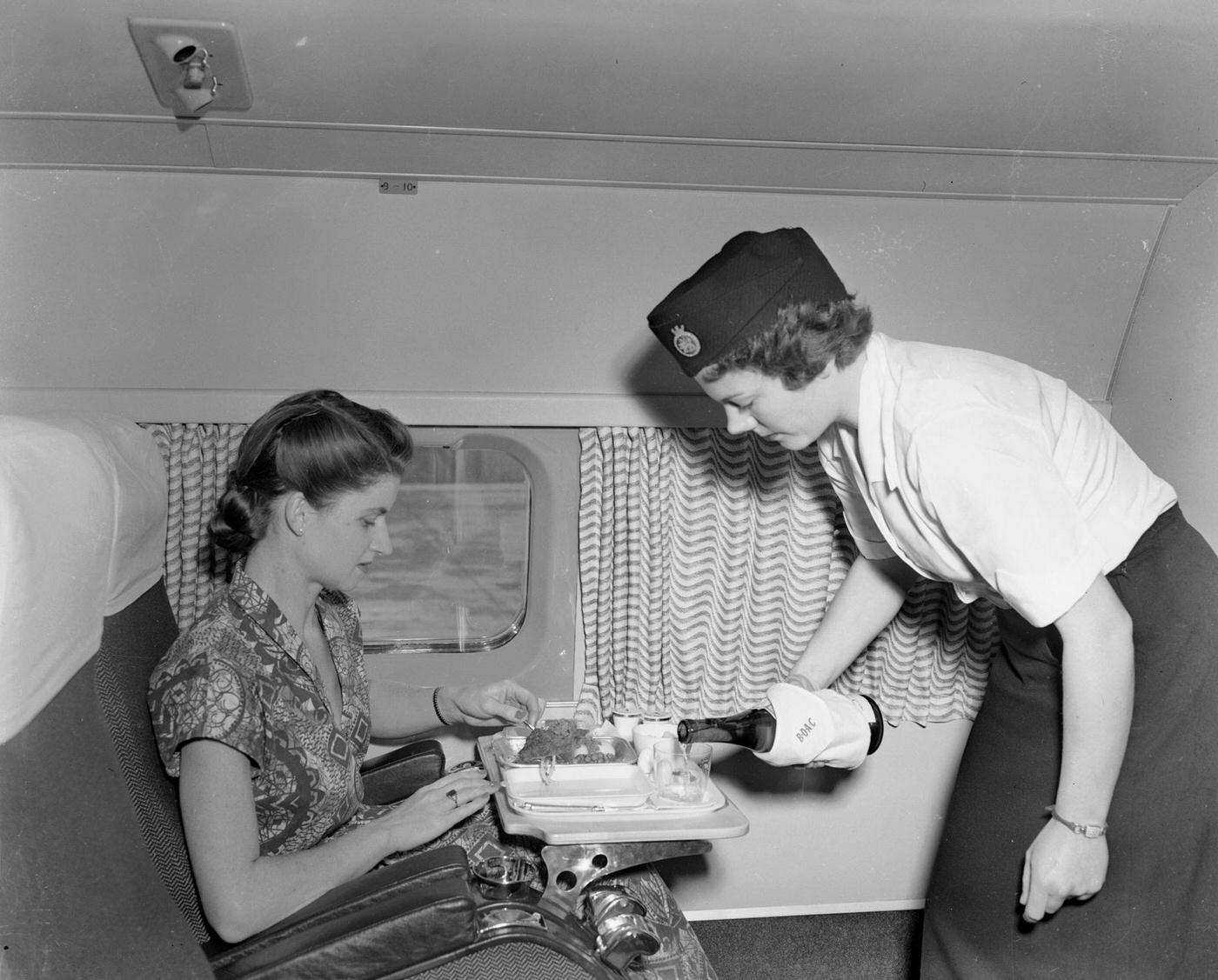
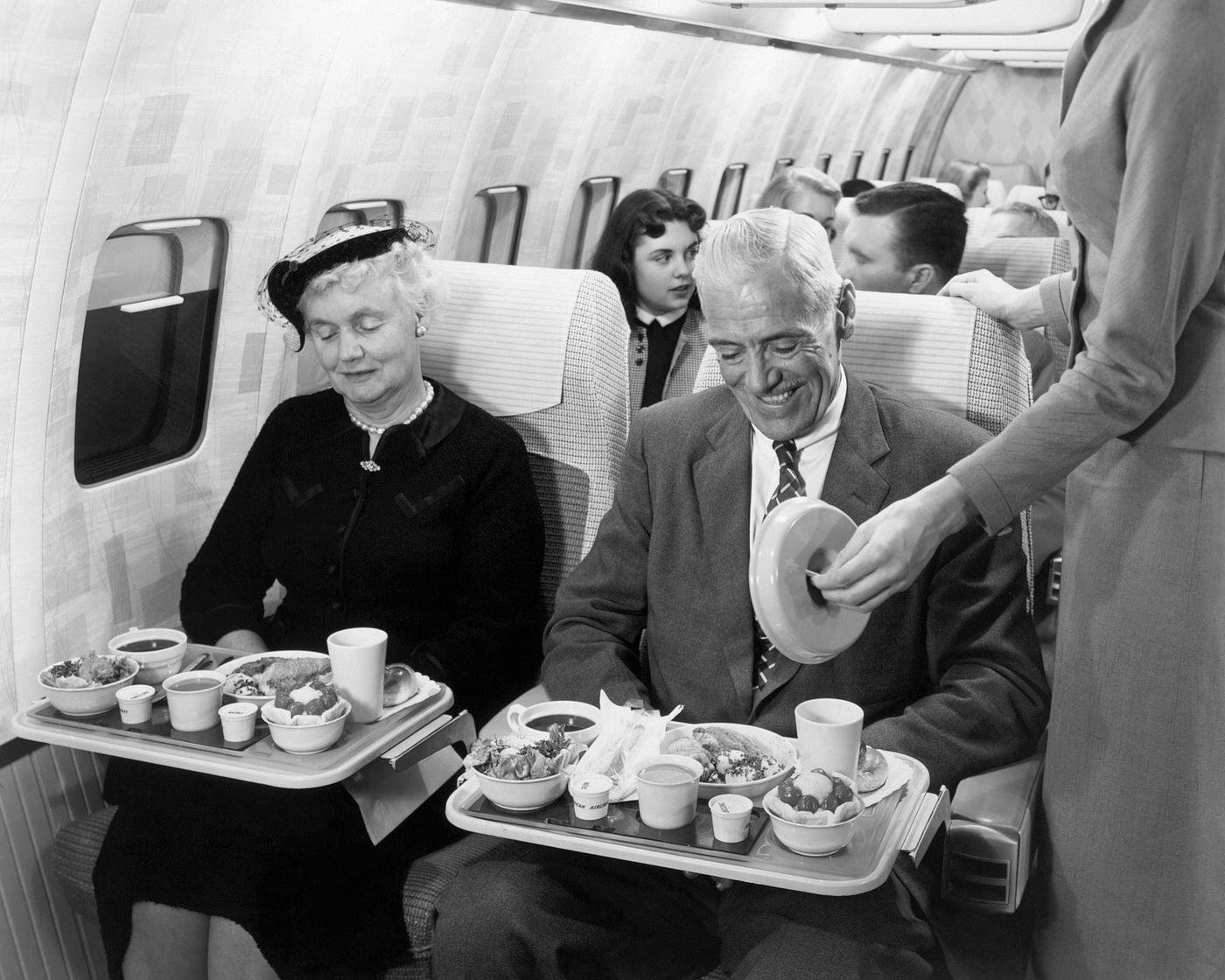
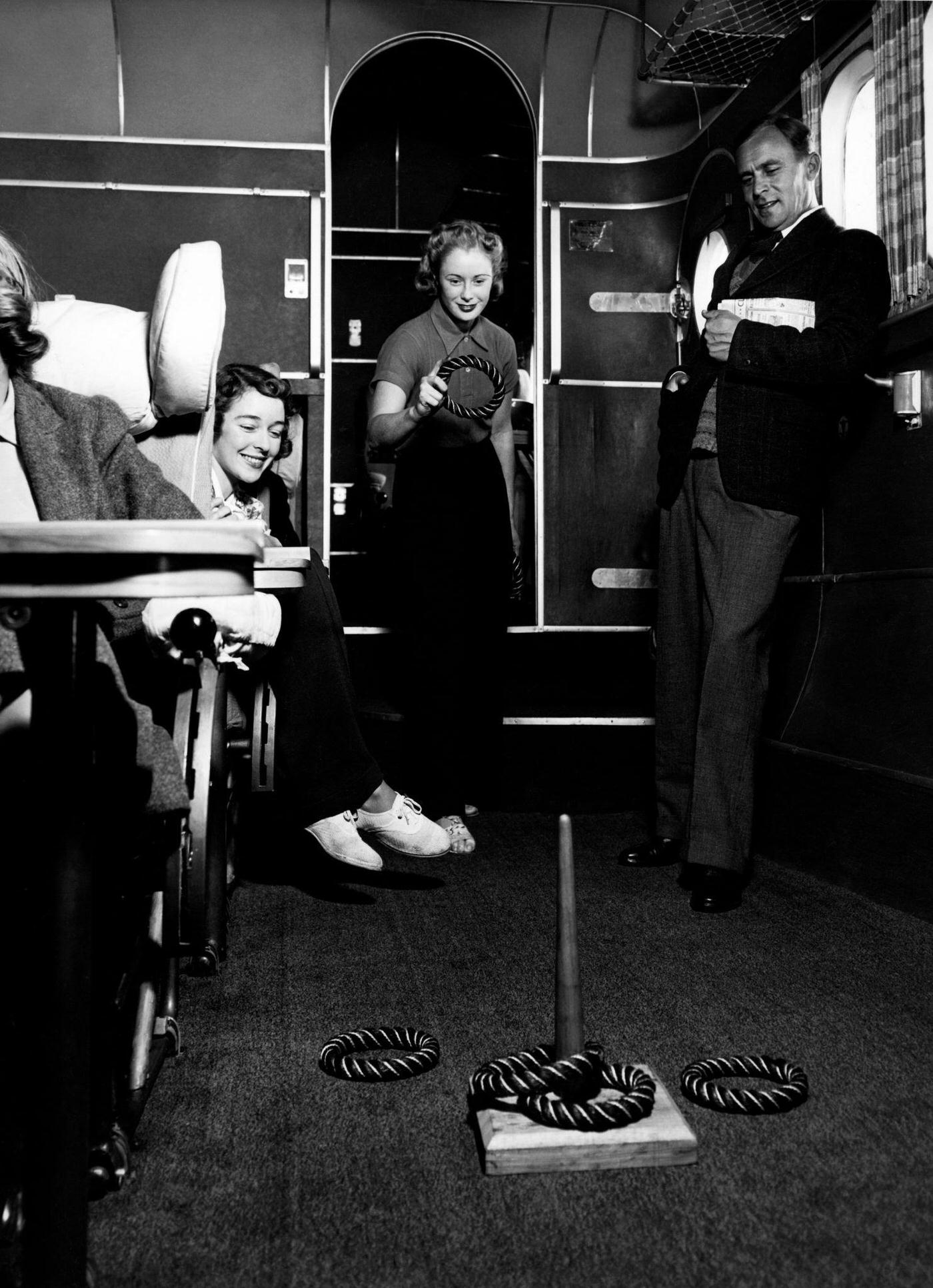
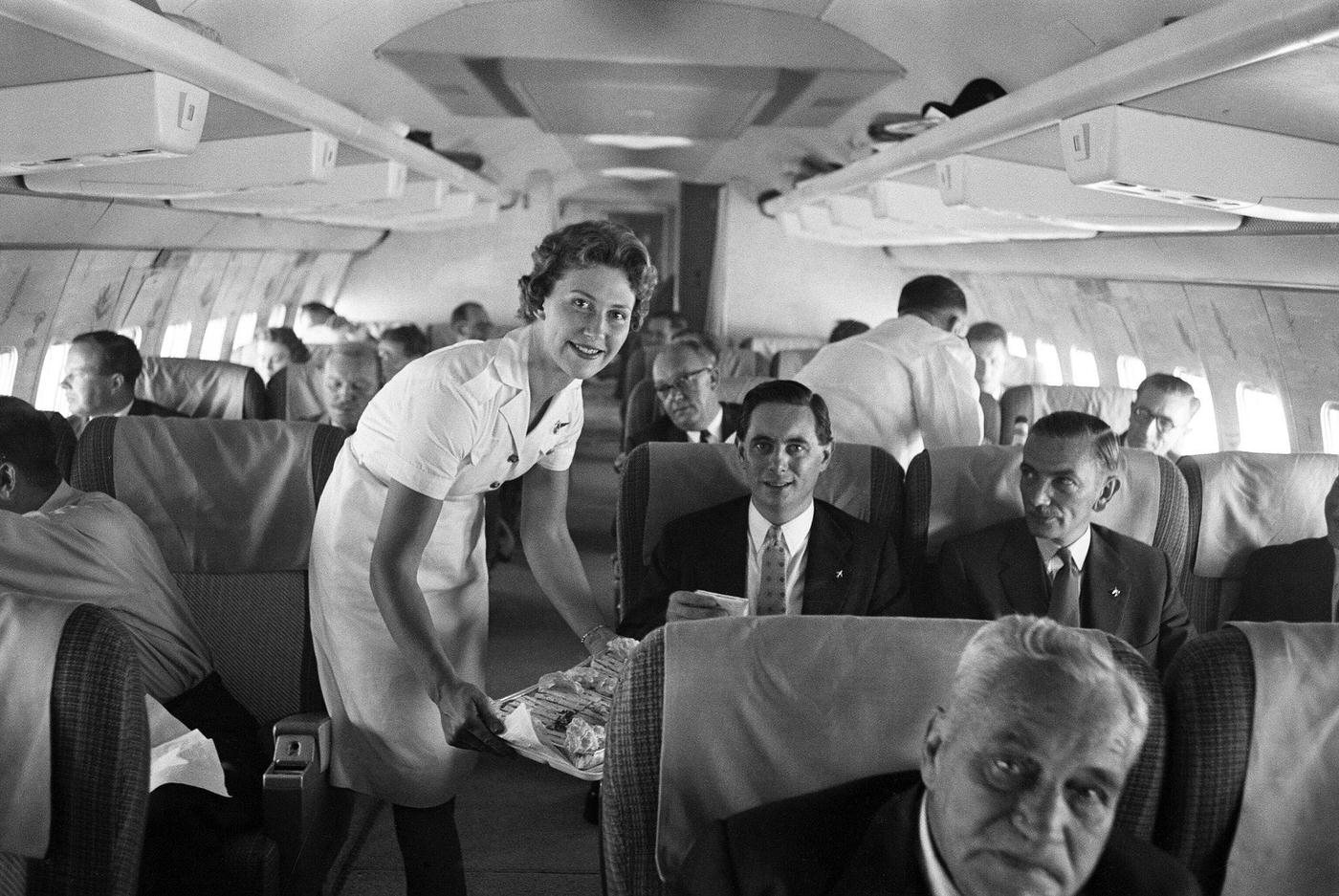
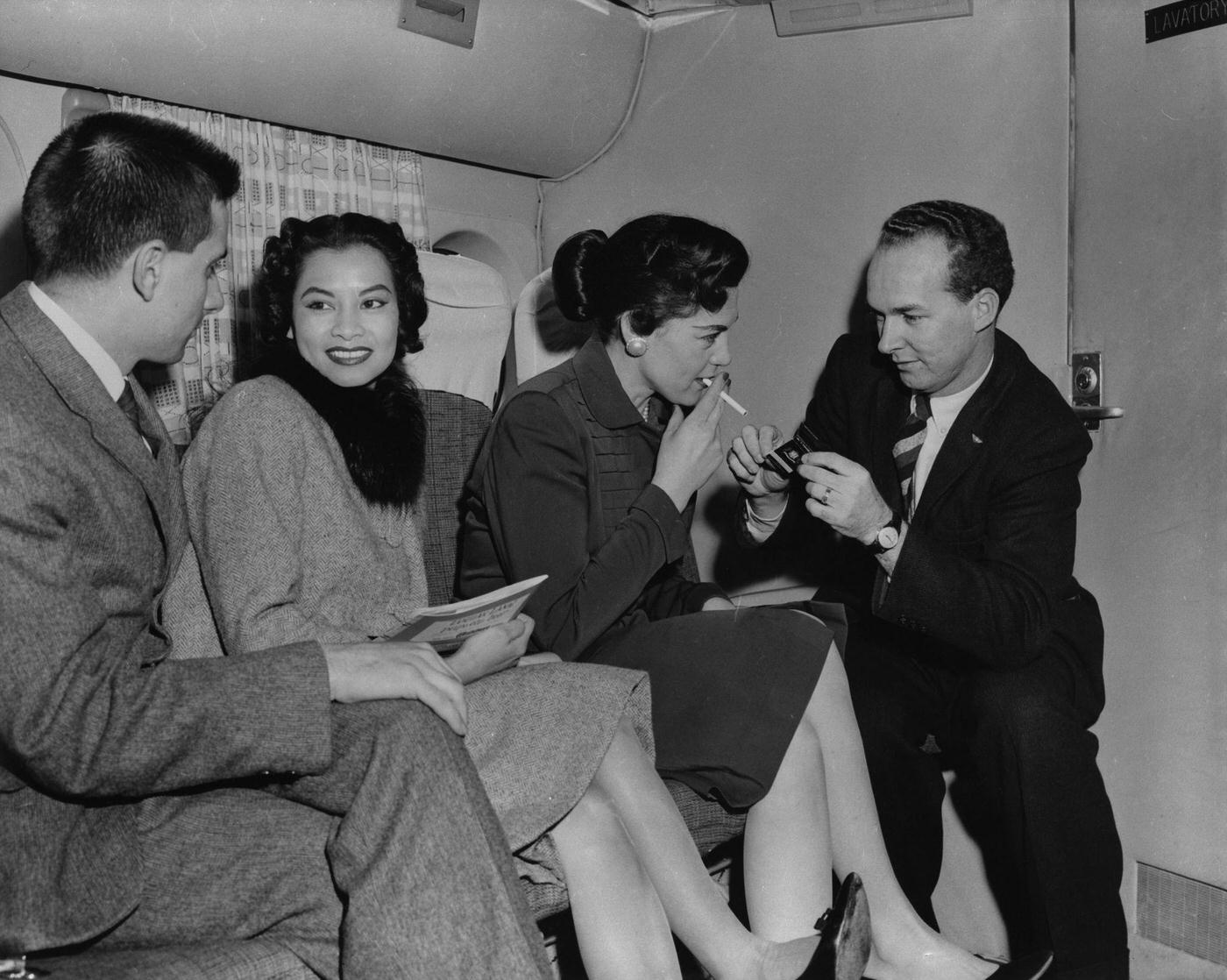
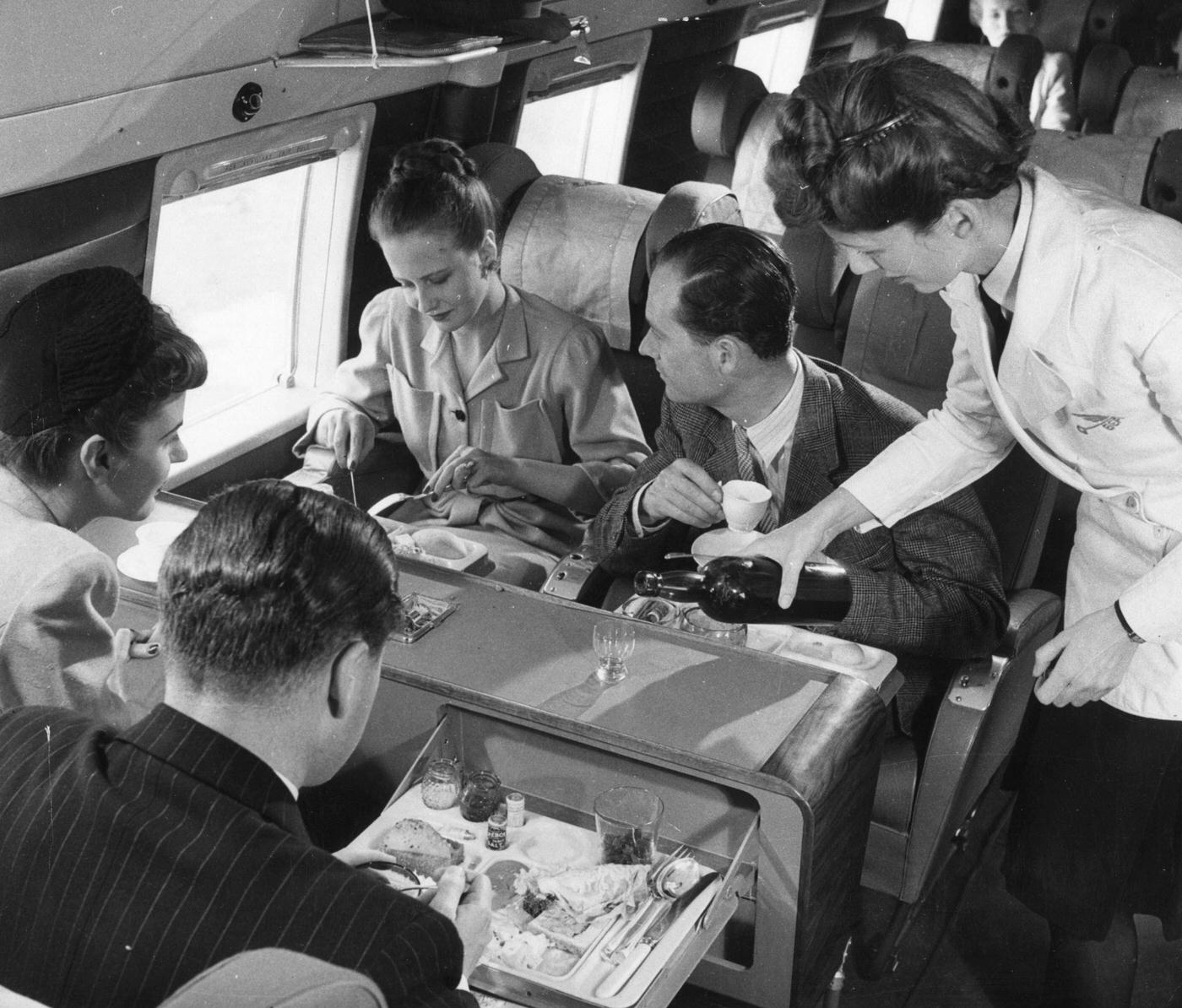
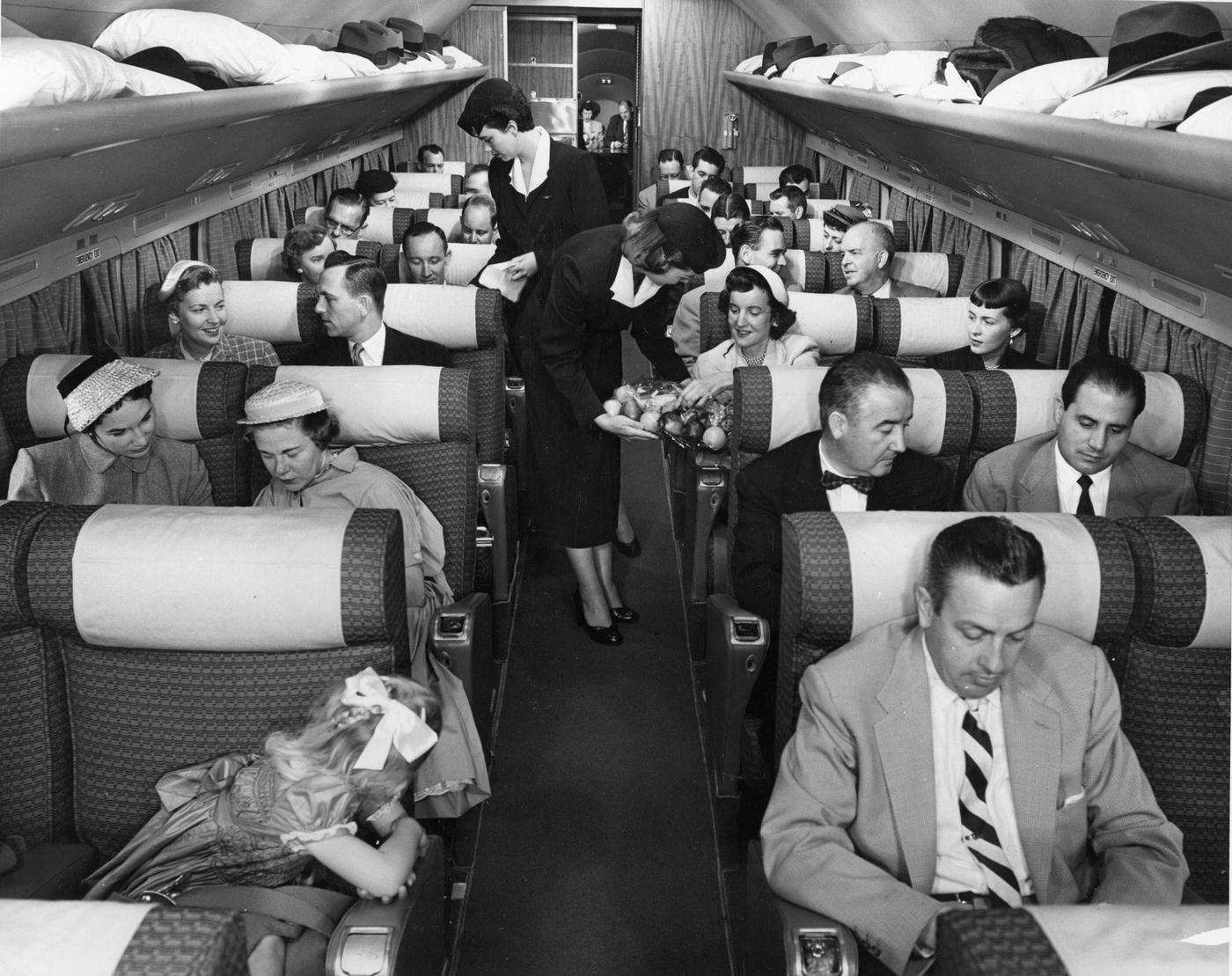
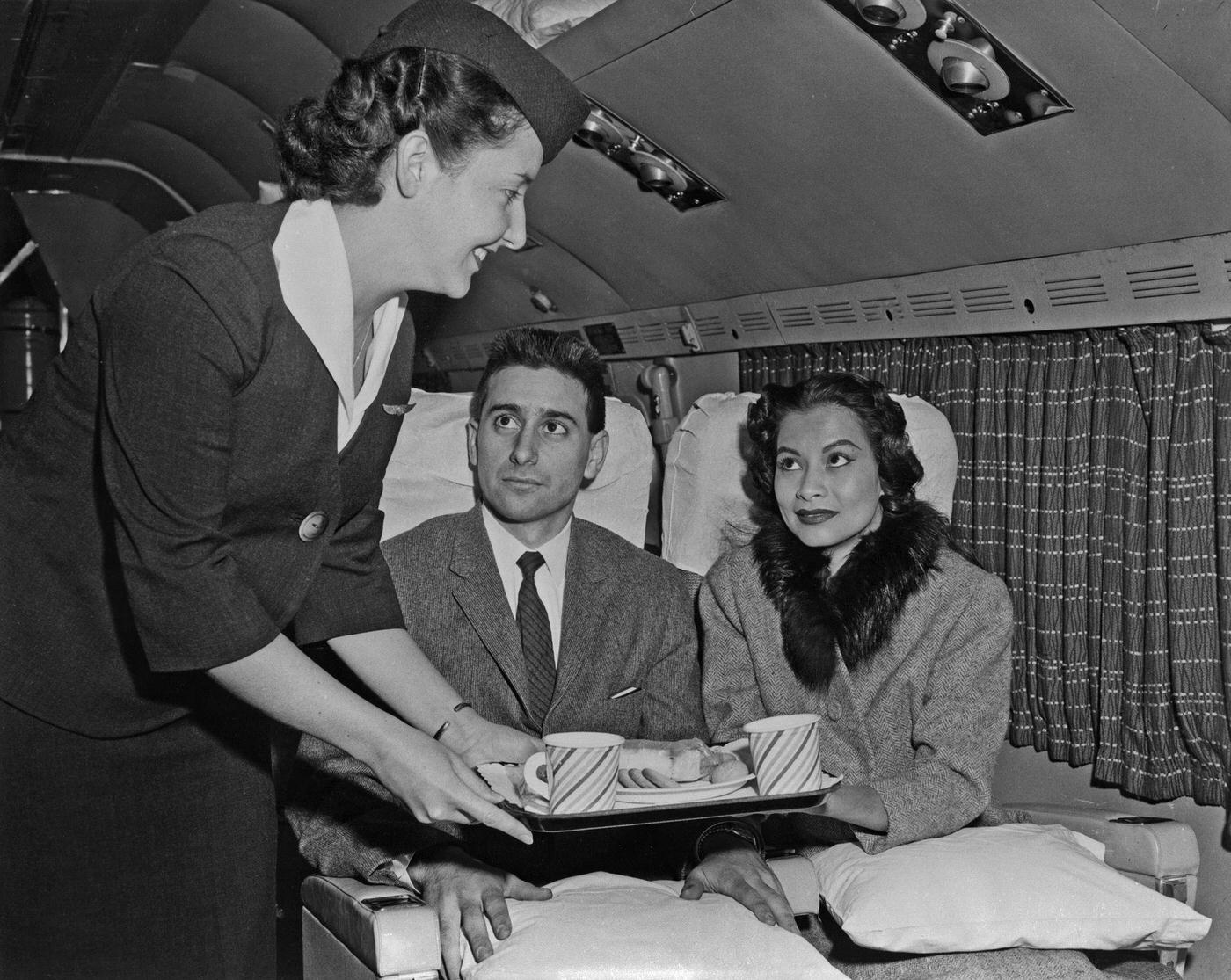
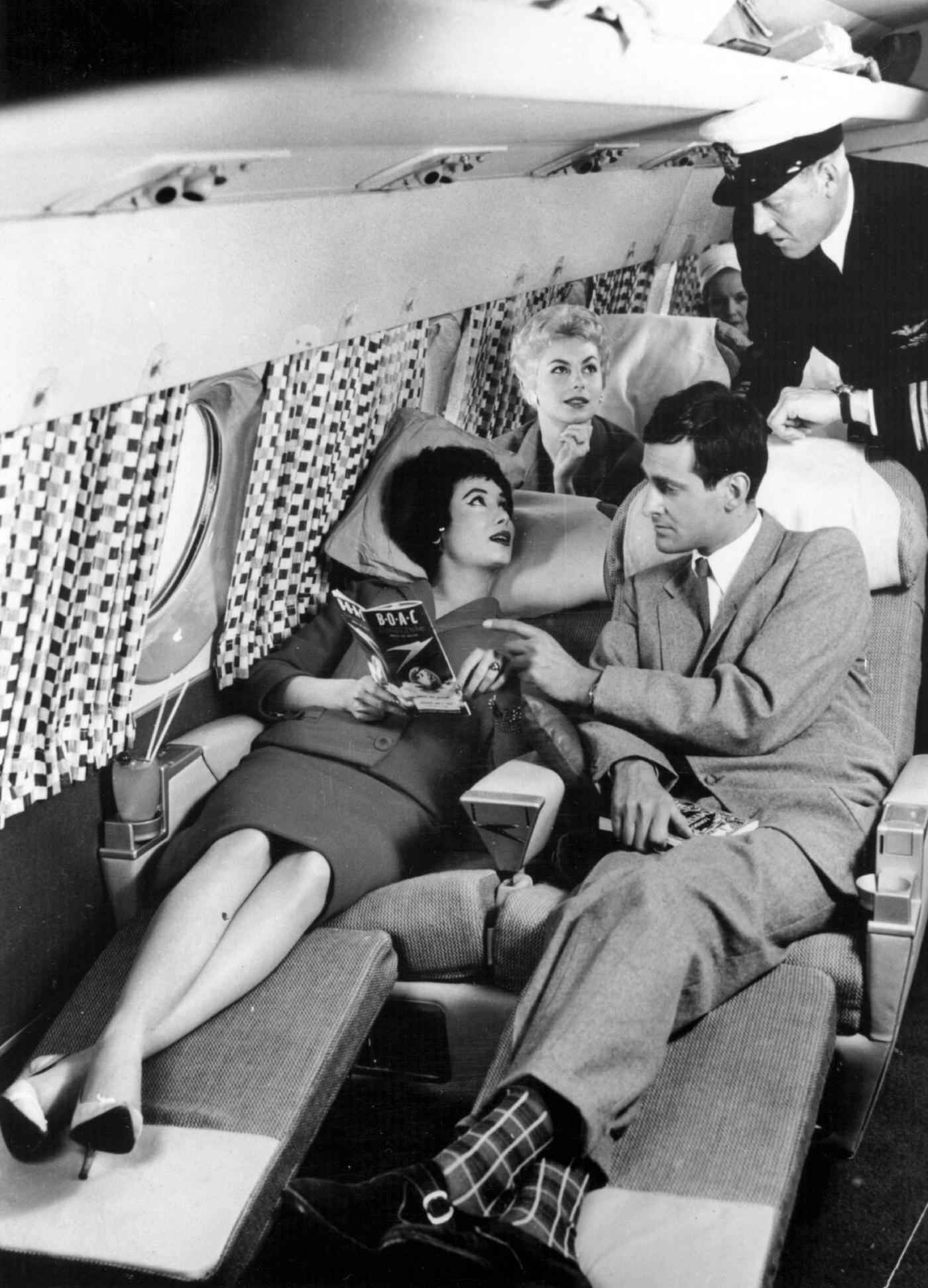
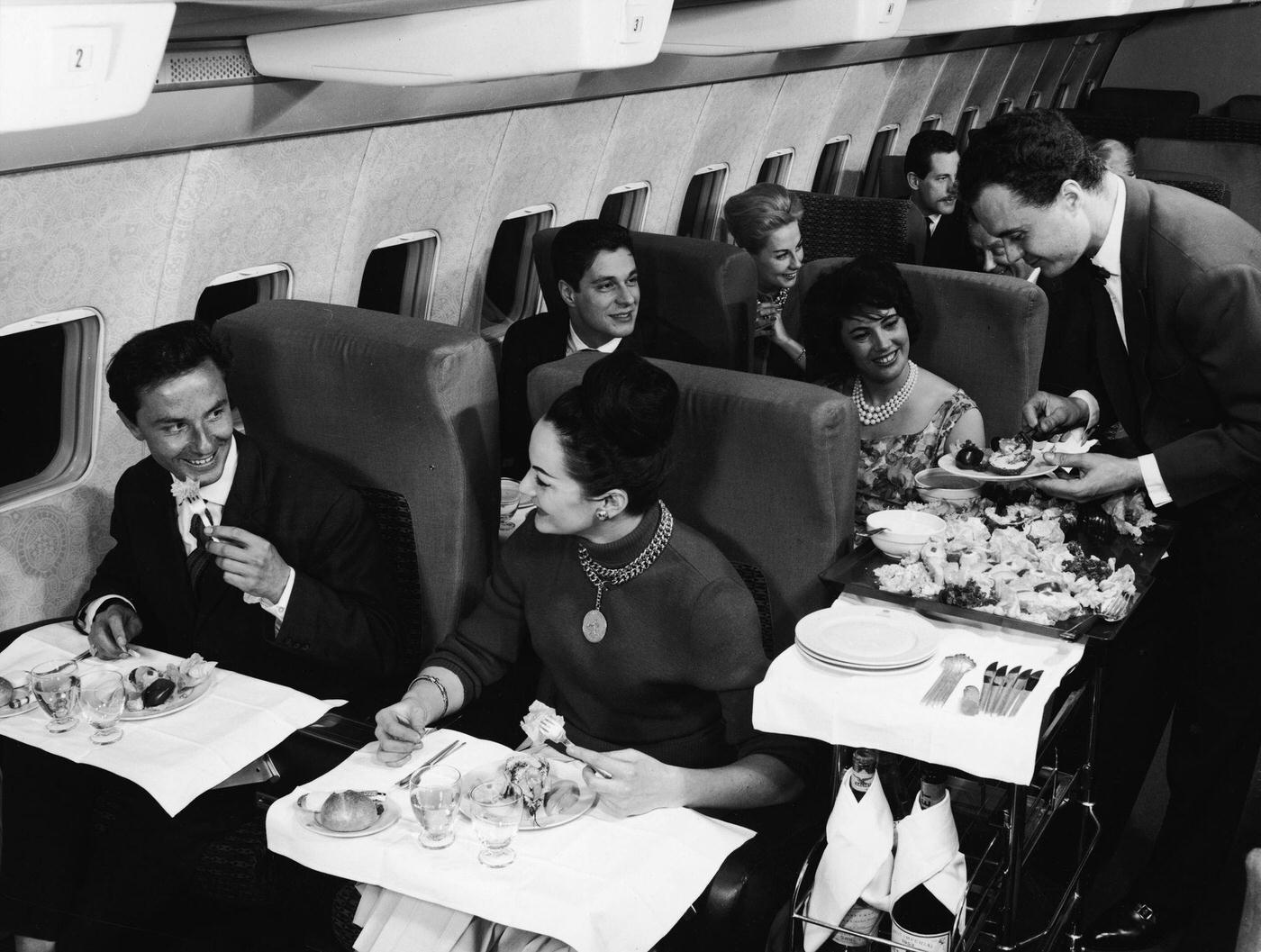
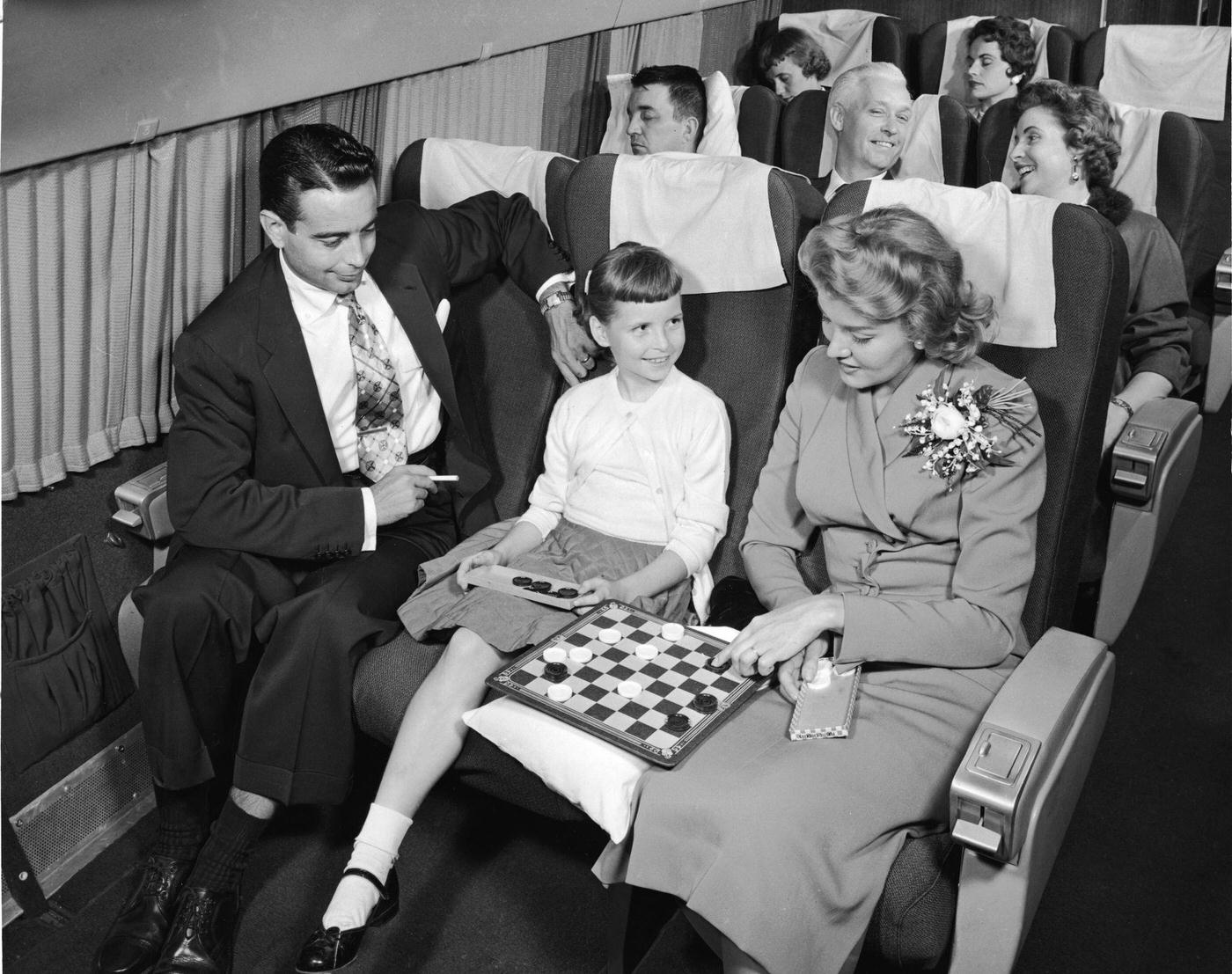
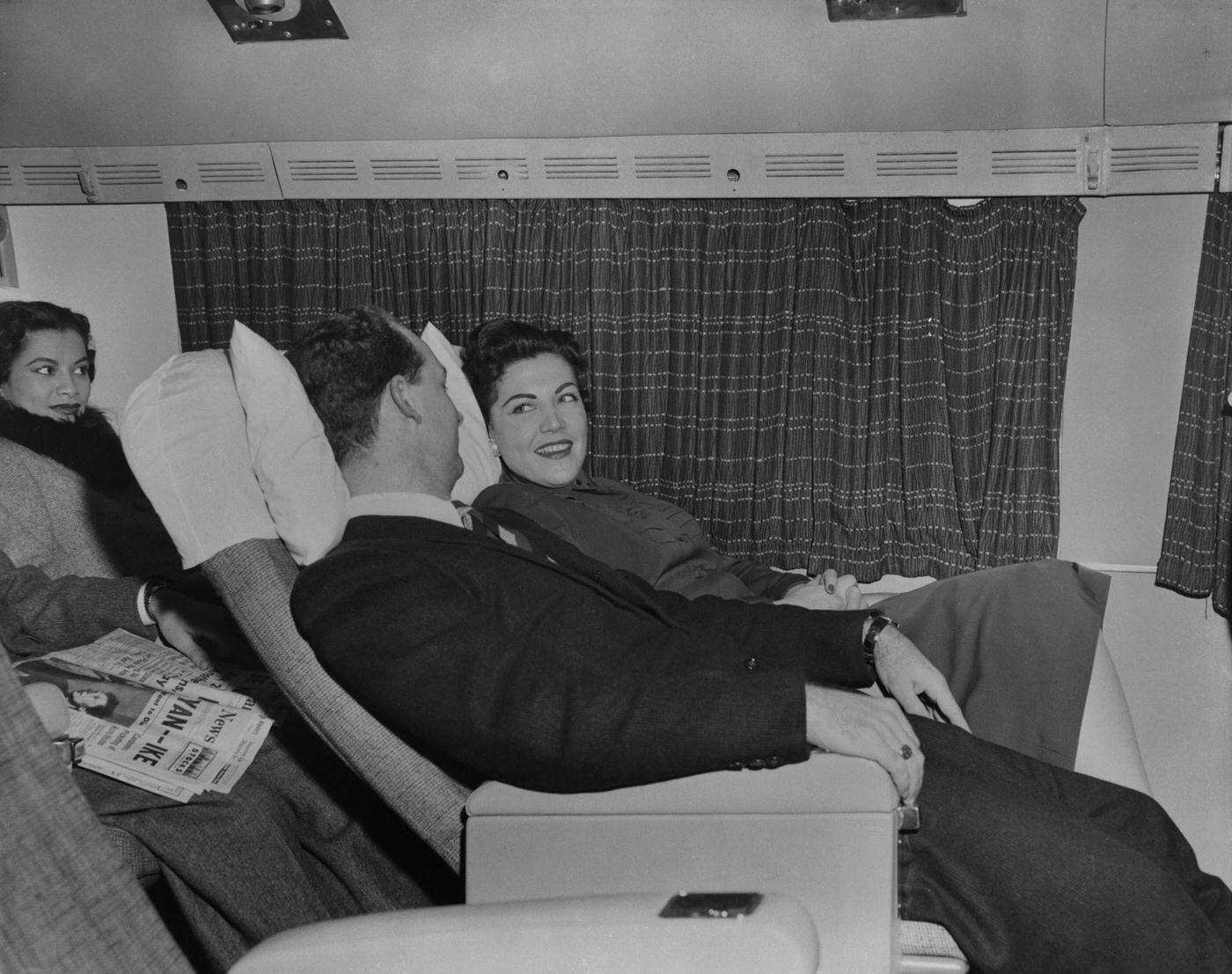
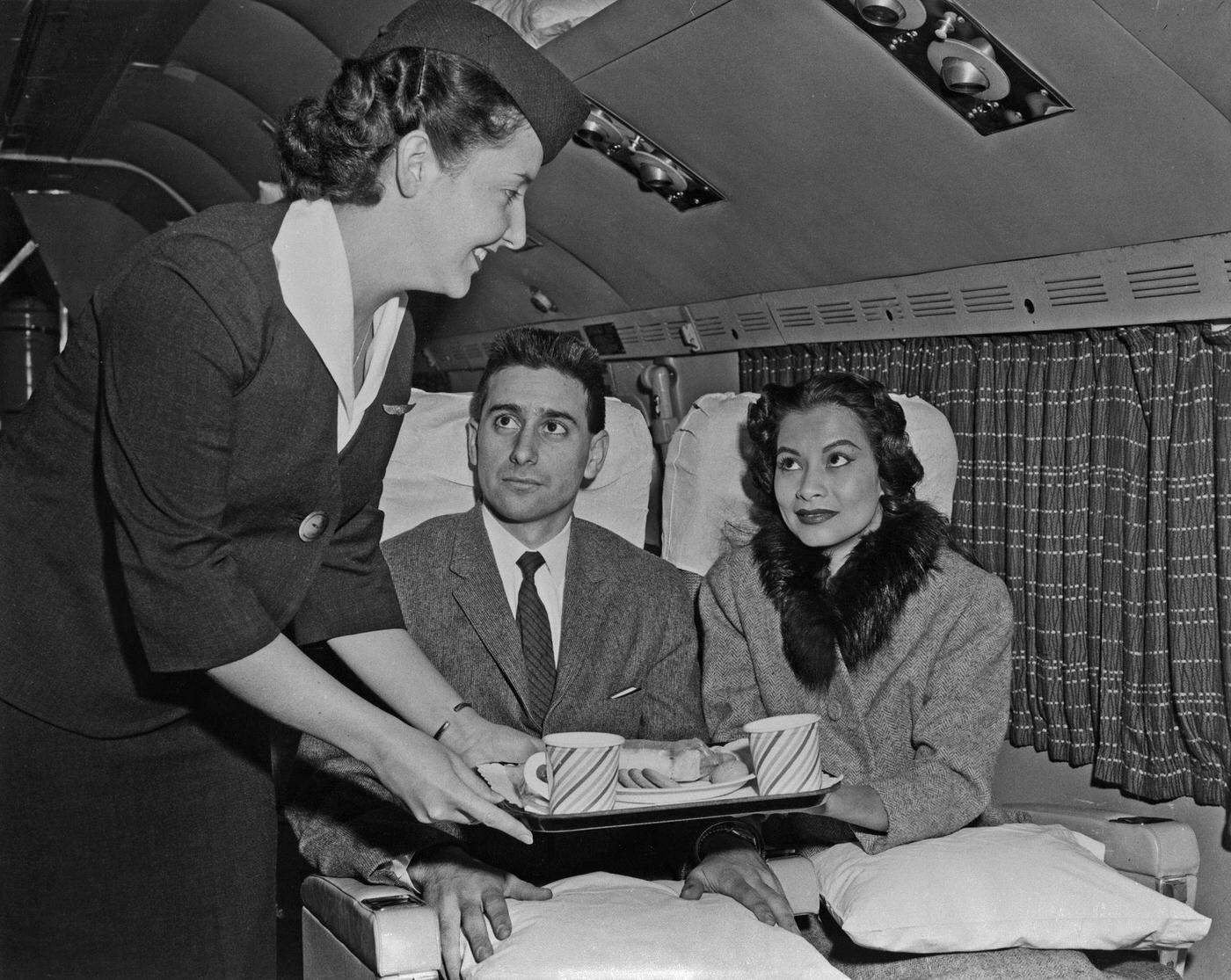
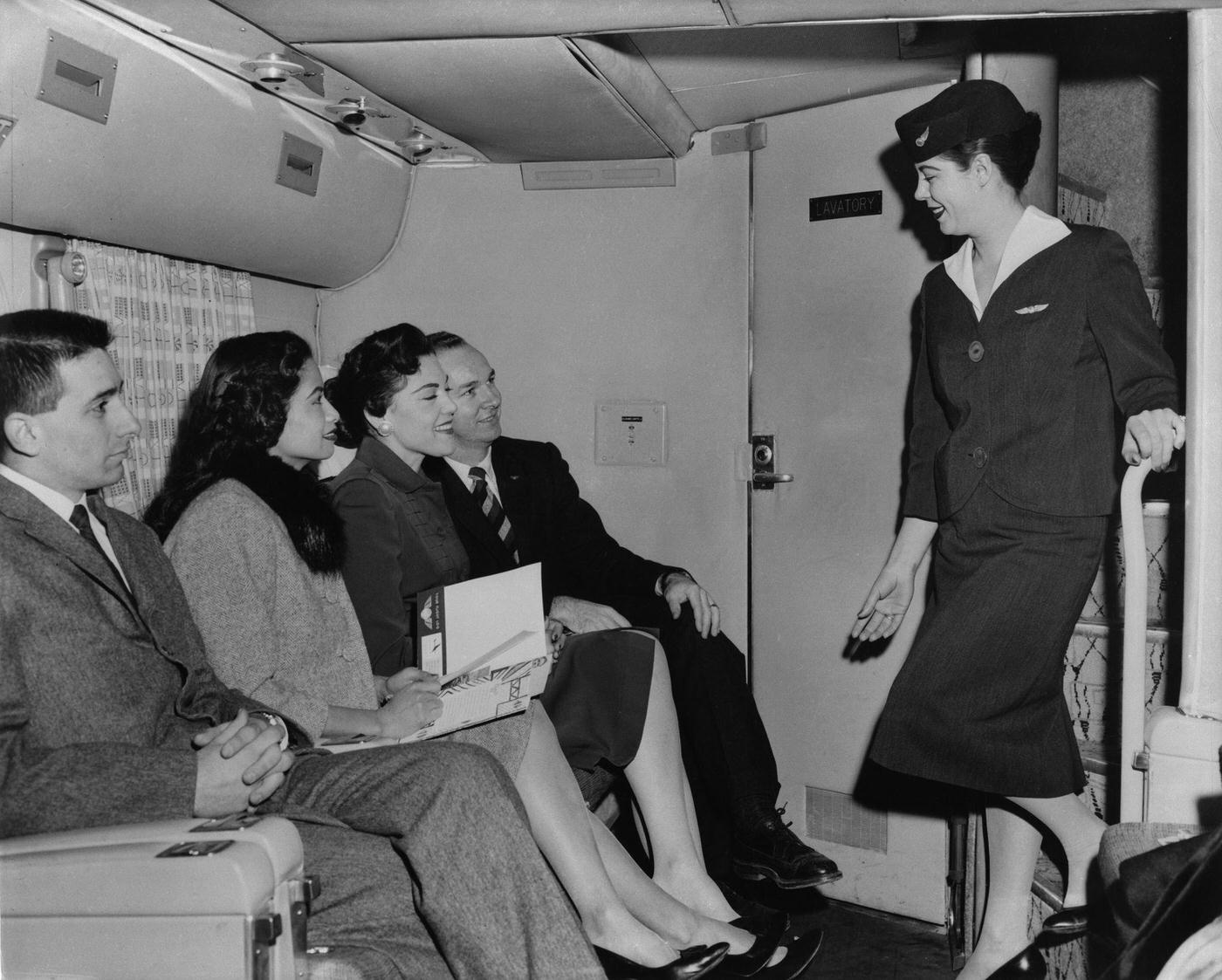
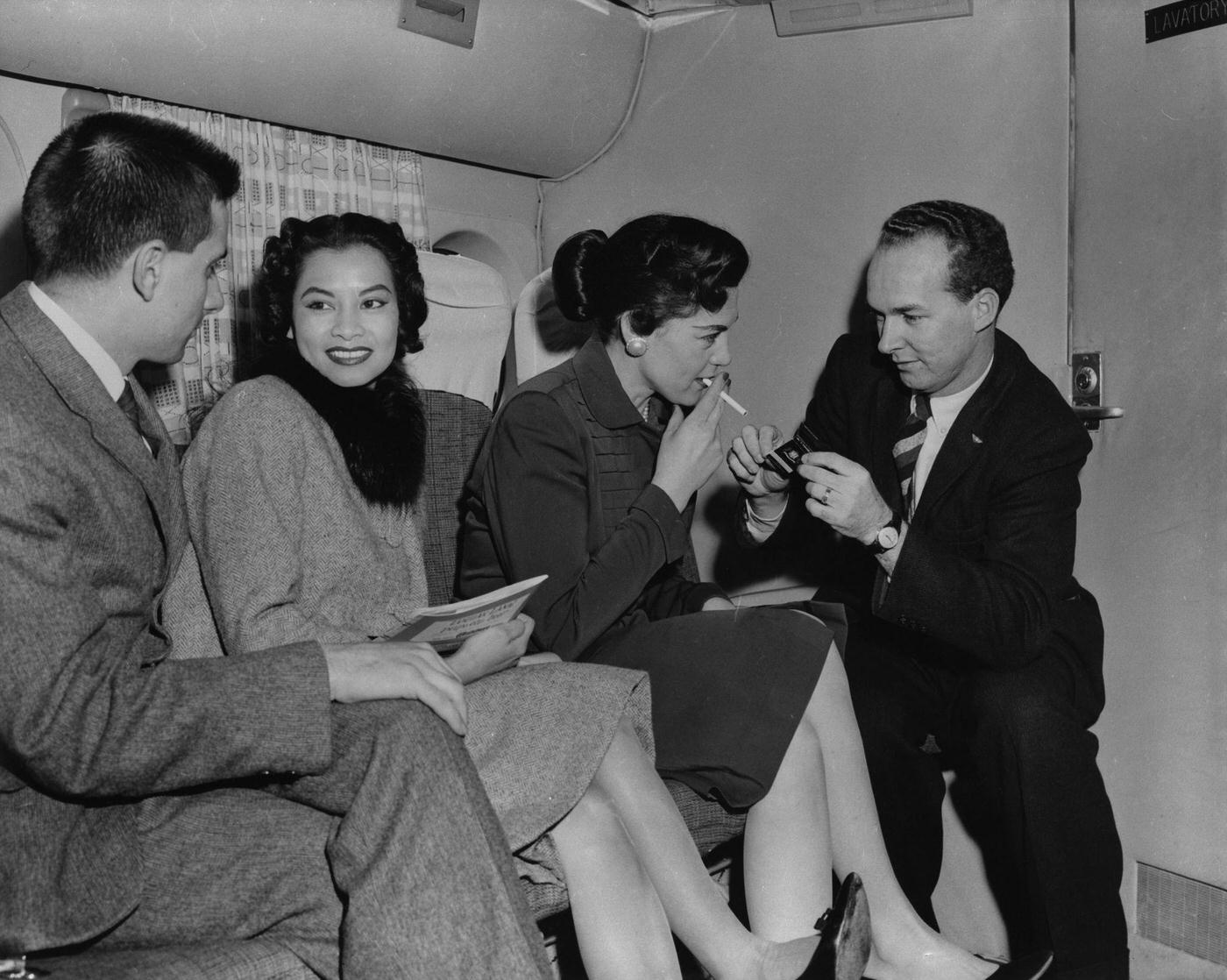
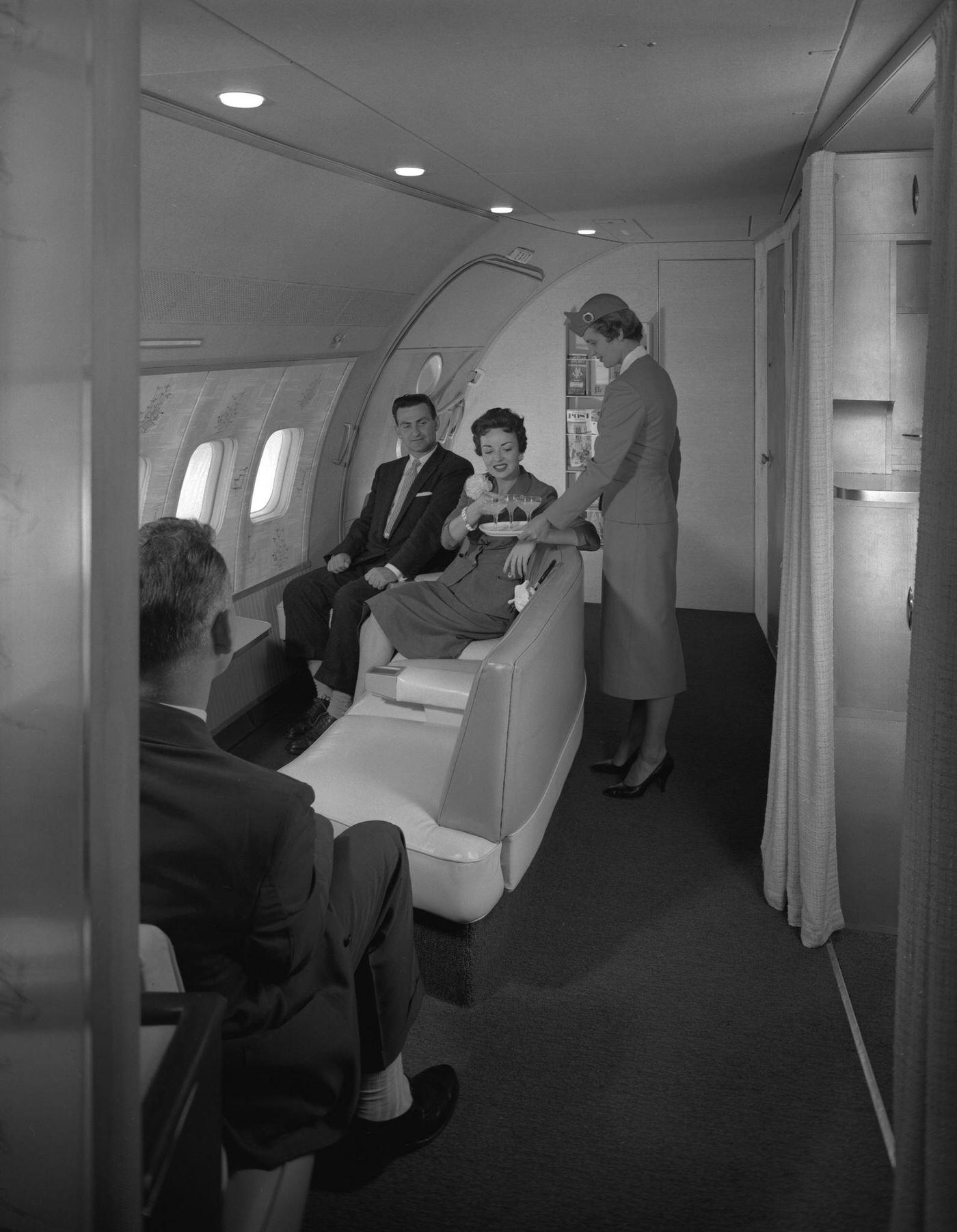
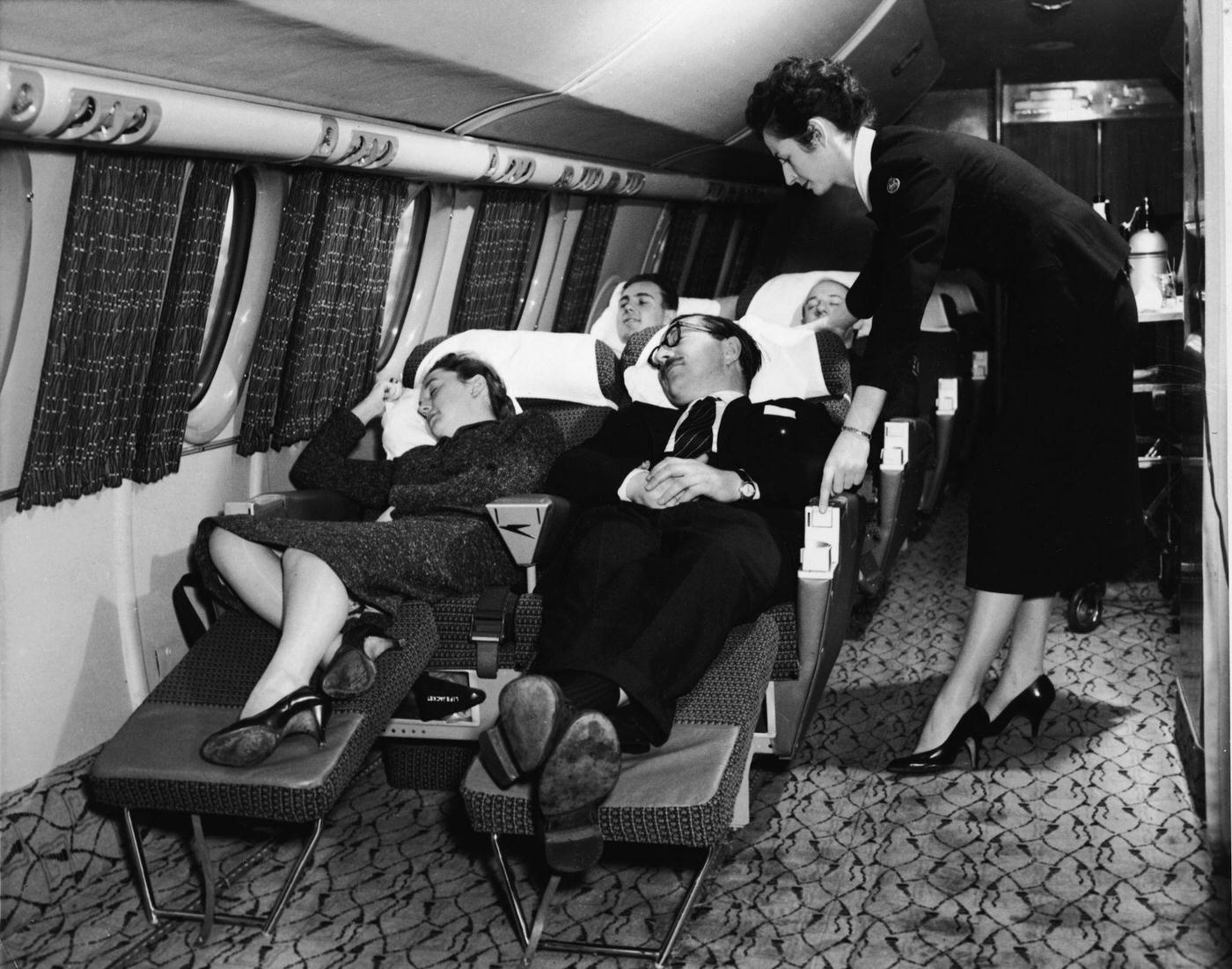
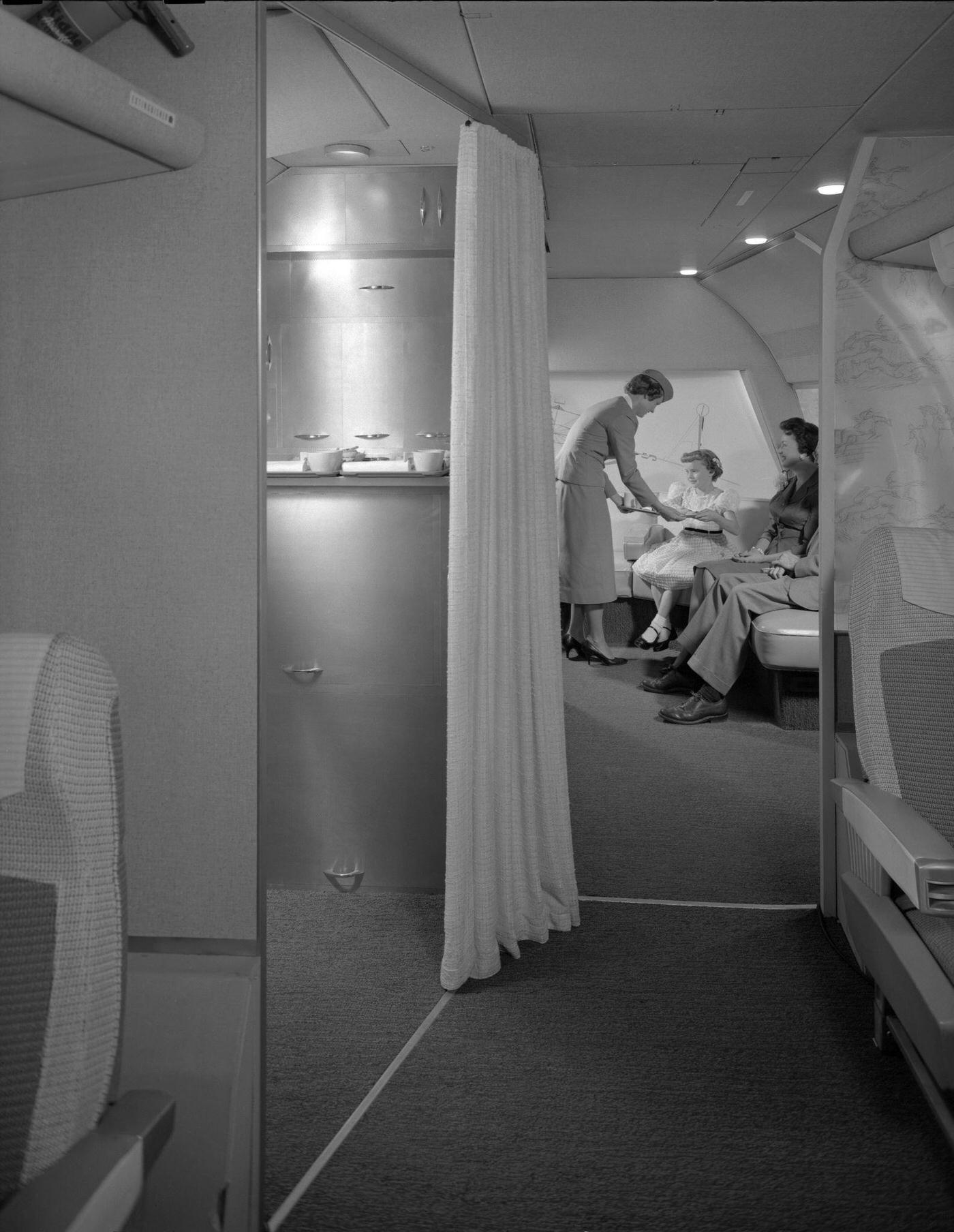
Passenger services during this time continued to improve, with in-flight meals, drinks, and entertainment becoming more common. Airlines also began to offer different classes of service, with first-class offering more luxurious amenities than economy class. Flight attendants were also becoming more commonplace, and their role expanded to include safety, customer service, and in-flight service.
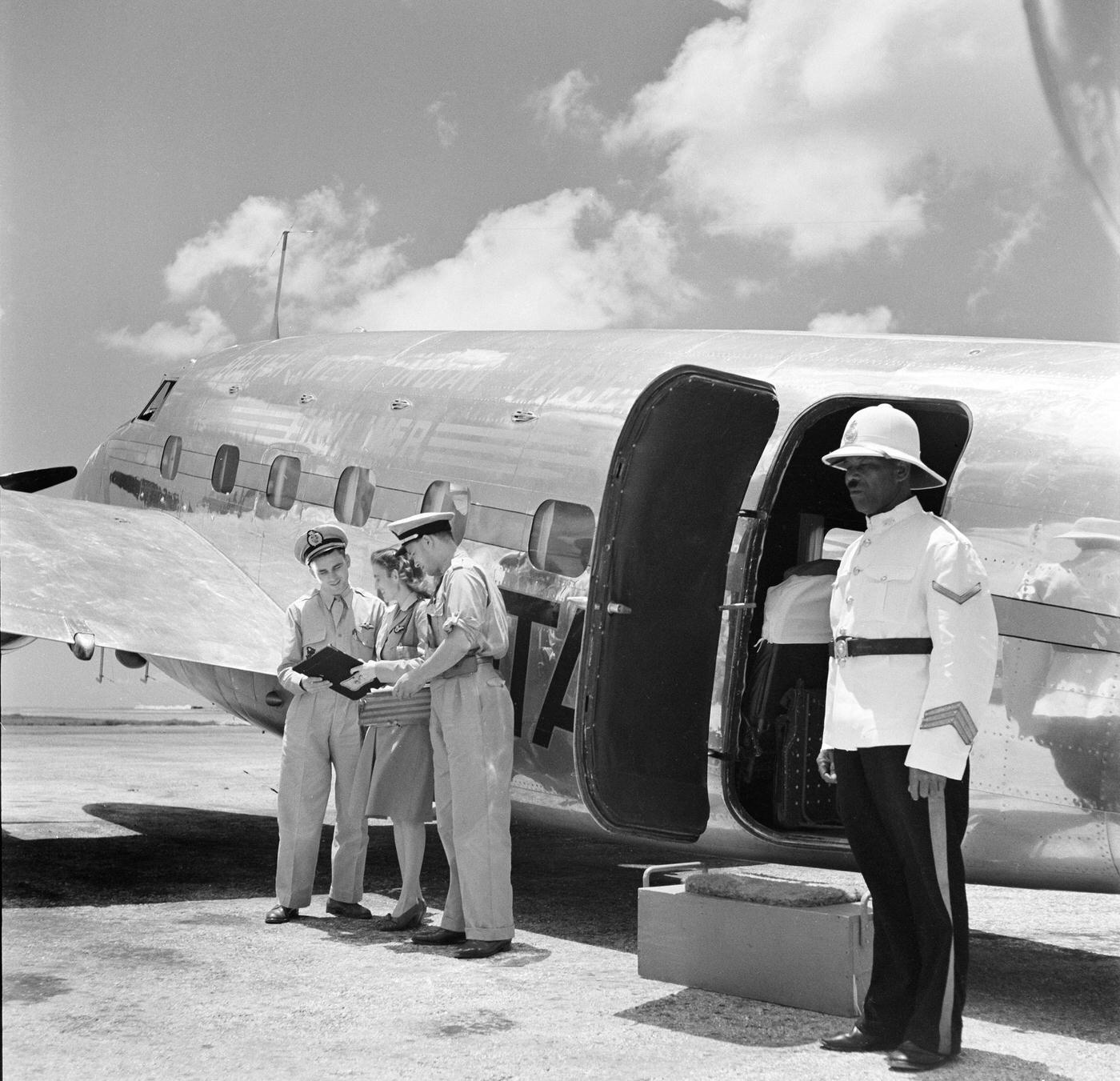
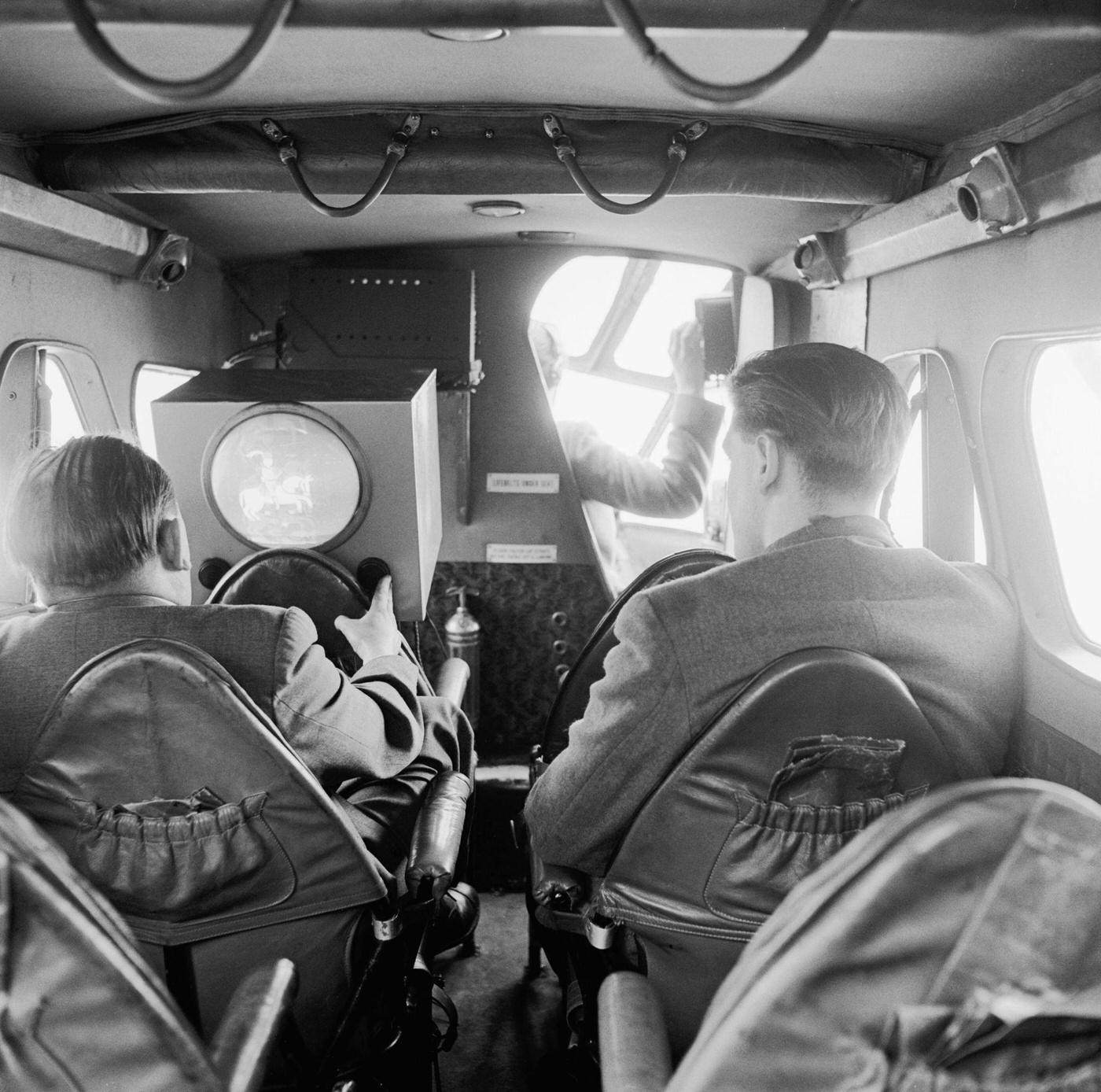
The flight crews of the 1950s were composed of highly trained and experienced pilots, navigators, and radio operators. With the introduction of jet airliners, the flight crews were also larger than before, with a pilot, co-pilot, flight engineer, navigator, and sometimes a flight attendant as a standard crew.